Suzuki GS750 fuel line diagram, a roadmap to the heart of your motorcycle’s fuel system, unlocks the secrets of how gasoline travels from tank to engine. This diagram is more than just a collection of lines and symbols; it’s a blueprint for understanding the intricate dance of fuel delivery, revealing the vital role each component plays in ensuring smooth and efficient power.
The fuel line diagram serves as a guide for maintenance and troubleshooting, allowing you to diagnose fuel-related issues with precision. From identifying the path of fuel through the system to understanding the purpose of each connection and fitting, this diagram empowers you to become a more informed and capable motorcycle owner.
Introduction to the Suzuki GS750 Fuel System
The fuel system of a Suzuki GS750 motorcycle plays a crucial role in delivering fuel to the engine for combustion, enabling the motorcycle to run. Understanding the components and their functions is essential for maintaining and troubleshooting fuel-related issues. This document provides an overview of the fuel system components on a Suzuki GS750 and explains the basic principles of fuel delivery in a motorcycle.
It also highlights the significance of understanding the fuel line diagram for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Components of the Suzuki GS750 Fuel System
The fuel system of a Suzuki GS750 consists of several interconnected components that work together to deliver fuel to the engine.
- Fuel Tank:The fuel tank stores the fuel for the motorcycle. It typically has a capacity of around 4.5 gallons.
- Fuel Pump:The fuel pump is responsible for drawing fuel from the tank and delivering it to the carburetor(s) under pressure.
- Fuel Lines:Fuel lines are hoses that connect the fuel tank, fuel pump, and carburetor(s), allowing the flow of fuel.
- Fuel Filter:The fuel filter traps impurities and debris from the fuel, preventing them from reaching the carburetor(s) and damaging the engine.
- Carburetor(s):The carburetor(s) are responsible for mixing air and fuel in the correct proportions for combustion.
- Fuel Valve:The fuel valve controls the flow of fuel from the tank to the fuel pump. It is typically located near the fuel tank.
- Fuel Gauge:The fuel gauge provides an indication of the amount of fuel remaining in the tank.
Fuel Delivery in a Motorcycle
Fuel delivery in a motorcycle involves the following steps:
- Fuel is drawn from the tank:When the engine is running, the fuel pump draws fuel from the tank through the fuel lines.
- Fuel is filtered:The fuel passes through the fuel filter, which removes impurities and debris.
- Fuel is delivered to the carburetor(s):The fuel pump delivers the filtered fuel to the carburetor(s) under pressure.
- Fuel is mixed with air:In the carburetor(s), the fuel is mixed with air in the correct proportions for combustion.
- Fuel-air mixture is delivered to the engine:The fuel-air mixture is delivered to the engine cylinders, where it is ignited by the spark plugs.
Understanding the Fuel Line Diagram
The fuel line diagram is a visual representation of the fuel system components and their connections. It shows the flow of fuel from the tank to the engine, including the fuel lines, fuel pump, carburetor(s), and other components.
Understanding the fuel line diagram is crucial for:
- Troubleshooting fuel-related issues:By tracing the fuel lines on the diagram, you can identify potential problems with the fuel system. For example, if the fuel is not reaching the carburetor(s), you can check the fuel lines for blockages or leaks.
- Performing maintenance:The fuel line diagram helps you identify the location of the fuel filter, fuel pump, and other components, making it easier to access them for maintenance.
- Replacing parts:When replacing parts, the fuel line diagram can help you identify the correct components and ensure that they are connected correctly.
Fuel Line Diagram Components
The fuel line diagram for the Suzuki GS750 motorcycle provides a visual representation of the fuel delivery system, illustrating the flow of fuel from the tank to the engine. Understanding the components of this diagram is crucial for troubleshooting fuel-related issues and performing maintenance on the motorcycle.
Components of the Fuel Line Diagram
This section will describe the various components of the Suzuki GS750 fuel line diagram and their roles in the fuel delivery process.
| Component Name | Function | Location | Diagram Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fuel Tank | Stores the fuel supply for the motorcycle. | Located at the rear of the motorcycle, typically above the rear wheel. | Refer to the fuel line diagram for visual representation. |
| Fuel Tank Cap | Seals the fuel tank opening, preventing fuel spillage and contamination. | Located on the top of the fuel tank. | Refer to the fuel line diagram for visual representation. |
| Fuel Pump | Draws fuel from the tank and delivers it to the carburetor(s) under pressure. | Mounted near the fuel tank, typically on the left side of the motorcycle. | Refer to the fuel line diagram for visual representation. |
| Fuel Filter | Removes impurities from the fuel before it reaches the carburetor(s), protecting the engine from damage. | Located in the fuel line, typically between the fuel pump and the carburetor(s). | Refer to the fuel line diagram for visual representation. |
| Fuel Lines | Carry fuel from the tank to the carburetor(s). | Connect the fuel tank, fuel pump, filter, and carburetor(s). | Refer to the fuel line diagram for visual representation. |
| Fuel Cock (Petcock) | Controls the flow of fuel from the tank to the fuel pump. | Located on the fuel tank, typically on the bottom or side. | Refer to the fuel line diagram for visual representation. |
| Carburetor(s) | Mixes fuel and air in the correct proportions for combustion in the engine. | Located on the engine, typically near the intake manifold. | Refer to the fuel line diagram for visual representation. |
Fuel Line Routing and Flow
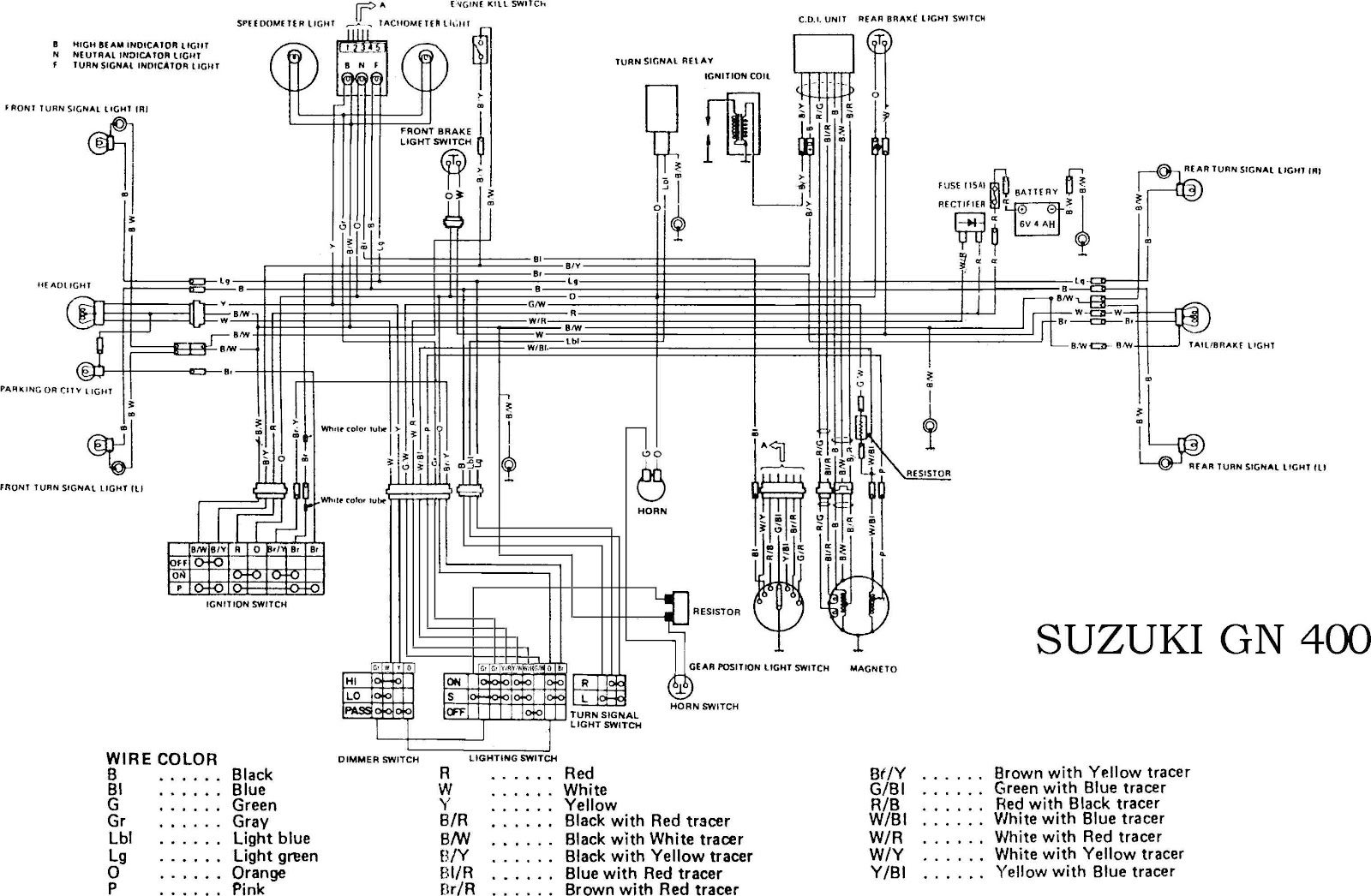
The fuel line routing on the Suzuki GS750 is a carefully designed system that ensures a consistent fuel supply to the engine. The fuel line diagram provides a visual representation of the path fuel takes from the tank to the carburetors, highlighting key components and connections.The fuel line routing and flow are critical for the proper functioning of the engine.
Understanding the path fuel takes and the pressure changes it undergoes is essential for troubleshooting fuel-related issues.
Tracing the Fuel Line Path
Tracing the fuel line path on a physical motorcycle is a straightforward process. It involves visually following the fuel line from the tank to the carburetors, identifying each component and connection along the way. Here’s a step-by-step guide for tracing the fuel line path on a Suzuki GS750:
- Start at the fuel tank: Locate the fuel tank outlet, where the fuel line connects to the tank. The outlet is typically located at the bottom of the tank.
- Follow the fuel line: Visually trace the fuel line from the tank outlet towards the engine. The fuel line will typically run along the frame of the motorcycle, sometimes passing through a fuel filter.
- Identify the fuel filter: The fuel filter is a cylindrical component that removes impurities from the fuel before it reaches the engine. It’s typically located in the fuel line, near the tank.
- Locate the fuel pump: The fuel pump is responsible for pressurizing the fuel and delivering it to the carburetors. On some models, the fuel pump may be integrated with the fuel tank.
- Trace the fuel line to the carburetors: After passing through the fuel pump, the fuel line will continue towards the carburetors. Each carburetor will have its own dedicated fuel line connection.
Fuel Line Connections and Fittings: Suzuki Gs750 Fuel Line Diagram

The fuel line connections and fittings play a crucial role in the proper functioning and safety of the Suzuki GS750 fuel system. They ensure a secure and leak-proof connection between the fuel tank, fuel pump, carburetor, and other components, allowing for a consistent and uninterrupted flow of fuel.
Types of Connections and Fittings
The fuel line system of the Suzuki GS750 utilizes various types of connections and fittings to ensure a secure and reliable fuel flow. These include:
- Quick-connect Fittings:These fittings are designed for easy and secure connection and disconnection of fuel lines. They feature a spring-loaded mechanism that allows for quick and simple attachment, while also ensuring a tight seal to prevent leaks.
- Compression Fittings:Compression fittings utilize a compression sleeve to secure the fuel line to the fitting. The sleeve compresses the fuel line against the fitting, creating a tight seal. This type of fitting is commonly used for fuel lines that are exposed to vibration or pressure fluctuations.
- Barb Fittings:Barb fittings feature a small, raised ridge or “barb” that grips the fuel line. The line is then secured by a clamp or hose clamp, creating a secure connection. Barb fittings are commonly used for fuel lines that require a secure and leak-proof connection.
- Fuel Line Clamps:These clamps are used to secure the fuel lines to the fittings. They are typically made of metal or plastic and are tightened with a screwdriver or wrench. The clamps provide a secure connection and prevent the fuel line from slipping off the fitting.
Importance of Proper Connections and Fittings
Proper connections and fittings are essential for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of the fuel system.
- Fuel Flow:Improper connections can restrict fuel flow, leading to engine performance issues, such as stalling, hesitation, and reduced power. This is due to the restriction in fuel delivery, preventing the engine from receiving the necessary amount of fuel for optimal combustion.
- Fuel Leaks:Loose or damaged connections can cause fuel leaks, posing a safety hazard. Fuel is highly flammable and can ignite if exposed to an open flame or spark. Leaks can also lead to environmental damage, as spilled fuel can contaminate soil and water.
- System Integrity:Proper connections and fittings ensure the integrity of the fuel system, preventing air from entering the fuel lines. Air in the fuel lines can cause vapor lock, a condition that prevents fuel from reaching the carburetor. This can result in engine stalling or difficulty starting.
Inspecting and Maintaining Fuel Line Connections
Regular inspection and maintenance of fuel line connections are crucial for ensuring the safe and reliable operation of the Suzuki GS750 fuel system.
- Visual Inspection:Regularly inspect fuel line connections for any signs of damage, such as cracks, corrosion, or loose fittings. Look for any signs of fuel leakage, indicating a potential problem with the connection.
- Tightness Check:Ensure all connections are tight and secure. Use a wrench or screwdriver to tighten any loose fittings.
- Clamp Inspection:Check the condition of fuel line clamps. Ensure they are in good condition and not damaged or cracked. Replace any worn or damaged clamps.
- Fuel Line Condition:Inspect the fuel lines for any signs of damage, such as cracks, kinks, or deterioration. Replace any damaged or worn fuel lines.
- Professional Inspection:If you are unsure about inspecting or maintaining fuel line connections, it is recommended to consult a qualified motorcycle mechanic for professional assistance.
Fuel Line Diagram Interpretation
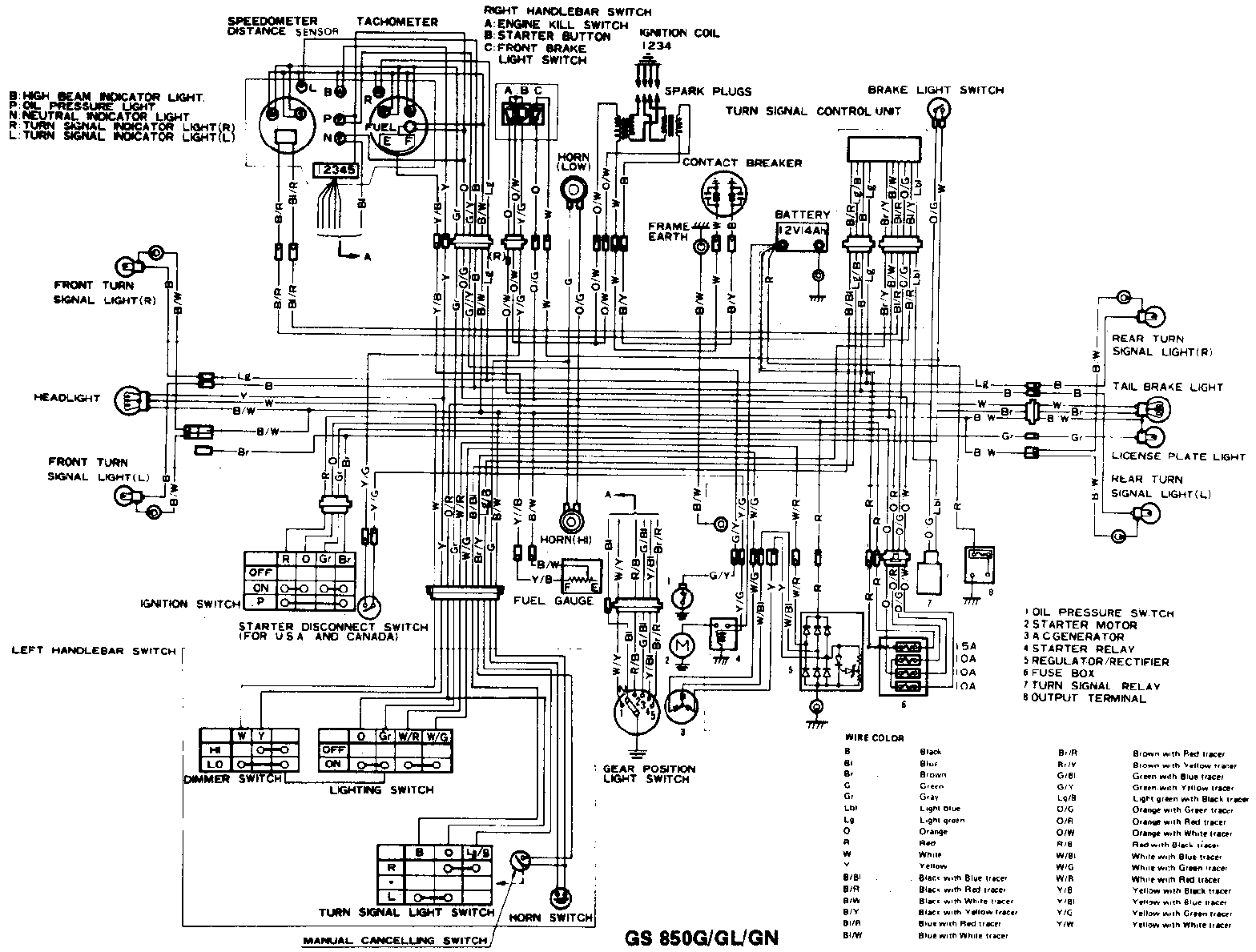
The fuel line diagram for your Suzuki GS750 provides a visual representation of the fuel system’s components and their connections. Understanding the diagram is essential for effective troubleshooting and maintenance of your motorcycle’s fuel system.
Common Symbols and Their Meanings
This table presents a list of common symbols found on fuel line diagrams and their corresponding meanings. Understanding these symbols will help you accurately interpret the diagram and identify the components involved in the fuel delivery process.
| Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|
| ● | Fuel Tank |
| ○ | Fuel Pump |
| ◎ | Fuel Filter |
| ● | Fuel Line |
| ◎ | Carburetor |
| ○ | Fuel Valve |
| ● | Fuel Pressure Regulator |
Troubleshooting Fuel-Related Issues
The fuel line diagram serves as a roadmap for diagnosing fuel-related issues. By following the fuel flow path depicted in the diagram, you can pinpoint the potential source of problems. For example, if your motorcycle experiences a sudden loss of power, the fuel line diagram can help you determine whether the issue lies in the fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel filter, or the fuel lines themselves.
By tracing the fuel flow from the tank to the carburetor, you can identify any potential blockages, leaks, or component failures that might be causing the problem.
The diagram is a visual tool that can be used to identify the location of potential issues.
Fuel Line Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Maintaining the fuel lines in your Suzuki GS750 is crucial for ensuring a reliable and efficient fuel delivery system. Regular inspection and cleaning can prevent fuel line problems and ensure optimal engine performance.
Common Fuel Line Problems and Their Causes
Fuel line problems can arise from various factors, including wear and tear, contamination, and improper installation. Understanding these issues is essential for effective troubleshooting.
- Clogged Fuel Lines:This is a common problem caused by the accumulation of dirt, debris, or rust within the fuel lines. It can restrict fuel flow and lead to engine stalling or difficulty starting.
- Fuel Line Leaks:Leaks can occur due to cracks, holes, or loose connections in the fuel lines. They can result in fuel loss, engine performance issues, and even fire hazards.
- Fuel Line Collapse:This can happen when fuel lines are exposed to excessive heat or pressure. It can restrict fuel flow and lead to engine problems.
- Fuel Line Deterioration:Over time, fuel lines can deteriorate due to exposure to fuel, chemicals, and environmental factors. This can lead to leaks, cracks, and other problems.
Troubleshooting Fuel Line Issues Using the Diagram
The fuel line diagram is an invaluable tool for troubleshooting fuel line problems. It provides a visual representation of the fuel system components and their connections, allowing you to identify potential issues and trace fuel flow.
- Visual Inspection:Start by visually inspecting the fuel lines for any signs of damage, leaks, or corrosion. Look for cracks, holes, bulges, or areas where the lines are rubbing against other components.
- Fuel Line Routing:Refer to the fuel line diagram to ensure the lines are routed correctly. Incorrect routing can lead to kinks, restrictions, or damage.
- Fuel Line Connections:Check all fuel line connections for tightness and proper sealing. Loose or leaking connections can cause fuel loss and engine problems.
- Fuel Flow Test:If you suspect a fuel line blockage, you can test fuel flow by disconnecting the fuel line at the fuel tank and checking for fuel flow when the engine is running.
- Fuel Filter Inspection:Inspect the fuel filter for dirt, debris, or blockage. A clogged filter can restrict fuel flow and cause engine problems.
Fuel Line Modifications and Upgrades
Modifying the fuel line system on a Suzuki GS750 can improve performance, reliability, and even aesthetics. While the stock system is generally sufficient, upgrades can address specific issues or enhance overall functionality.
Fuel Line Material Upgrades
Upgrading the fuel line material can offer benefits like improved fuel flow, increased durability, and better resistance to fuel degradation.
- Stainless Steel Fuel Lines:Stainless steel fuel lines are known for their corrosion resistance, strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures. They offer excellent durability and can handle higher fuel pressures, making them ideal for performance-oriented modifications.
- High-Performance Rubber Fuel Lines:While traditional rubber fuel lines are prone to cracking and degradation over time, high-performance rubber lines are designed for superior resistance to fuel, heat, and abrasion. They offer improved flexibility and are suitable for both stock and modified systems.
- Nylon Fuel Lines:Nylon fuel lines are lightweight and offer good resistance to chemicals and abrasion. They are often used in applications where weight reduction is a priority, such as racing applications.
Fuel Line Routing Modifications
Adjusting the fuel line routing can improve fuel flow, reduce fuel line stress, and enhance the overall aesthetics of the motorcycle.
- Shortening Fuel Lines:Reducing the overall length of the fuel lines can minimize pressure drop and improve fuel flow. This is particularly beneficial when using higher-performance fuel pumps or when running a modified engine with increased fuel demands.
- Optimizing Fuel Line Bends:Sharp bends in fuel lines can restrict fuel flow and increase pressure drop. Optimizing the fuel line routing to avoid sharp bends can improve fuel delivery efficiency.
- Relocating Fuel Lines:Relocating fuel lines can improve accessibility for maintenance and repairs, reduce clutter in the engine bay, and enhance the overall aesthetics of the motorcycle. It’s essential to ensure that the new routing doesn’t compromise the fuel line’s integrity or create potential hazards.
Fuel Filter Upgrades
Upgrading the fuel filter can improve fuel quality, protect the engine from contaminants, and enhance overall performance.
- High-Flow Fuel Filters:High-flow fuel filters are designed to handle increased fuel flow rates, which is crucial for modified engines or performance applications. They typically have a larger filter surface area and lower flow resistance, ensuring efficient fuel delivery.
- Micron-Rated Fuel Filters:Micron-rated fuel filters offer superior filtration capabilities, removing even the smallest particles from the fuel. This can improve fuel quality, reduce wear and tear on engine components, and extend engine life.
Fuel Pump Upgrades
Upgrading the fuel pump can improve fuel delivery, increase fuel pressure, and support higher engine power output.
Yo, if you’re trying to get that classic Suzuki GS750 running smooth, you gotta check out the fuel line diagram. It’s like the blueprint for your engine’s fuel system, showing you how everything connects. And if you’re new to this whole motorcycle thing, you might wanna check out Hello world! , it’s a cool site for learning about all sorts of stuff.
Anyway, once you’ve got that fuel line diagram memorized, you’ll be able to troubleshoot any fuel issues and get your GS750 back on the road in no time.
- High-Flow Fuel Pumps:High-flow fuel pumps are designed to deliver a larger volume of fuel, ensuring adequate supply even at high engine speeds and under heavy load conditions. This is essential for performance-oriented modifications.
- Adjustable Fuel Pressure Regulators:Adjustable fuel pressure regulators allow for precise control of fuel pressure, ensuring optimal fuel delivery to the engine. This can be beneficial for tuning and maximizing engine performance.
Safety Considerations
Working on the fuel system of a motorcycle requires careful attention to safety. Gasoline is highly flammable and can cause serious injury or death if not handled properly. This section discusses the importance of fuel system safety precautions, potential hazards, and tips for safe handling of fuel and working on the fuel system.
Yo, if you’re trying to get that Suzuki GS750 running smooth, you gotta know your fuel lines. It’s like knowing the lyrics to your favorite song, man. And if you’re feeling lost, check out Educational Word Searches – they’ve got some sick word puzzles that can help you learn new stuff.
But back to the GS750, once you’ve got that fuel line diagram down, you’ll be cruisin’ like a pro.
Potential Hazards Associated with Fuel System Maintenance and Modifications
Fuel system maintenance and modifications involve potential hazards that must be addressed to ensure safety.
- Fire Hazard:Gasoline is highly flammable and can ignite easily. It is crucial to work in a well-ventilated area, away from any potential sources of ignition, such as open flames, sparks, or heat.
- Explosion Hazard:Gasoline vapors can form explosive mixtures in the air. Avoid creating sparks or static electricity, as this can ignite the vapors.
- Toxicity:Gasoline is toxic and can cause skin irritation, respiratory problems, and other health issues. Avoid prolonged exposure to gasoline and wear appropriate protective gear, such as gloves and eye protection.
- Fuel Spills:Spilled gasoline can create a slip hazard and can be difficult to clean up. Use absorbent materials to clean up spills immediately and dispose of them properly.
Tips for Handling Fuel and Working on the Fuel System Safely
It is essential to follow these tips when working on the fuel system of your Suzuki GS750:
- Work in a well-ventilated area:Ensure adequate airflow to prevent the accumulation of flammable vapors.
- Avoid sparks and static electricity:Wear appropriate clothing and footwear that minimize static electricity buildup.
- Use appropriate tools and equipment:Use tools and equipment that are specifically designed for working with fuel systems.
- Clean up spills immediately:Use absorbent materials to clean up spills and dispose of them properly.
- Handle fuel with care:Avoid spilling fuel and do not smoke or use open flames near fuel.
- Store fuel properly:Store fuel in approved containers and in a well-ventilated area away from heat and ignition sources.
- Seek professional assistance:If you are unsure about any aspect of fuel system maintenance or modifications, seek professional assistance from a qualified mechanic.
Fuel Line Disconnection and Fuel Line Leak Prevention
- Fuel Line Disconnection:When disconnecting fuel lines, always ensure the fuel supply is turned off. This prevents fuel from spilling and reduces the risk of fire or explosion. Use a fuel line clamp or pliers to disconnect the fuel lines, ensuring a secure grip and avoiding damage to the fuel lines or fittings.
- Fuel Line Leak Prevention:Use high-quality fuel line clamps and fittings to ensure a secure connection and prevent leaks. Inspect fuel lines for cracks, leaks, or damage before starting any work. Replace any damaged fuel lines or fittings immediately.
Fuel Line Diagram Resources
Locating accurate and reliable fuel line diagrams for your Suzuki GS750 is essential for understanding the fuel system, troubleshooting issues, and making any necessary repairs or modifications. This section will provide you with a list of resources that can help you obtain the diagrams you need.
Online Forums and Communities
Online forums and communities dedicated to Suzuki motorcycles, particularly the GS750 model, are valuable resources for obtaining fuel line diagrams and discussing fuel system issues. These platforms offer a space for owners to share their experiences, knowledge, and troubleshooting tips.
Members often post diagrams, schematics, and technical information related to various aspects of the motorcycle, including the fuel system.
Manufacturer Websites and Service Manuals
The most reliable source for fuel line diagrams is often the manufacturer’s website or service manuals. Suzuki’s official website may provide access to downloadable diagrams or service manuals for your specific model year. These documents are usually detailed and accurate, offering a comprehensive understanding of the fuel system components and their connections.
While some manufacturers may offer free access to basic diagrams, service manuals are often available for purchase through authorized dealers or online retailers.
Third-Party Resources
Several third-party websites and online retailers specialize in providing motorcycle repair manuals, including those for the Suzuki GS750. These resources can offer a comprehensive collection of service manuals and diagrams, often including fuel line schematics.
It is important to ensure the reliability of these sources by checking customer reviews and verifying the accuracy of the information provided.
Additional Information
Fuel line issues can significantly impact the performance of a motorcycle engine. A properly functioning fuel line ensures a consistent and adequate supply of fuel to the engine, allowing for optimal combustion and power output. Conversely, a faulty fuel line can lead to various problems that hinder engine performance and fuel efficiency.
Impact of Fuel Line Issues on Engine Performance
A faulty fuel line can cause various problems that negatively affect engine performance. Some common issues include:
- Reduced Power Output:A restricted or blocked fuel line can limit the amount of fuel reaching the engine, resulting in a noticeable decrease in power output. The engine may feel sluggish, struggle to accelerate, and have difficulty reaching its full potential.
- Rough Idling:An inconsistent fuel supply can cause the engine to idle erratically, leading to rough idling and stalling. This can be caused by fuel line leaks, blockages, or a compromised fuel pump.
- Backfiring:A faulty fuel line can cause fuel to enter the exhaust system, leading to backfiring. This occurs when the fuel-air mixture is not properly ignited in the combustion chamber and burns in the exhaust system instead.
- Engine Stalling:A complete blockage in the fuel line can prevent fuel from reaching the engine, resulting in stalling. This can happen during acceleration or at idle, depending on the location of the blockage.
Impact of Fuel Line Issues on Fuel Efficiency
A faulty fuel line can lead to decreased fuel efficiency due to various factors:
- Fuel Leaks:Leaks in the fuel line can cause fuel to be lost, resulting in reduced fuel efficiency. Even small leaks can significantly impact fuel consumption over time.
- Restricted Fuel Flow:A partially blocked fuel line can restrict the fuel flow to the engine, forcing it to work harder to draw fuel. This increased effort can lead to higher fuel consumption.
- Fuel Pressure Issues:A faulty fuel line can affect fuel pressure, leading to an imbalance in the fuel-air mixture. This can result in a richer or leaner mixture, both of which can impact fuel efficiency.
History and Evolution of Fuel Line Systems, Suzuki gs750 fuel line diagram
Fuel line systems in motorcycles have evolved significantly over time, driven by advancements in engine technology and fuel delivery systems.
- Early Motorcycles:Early motorcycles often employed simple gravity-fed fuel systems, where fuel flowed from the tank to the carburetor by gravity. These systems were prone to fuel leaks and had limited fuel capacity.
- Introduction of Fuel Pumps:The development of fuel pumps revolutionized fuel delivery systems. Fuel pumps provided a more consistent and reliable fuel supply, allowing for larger fuel tanks and improved engine performance.
- Modern Fuel Injection Systems:Modern motorcycles often utilize fuel injection systems, where fuel is precisely metered and injected into the engine by electronic control units. These systems require more complex fuel lines and components, including fuel rails, injectors, and sensors.
Questions and Answers
What are the common fuel line problems on a Suzuki GS750?
Common fuel line problems include leaks, clogs, cracked lines, and faulty connections. These can lead to fuel starvation, poor engine performance, and even fire hazards.
Where can I find a fuel line diagram for my Suzuki GS750?
You can find fuel line diagrams in service manuals, online forums dedicated to Suzuki motorcycles, and on manufacturer websites.
How often should I inspect my fuel lines?
It’s recommended to inspect your fuel lines at least once a year, or more frequently if you notice any signs of wear or damage.
What are the safety precautions when working on the fuel system?
Always work in a well-ventilated area, wear safety glasses and gloves, and never smoke or use open flames near fuel.