The Suzuki GS750 fuel line diagram is an essential tool for understanding the intricate workings of your motorcycle’s fuel system. This diagram serves as a visual roadmap, guiding you through the path of fuel from the tank to the carburetor, highlighting each component’s role in delivering the lifeblood of your engine.
Understanding the fuel line diagram is crucial for diagnosing fuel-related issues, performing maintenance, and even exploring potential modifications.
This guide delves into the components of the Suzuki GS750 fuel line system, explaining their functions and how they work together. We’ll explore the conventions used in the diagram, interpret the flow of fuel, and provide a step-by-step example of tracing the fuel line path.
We’ll also discuss common fuel line problems, troubleshooting steps, maintenance procedures, and safety considerations. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of your Suzuki GS750’s fuel system and the tools to keep it running smoothly.
Introduction to the Suzuki GS750 Fuel System

The Suzuki GS750, a legendary motorcycle from the 1970s, features a fuel system designed to deliver the right amount of fuel to the engine for optimal performance. This system involves a series of components, each playing a vital role in ensuring smooth and efficient operation.
Understanding the fuel system and its components is crucial for proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
Fuel Lines
The fuel lines in the GS750 fuel system are responsible for transporting gasoline from the fuel tank to the carburetor. These lines are typically made of rubber or plastic, and they are designed to be flexible and resistant to fuel and environmental conditions.
The fuel lines are routed through the motorcycle frame and engine compartment, connecting the fuel tank to the carburetor.
Fuel Line Diagram Significance
A fuel line diagram provides a visual representation of the fuel system, outlining the layout and connections of all the fuel lines. This diagram is an essential tool for mechanics and enthusiasts, as it allows them to understand the flow of fuel through the system and identify potential issues or leaks.
The diagram can also help in troubleshooting fuel-related problems, such as engine stalling or poor fuel delivery.
Components of the Suzuki GS750 Fuel Line System
The Suzuki GS750 fuel line system is responsible for delivering fuel from the tank to the engine’s combustion chambers. It’s a complex system with many components working together to ensure a smooth and consistent fuel flow. Here’s a breakdown of the key components and their functions.
Fuel Tank
The fuel tank is the heart of the fuel system. It’s a sealed container that stores the fuel. The fuel tank on the GS750 is usually made of steel, but some models may have aluminum tanks. It has a vent to allow air to enter as fuel is drawn out, preventing a vacuum from forming and hindering fuel flow.
Fuel Cap
The fuel cap seals the tank, preventing fuel from spilling and protecting the fuel from contamination. It’s usually a threaded cap that locks into place, providing a secure seal.
Fuel Pump
The fuel pump is the muscle of the fuel system. It’s an electric motor that draws fuel from the tank and pushes it through the fuel lines to the carburetor(s). The GS750’s fuel pump is typically located inside the fuel tank, ensuring a constant supply of fuel.
Fuel Filter
The fuel filter acts as a guardian, protecting the fuel system from debris and contaminants that can clog the fuel lines and carburetor jets. It’s a small, cylindrical filter that is usually located in the fuel line between the fuel pump and the carburetor(s).
Fuel Lines
Fuel lines are the pathways that carry fuel from the fuel pump to the carburetor(s). These lines are typically made of rubber or plastic and are designed to withstand the pressure and temperature fluctuations of the fuel system.
Fuel Shutoff Valve
The fuel shutoff valve is a manual valve that controls the flow of fuel to the carburetor(s). It’s usually located near the fuel tank and allows you to stop the flow of fuel when the engine is not running.
Carburetor(s)
The carburetor(s) are the brains of the fuel system. They mix the fuel with air in the correct ratio for combustion. The GS750 has four carburetors, one for each cylinder. Each carburetor has a series of jets that control the amount of fuel and air that enters the engine.
Fuel Line System Connection
The connection between these components is crucial for fuel delivery. The fuel pump draws fuel from the tank and pushes it through the fuel lines to the carburetor(s). The fuel filter prevents contaminants from reaching the carburetor(s), while the fuel shutoff valve allows you to control the flow of fuel.
The carburetor(s) then mix the fuel with air and deliver it to the engine’s combustion chambers.
Reading and Understanding the Fuel Line Diagram

Fuel line diagrams are essential for understanding how fuel flows through the system and for diagnosing and troubleshooting problems. They provide a visual representation of the fuel lines, components, and their connections.
Diagram Conventions
Fuel line diagrams use various conventions to represent the different components and their connections.
- Lines:Solid lines represent fuel lines, while dashed lines might represent vacuum lines or electrical wires. The thickness of the line can indicate the size of the fuel line.
- Symbols:Different symbols are used to represent components like the fuel tank, fuel pump, carburetor, and filters.
These symbols are standardized, so you can easily recognize them across different diagrams.
- Arrows:Arrows indicate the direction of fuel flow. They show how fuel travels from the tank to the carburetor.
- Labels:Labels identify the components and their connections.
Fuel Line Routing and Placement
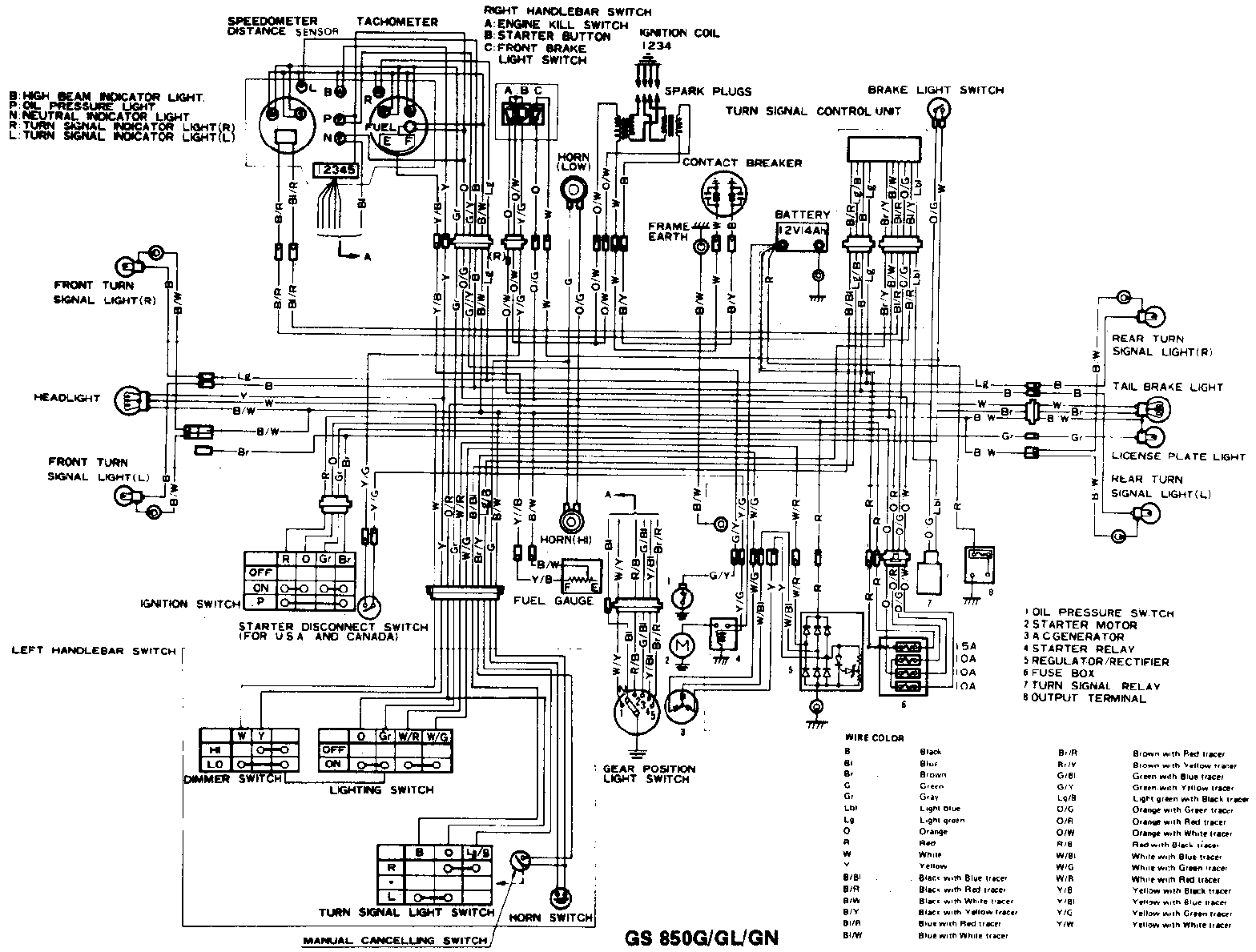
The fuel line routing on a Suzuki GS750 is meticulously designed to ensure efficient fuel delivery while minimizing potential issues. This section delves into the specific path of the fuel lines, the rationale behind their placement, and potential issues associated with their positioning.
Fuel Line Routing
The fuel lines on a Suzuki GS750 follow a specific path from the fuel tank to the carburetor. The fuel line typically originates from the fuel tank outlet, usually located at the bottom of the tank. From there, it travels towards the front of the motorcycle, often routed along the frame or under the seat.
The fuel line then passes near the engine, typically along the left side, before finally connecting to the carburetor inlet.
Reasons for Fuel Line Routing
- Minimizing Fuel Line Length:Shorter fuel lines are preferred to reduce the amount of fuel that is stored within the lines. This helps prevent fuel evaporation and potential fuel line pressure issues.
- Avoiding Heat Sources:Fuel lines are routed away from heat sources, such as the engine and exhaust system, to prevent fuel vaporization and potential fire hazards.
- Ensuring Proper Fuel Flow:The fuel line routing ensures that the fuel flows smoothly and efficiently from the tank to the carburetor, preventing fuel starvation and ensuring optimal engine performance.
- Avoiding Kinks and Bends:The fuel line is routed to minimize sharp bends and kinks, which can restrict fuel flow and damage the fuel line.
Potential Issues with Fuel Line Placement
- Fuel Line Wear and Tear:Fuel lines are susceptible to wear and tear due to vibration, heat, and abrasion from other motorcycle components. Improper routing can exacerbate these issues.
- Fuel Line Leaks:Leaks can occur if the fuel line is damaged, worn, or improperly routed. This can lead to fuel spills, safety hazards, and performance issues.
- Fuel Line Kinks:Kinks in the fuel line can restrict fuel flow, leading to engine performance problems and potential fuel starvation.
- Fuel Line Routing Interference:In some cases, the fuel line may interfere with other motorcycle components, such as the airbox or exhaust system, leading to potential damage or performance issues.
Common Fuel Line Problems and Troubleshooting: Suzuki Gs750 Fuel Line Diagram
The Suzuki GS750 fuel line system is vital for delivering fuel to the engine, and problems with the fuel lines can lead to various issues like engine stalling, rough running, and difficulty starting. This section explores common fuel line problems on the GS750 and how to troubleshoot them.
Fuel Line Leaks
Fuel line leaks are a common problem on motorcycles, and they can occur due to several factors, including:
- Cracked or worn fuel lines: Over time, fuel lines can become brittle and crack, especially if they are exposed to extreme temperatures or chemicals. This can lead to leaks, which can be dangerous.
- Loose or damaged fuel line connections: If the fuel line connections are loose or damaged, they can leak fuel. This can be caused by overtightening the fittings, corrosion, or vibrations.
- Damaged fuel line clamps: Fuel line clamps hold the fuel lines in place, and if they are damaged or loose, they can allow the fuel lines to move and leak.
To troubleshoot fuel line leaks, you should first inspect the fuel lines for any visible cracks or damage. Check the fuel line connections for tightness and signs of corrosion. Also, inspect the fuel line clamps for damage or looseness. If you find any problems, you should replace the damaged components.
If you can’t find any visible leaks, you can use a fuel pressure tester to check for leaks. A fuel pressure tester will measure the pressure in the fuel system, and if it drops below the specified pressure, it indicates a leak.
If you suspect a leak, it’s important to address it promptly to prevent fuel spills and potential fire hazards.
Fuel Line Clogging
Fuel line clogging is another common problem that can affect the Suzuki GS
750. Clogging can occur due to
- Dirty fuel: Fuel can become contaminated with dirt, debris, or water, which can clog the fuel lines and restrict fuel flow.
- Old fuel: Over time, fuel can degrade and form varnish or sediment, which can also clog the fuel lines.
- Fuel filter blockage: The fuel filter is designed to trap contaminants in the fuel, but it can become clogged over time. A clogged fuel filter can restrict fuel flow and cause engine problems.
To troubleshoot fuel line clogging, you should first check the fuel filter for blockage. If the fuel filter is clogged, you should replace it. You can also try flushing the fuel lines with a fuel line cleaner. This can help to remove any debris or sediment that may be clogging the lines.
If you suspect a fuel line clog, it’s essential to address it promptly to prevent engine damage and ensure proper fuel flow.
Fuel Line Routing and Placement
Fuel line routing and placement are crucial for the proper functioning of the fuel system. Incorrect routing can lead to:
- Kinks and bends in the fuel lines: Incorrect routing can cause kinks and bends in the fuel lines, restricting fuel flow and potentially damaging the lines.
- Fuel lines rubbing against hot components: Improper placement can cause fuel lines to rub against hot engine components, potentially causing damage or leaks.
- Fuel lines being exposed to extreme temperatures: Fuel lines should be routed away from extreme temperatures, such as the exhaust system, to prevent damage and ensure proper fuel flow.
To troubleshoot fuel line routing and placement issues, you should carefully inspect the fuel lines to ensure they are routed correctly and are not kinked or bent. Make sure the fuel lines are secured with clamps and are not rubbing against hot components.
You should also check that the fuel lines are not exposed to extreme temperatures. If you find any issues, you should address them immediately to prevent problems with the fuel system.
Yo, trying to figure out the fuel line diagram for my Suzuki GS750? It’s like, totally essential to keep things running smooth. And speaking of running smooth, I found this sick volvo penta 5.7 thermostat housing diagram that might help with that too.
Anyway, back to the GS750, I think I’m gonna check out some forums to see if anyone else has had the same issue.
Fuel Line Maintenance and Replacement
Maintaining your Suzuki GS750’s fuel lines is crucial for ensuring a smooth and reliable ride. Over time, these lines can become brittle, cracked, or clogged, leading to fuel leaks, engine problems, and even fire hazards. Regular inspection and replacement are essential to prevent these issues and keep your bike running in tip-top shape.
Inspecting Fuel Lines
Inspecting your fuel lines is a simple but essential step in maintaining your Suzuki GS750. This process helps you identify any potential problems before they become major issues.
- Visual Inspection:Look for any visible signs of damage, such as cracks, leaks, or bulges. Pay close attention to areas where the fuel lines are routed near hot components, as these areas are prone to wear and tear.
- Flexibility Test:Gently bend the fuel lines to check for any signs of brittleness or cracking. If the lines feel stiff or break easily, they should be replaced.
- Pressure Test:This is a more thorough inspection method that involves applying pressure to the fuel lines to check for leaks. This is typically done by a mechanic using specialized equipment.
Replacing Fuel Lines
If your fuel lines show signs of wear or damage, it’s time to replace them. This is a relatively straightforward process that can be done by a skilled motorcycle mechanic.
- Gather the necessary tools and materials:You’ll need a set of wrenches, a fuel line cutter, new fuel lines, and possibly some fuel line clamps.
- Drain the fuel tank:This is important to prevent fuel spills during the replacement process.
- Disconnect the old fuel lines:Carefully disconnect the old fuel lines from the fuel tank, carburetor, and other components.
- Install the new fuel lines:Connect the new fuel lines to the fuel tank, carburetor, and other components, ensuring they are securely fastened.
- Test for leaks:After installation, start the engine and check for any leaks. If there are leaks, tighten the connections or re-install the lines.
Fuel Line Materials and Construction
The fuel line is a crucial component of the Suzuki GS750 fuel system, responsible for transporting fuel from the tank to the carburetor. Choosing the right fuel line material is important for ensuring reliable fuel delivery, preventing leaks, and maintaining the motorcycle’s performance.
Fuel Line Materials
Fuel lines in motorcycles are typically made from various materials, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common materials include:
- Rubber:Rubber fuel lines are flexible, durable, and resistant to chemicals, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. However, rubber can deteriorate over time, becoming brittle and prone to cracking.
- Plastic:Plastic fuel lines are lightweight, affordable, and resistant to corrosion. They are often used in modern motorcycles due to their ease of manufacture and compatibility with various fuel additives. However, plastic can be susceptible to damage from high temperatures and certain chemicals.
- Steel:Steel fuel lines are strong, durable, and resistant to high temperatures. They are commonly used in older motorcycles and can be found in some modern applications where durability is paramount. However, steel can be susceptible to corrosion, especially in environments with high humidity or salt exposure.
- Aluminum:Aluminum fuel lines are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and have good thermal conductivity. They are often used in racing applications where weight reduction is crucial. However, aluminum can be more expensive than other materials and may require specialized fittings.
Fuel Line Construction
Fuel lines are typically constructed with a layered structure to ensure proper fuel flow and durability. The construction often includes:
- Inner Liner:The inner liner of the fuel line is typically made from a smooth, non-porous material like rubber or plastic to prevent fuel from adhering to the line’s walls and to ensure smooth fuel flow.
- Reinforcement:A layer of reinforcement is often added to the fuel line to enhance its strength and prevent kinking or collapsing under pressure. This reinforcement can be made from materials like nylon, fiberglass, or steel wire mesh.
- Outer Cover:The outer cover of the fuel line provides protection against abrasion, weather elements, and other environmental factors. It is typically made from rubber or plastic, with a smooth finish to reduce friction and wear.
Fuel Line Safety Considerations
Fuel lines are the lifelines of your Suzuki GS750, carrying the precious fuel that powers your engine. But just like any lifeline, they need to be treated with respect and caution. Fuel, being highly flammable, poses a serious fire hazard if not handled properly.
So, it’s essential to understand the potential risks involved and take necessary precautions when working with your fuel lines.
Fuel Line Hazards
Fuel lines, when damaged or leaking, can pose a significant safety risk.
- Fire Hazard:Leaking fuel can easily ignite, leading to a dangerous fire. This is especially true in the presence of heat sources like the engine or exhaust.
- Explosion Risk:Fuel vapors can accumulate in enclosed spaces, creating an explosive mixture. This is a significant risk if you’re working on your fuel system in a garage or enclosed area.
- Health Hazards:Fuel fumes can be toxic and cause respiratory problems, dizziness, and even unconsciousness. Always work in a well-ventilated area and avoid inhaling fuel fumes.
Fuel Line Safety Precautions
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area:Always work on your fuel lines in a well-ventilated area, preferably outdoors. This will help dissipate fuel vapors and reduce the risk of fire or explosion.
- Avoid Sparks and Flames:Keep any potential sources of ignition, like open flames, electrical sparks, or even static electricity, away from your work area.
- Use Proper Tools:Use only the correct tools for the job, as using the wrong tools can damage the fuel lines and increase the risk of leaks.
- Inspect for Leaks:After working on your fuel lines, always thoroughly inspect for leaks. Use a soapy water solution to check for bubbles, which indicate a leak.
- Wear Protective Gear:Always wear appropriate protective gear, including gloves, eye protection, and a respirator, when working with fuel lines.
- Store Fuel Safely:Always store fuel in approved containers in a well-ventilated area, away from heat and open flames.
Fuel Line Safety Tips, Suzuki gs750 fuel line diagram
- Never work on your fuel system while the engine is running.
- Always disconnect the battery before working on your fuel system.
- Never use a lighter or match to check for leaks.Use a soapy water solution instead.
- If you smell fuel, stop working immediately and investigate the source of the leak.
- If you have any doubts about your ability to safely work on your fuel system, consult a qualified mechanic.
Fuel Line Modifications and Upgrades
Modifying or upgrading the fuel line system on your Suzuki GS750 can improve performance, fuel efficiency, and reliability. While some modifications are simple and can be done by the average rider, others are more complex and require professional assistance.
Fuel Line Replacement
Replacing the original fuel lines with high-quality alternatives can significantly enhance the fuel system’s performance and longevity. Modern fuel lines are often made from materials like PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), which is known for its excellent resistance to chemicals, heat, and abrasion.
This can help prevent fuel leaks, improve fuel flow, and extend the lifespan of the fuel system.
Fuel Line Resources and Further Information
Want to delve deeper into the world of fuel lines for your Suzuki GS750? There’s a ton of resources out there to help you become a fuel line expert. Whether you’re looking for technical manuals, troubleshooting tips, or just want to chat with other GS750 owners, you’ll find something here.
Relevant Online Resources
These online resources offer a wealth of information about fuel lines, from basic maintenance to advanced troubleshooting:
- Suzuki Motorcycle Owners’ Club:This forum is a great place to connect with other GS750 owners and get advice on fuel line issues. You can search for specific problems or ask questions in the forum’s dedicated “Fuel System” section.
- Haynes Repair Manuals:Haynes manuals provide detailed information about all aspects of the Suzuki GS750, including the fuel system. They’re a great resource for DIY repairs and troubleshooting.
- Motorcycle Fuel Line Suppliers:Websites like Amazon, eBay, and specialized motorcycle parts suppliers offer a wide selection of fuel lines, fittings, and accessories.
- YouTube Tutorials:Numerous YouTube channels offer video tutorials on fuel line maintenance, replacement, and troubleshooting. Search for s like “Suzuki GS750 fuel line replacement” or “fuel line troubleshooting” to find relevant videos.
Recommended Books
If you prefer a more in-depth and comprehensive approach, these books offer detailed insights into fuel lines and their maintenance:
- “Motorcycle Maintenance and Repair” by John Haynes:This classic motorcycle repair manual covers a wide range of topics, including fuel system maintenance and repair.
- “The Complete Idiot’s Guide to Motorcycle Maintenance” by Peter Egan:This guide provides a beginner-friendly introduction to motorcycle maintenance, including fuel line basics and troubleshooting.
Essential FAQs
What are the most common materials used for fuel lines?
Fuel lines are typically made of rubber, plastic, or metal. Rubber lines are flexible and resistant to vibration, while plastic lines are lightweight and affordable. Metal lines offer durability and resistance to high temperatures but can be more rigid.
How often should I inspect my fuel lines?
It’s recommended to inspect your fuel lines at least once a year, or more frequently if you notice any leaks, cracks, or signs of wear.
What are some signs of a fuel line problem?
Common signs include fuel leaks, difficulty starting, engine sputtering, and a decrease in power.
Can I replace fuel lines myself?
While replacing fuel lines is a relatively simple task, it’s important to follow proper safety procedures and use high-quality replacement parts. If you’re not comfortable working with fuel lines, it’s best to consult a professional mechanic.