Fuse Box Diagram for 2006 Dodge Charger RT sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with enthusiastic presentation style and brimming with originality from the outset. Imagine your 2006 Dodge Charger RT, a powerful machine with a heart of electrical circuits.
But what happens when those circuits encounter a hiccup? That’s where the fuse box diagram comes in, acting as your roadmap to understanding and resolving electrical issues.
This comprehensive guide will take you through the intricacies of the fuse box, from its location and physical characteristics to interpreting its diagram and troubleshooting common problems. You’ll learn how to identify blown fuses, replace them safely, and understand the role of relays in keeping your Charger running smoothly.
Get ready to unlock the secrets of your car’s electrical system!
Introduction
The 2006 Dodge Charger RT is a powerful and stylish muscle car known for its performance and aggressive design. Understanding the fuse box diagram is crucial for maintaining the vehicle’s electrical system and troubleshooting any potential problems.
Fuse Box Diagram Importance
A fuse box diagram provides a visual representation of the fuses and relays within a vehicle’s electrical system. This diagram is essential for identifying and replacing blown fuses, which protect circuits from overloads and potential damage.
Fuse Function
Fuses are safety devices designed to protect electrical circuits from excessive current flow. When a circuit experiences an overload, the fuse’s thin wire melts, interrupting the flow of electricity and preventing damage to the components connected to that circuit.
Location of the Fuse Box
The 2006 Dodge Charger RT features a primary fuse box that serves as the central control point for electrical components throughout the vehicle. This fuse box houses a variety of fuses and relays, each responsible for a specific circuit.
Fuse Box Location
The primary fuse box is located in the passenger compartment, on the driver’s side of the dashboard. To access the fuse box, follow these steps:
- Open the driver’s side door and look at the dashboard.
- Locate a small black cover on the driver’s side of the dashboard, near the steering column. This cover is typically located below the steering wheel and above the driver’s left knee.
- Pull the cover towards you to release the fuse box.
The fuse box is a rectangular black plastic box with a hinged lid. The lid is typically held in place by a clip or latch. Inside the fuse box, you will find a diagram that identifies the location and function of each fuse.
Fuse Box Diagram Interpretation: Fuse Box Diagram For 2006 Dodge Charger Rt
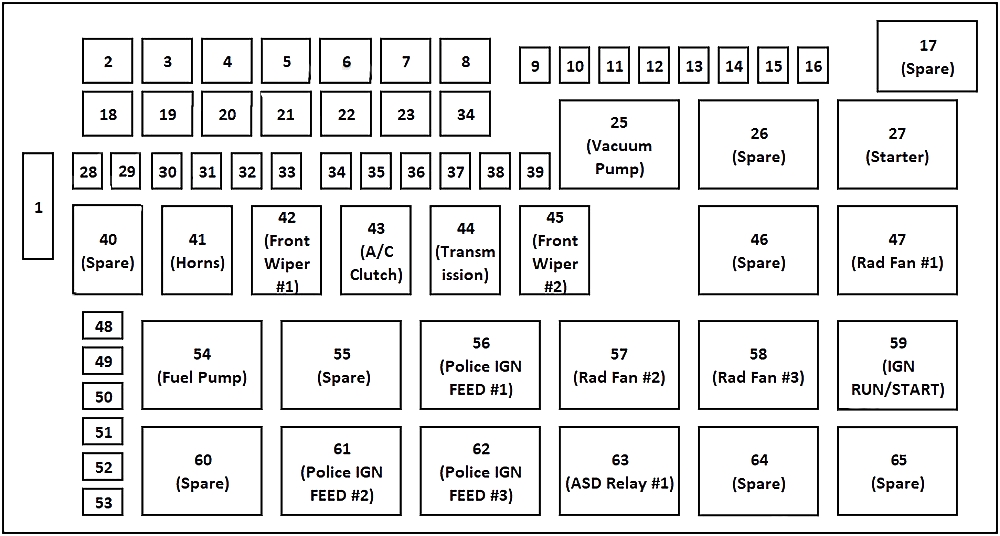
The fuse box diagram is a crucial tool for understanding the electrical system of your 2006 Dodge Charger RT. It provides a visual representation of the fuses and relays that protect and control various circuits in the vehicle. By interpreting this diagram correctly, you can troubleshoot electrical issues, replace blown fuses, and ensure the safe operation of your vehicle.
Fuse Box Diagram Components
The fuse box diagram typically consists of several sections or compartments, each dedicated to a specific group of circuits. These sections are often labeled with letters or numbers for easy identification. For instance, a typical fuse box might have sections labeled “Engine,” “Body,” “Interior,” or “Accessories.” Each section houses a group of fuses and relays responsible for protecting and controlling the circuits associated with that particular area of the vehicle.
Color-Coding System
The fuse box diagram employs a color-coding system to identify the fuses and relays. This system helps to quickly and easily locate the correct fuse or relay for a specific circuit. Common color codes include:
Red
High amperage fuses, typically used for circuits with high current demands, such as headlights, starter motors, and power windows.
Blue
Low amperage fuses, used for circuits with lower current demands, such as interior lights, radio, and accessories.
Yellow
Relays, which are electromagnetic switches that control the flow of electricity to specific circuits.
Fuse Box Diagram Table
The following table provides a detailed breakdown of the fuses and relays found in the 2006 Dodge Charger RT fuse box:| Fuse Number | Amperage | Circuit | Description ||—|—|—|—|| 1 | 10A | Power Outlet | Provides power to the accessory power outlet in the center console.
|| 2 | 15A | Radio | Protects the radio and its associated circuits. || 3 | 10A | Headlights (Left) | Controls the left headlight. || 4 | 10A | Headlights (Right) | Controls the right headlight. || 5 | 20A | Tail Lights | Protects the tail lights, brake lights, and turn signals.
|| 6 | 10A | Parking Lights | Controls the parking lights. || 7 | 15A | Fog Lights | Controls the fog lights. || 8 | 10A | Power Seat (Driver) | Controls the driver’s power seat. || 9 | 10A | Power Seat (Passenger) | Controls the passenger’s power seat.
|| 10 | 15A | Air Conditioning | Protects the air conditioning system. || 11 | 10A | Power Windows | Controls the power windows. || 12 | 10A | Power Mirrors | Controls the power mirrors. || 13 | 15A | Horn | Protects the horn circuit.
|| 14 | 10A | ABS | Controls the Anti-lock Braking System. || 15 | 10A | Airbag | Protects the airbag system. || 16 | 20A | Fuel Pump | Controls the fuel pump. || 17 | 10A | Ignition | Controls the ignition system.
|| 18 | 10A | Starter | Controls the starter motor. || 19 | 10A | Instrument Panel | Protects the instrument panel gauges and lights. || 20 | 10A | Rear Defroster | Controls the rear window defroster. |
Interpreting the Diagram, Fuse box diagram for 2006 dodge charger rt
To interpret the fuse box diagram effectively, follow these steps:
1. Locate the fuse box
Identify the location of the fuse box in your vehicle, typically found under the hood or in the dashboard.
2. Identify the circuit
Determine the specific circuit you need to troubleshoot. This might be a malfunctioning headlight, a non-functioning radio, or a blown tail light.
Finding the right fuse box diagram for a 2006 Dodge Charger RT is essential for diagnosing electrical issues, and understanding the layout is crucial for proper maintenance. While you’re navigating through the intricacies of your car’s electrical system, it’s worth remembering that other powerful engines, like the 7.4 454 Vortec, also have their own specific sparkplug diagrams, like the one found here.
Once you’ve mastered the fuse box diagram for your Charger RT, you’ll be able to tackle any electrical problem with confidence.
3. Locate the fuse or relay
Use the diagram to locate the fuse or relay responsible for that circuit. Pay attention to the fuse number, amperage, and color code.
4. Inspect the fuse or relay
Visually inspect the fuse or relay for any signs of damage or burning. If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new one of the same amperage. If the relay is faulty, replace it with a new one.
5. Test the circuit
After replacing the fuse or relay, test the circuit to ensure it is functioning properly.Remember, it’s crucial to consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for specific information on your fuse box diagram and its components.
Common Fuse Problems
Fuses are designed to protect electrical circuits from damage caused by overloads or short circuits. In a 2006 Dodge Charger RT, fuse problems can arise due to various factors, leading to malfunctions in specific electrical components. Understanding these problems and how to address them is crucial for maintaining the vehicle’s electrical system.
Identifying a Blown Fuse
A blown fuse will typically have a broken or melted filament, creating an open circuit. To identify a blown fuse, visually inspect the fuse for the following:
- A visible break or gap in the filament
- A darkened or discolored appearance
- A melted or bulged fuse body
If any of these signs are present, the fuse is blown and needs to be replaced.
Replacing a Blown Fuse
Replacing a blown fuse requires a few simple steps:
- Locate the fuse box and identify the blown fuse using the fuse box diagram.
- Turn off the ignition and any related electrical components.
- Use fuse puller or pliers to carefully remove the blown fuse.
- Insert a new fuse of the same amperage rating into the empty fuse slot.
- Turn on the ignition and check if the electrical component is functioning correctly.
It is essential to use fuses with the correct amperage rating to avoid overloading the circuit and causing further damage.
Potential Causes of Blown Fuses
Blown fuses can occur due to several reasons:
- Short Circuit:A short circuit occurs when an electrical current takes an unintended path, often due to damaged wiring or a faulty component. This can cause a sudden surge of current, blowing the fuse.
- Overload:When a circuit draws more current than its designed capacity, it can overload the fuse, causing it to blow. This can happen when multiple electrical components are drawing excessive power or when a component malfunctions and draws more current than usual.
- Faulty Component:A malfunctioning electrical component, such as a faulty headlight or a malfunctioning power window motor, can draw excessive current, leading to a blown fuse.
- Corrosion:Corrosion on fuse terminals or wiring can create resistance, increasing the heat generated and causing the fuse to blow.
Important Fuses and Relays
The fuse box in your 2006 Dodge Charger RT houses several critical fuses that protect your vehicle’s electrical systems. Understanding the function of these fuses is essential for troubleshooting electrical issues and ensuring the safe operation of your vehicle.
Fuse Box Layout and Function
The fuse box is typically located in the engine compartment, near the battery. It contains a variety of fuses, each protecting a specific circuit in the vehicle. The fuse box diagram, which is often located on the inside of the fuse box cover, provides a visual representation of the fuse layout and the components they protect.
Important Fuses
The following are some of the most critical fuses in your 2006 Dodge Charger RT:
Headlights
The headlights are an essential safety feature, allowing you to see the road ahead at night. The headlight fuse is typically a high-amp fuse, as it needs to handle the high current required to power the headlights. If the headlight fuse blows, the headlights will not work.
Power Windows
The power window fuse controls the electrical circuit that operates the power windows. If this fuse blows, the power windows will not function. This can be a major inconvenience, especially if you are trying to roll down the windows in hot weather.
Ignition
The ignition fuse is responsible for supplying power to the ignition system, which includes the starter motor, ignition coil, and spark plugs. If this fuse blows, the engine will not start.
Relays
Relays are electromagnetic switches that control the flow of electricity to various components in the vehicle. They are used to protect the fuse box from the high current loads of certain components.
Relay Function
Relays typically have three terminals: an input terminal, an output terminal, and a control terminal. When a small current is applied to the control terminal, the relay activates, allowing current to flow from the input terminal to the output terminal.
Common Relays
Common relays in the fuse box include:* Headlight Relay:Controls the high-beam headlights.
Horn Relay
Controls the horn.
Fuel Pump Relay
Controls the fuel pump.
Cooling Fan Relay
Controls the cooling fan.
Troubleshooting Fuse Problems
If you suspect a fuse has blown, you can use a multimeter to test the fuse. A blown fuse will have an open circuit, meaning there is no continuity between the two ends of the fuse. If a fuse is blown, you should replace it with a fuse of the same amperage.
Troubleshooting Fuse Box Issues
Troubleshooting fuse box issues is a common task for car owners, especially when encountering electrical problems. This section will guide you through the process of identifying and resolving common fuse box problems in your 2006 Dodge Charger RT.
Using a Multimeter to Test Fuses and Circuits
A multimeter is an essential tool for testing fuses and circuits. It allows you to measure voltage, current, and resistance, helping you pinpoint the source of the problem.
- Identify the Fuse:Consult your owner’s manual or the fuse box diagram to locate the fuse associated with the malfunctioning component.
- Remove the Fuse:Carefully remove the fuse from its slot.
- Set the Multimeter:Set the multimeter to the “continuity” or “resistance” setting.
- Test the Fuse:Touch the multimeter probes to the fuse terminals. If the fuse is good, the multimeter will indicate continuity (usually a beep or a low resistance reading). If the fuse is blown, the multimeter will show an open circuit (no beep or a high resistance reading).
- Test the Circuit:If the fuse is blown, you need to test the circuit for a short circuit. Disconnect the component connected to the fuse and set the multimeter to the “voltage” setting. Touch one probe to the positive terminal of the fuse and the other probe to the negative terminal.
If the multimeter reads voltage, there is a short circuit in the circuit.
Note:Always disconnect the battery before working on electrical components.
Safety Precautions
Working with electrical components, including the fuse box, requires a high level of caution. Improper handling can lead to severe consequences, including electric shock and damage to the vehicle’s electrical system.
Disconnecting the Battery
Before working on the fuse box, it is crucial to disconnect the battery to prevent electrical hazards. Disconnecting the battery removes the electrical current from the system, minimizing the risk of electric shock. To disconnect the battery, follow these steps:
- Locate the battery, typically located in the engine compartment.
- Identify the positive (+) and negative (-) terminals of the battery.
- Using a wrench or socket, loosen the nut securing the negative terminal cable.
- Carefully remove the negative terminal cable from the battery post.
- Repeat the process for the positive terminal cable.
Risks of Improper Fuse Replacement
Using an incorrect fuse can lead to serious consequences, including:
- Overheating and Fire:Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating than required can cause the fuse to overheat and melt, potentially starting a fire.
- Damage to Electrical Components:Using a fuse with a lower amperage rating than required can cause the fuse to blow frequently, disrupting the electrical circuit and potentially damaging other electrical components.
- Electrical Malfunctions:Incorrect fuse replacement can cause electrical malfunctions, affecting various vehicle systems, including lighting, power windows, and engine performance.
It is essential to use only fuses with the correct amperage rating as specified in the fuse box diagram.
Additional Resources
For a comprehensive understanding of the 2006 Dodge Charger RT fuse box, it’s beneficial to explore additional resources that provide detailed information and support. These resources can offer in-depth explanations, troubleshooting guides, and expert insights to help you navigate any fuse-related issues effectively.
Online Resources
Exploring reputable online resources can provide valuable insights into the 2006 Dodge Charger RT fuse box. These resources offer detailed diagrams, fuse locations, and troubleshooting tips.
- Dodge Official Website:The official Dodge website often provides access to owner’s manuals, repair guides, and technical information, including fuse box diagrams. This is a reliable source for accurate and up-to-date information.
- Automotive Forums:Online forums dedicated to Dodge vehicles, such as Charger forums, can be a valuable resource for finding discussions, troubleshooting advice, and shared experiences related to fuse box issues. These forums often have experienced members who can provide guidance and support.
- Online Repair Manuals:Reputable online repair manuals, such as those from Chilton or Haynes, offer detailed information on various aspects of vehicle repair, including fuse box diagrams and troubleshooting procedures. These manuals provide a comprehensive understanding of the vehicle’s electrical system.
Automotive Repair Manuals
Automotive repair manuals provide detailed information on the electrical system and fuse box of the 2006 Dodge Charger RT. These manuals offer comprehensive guidance for troubleshooting and repairing fuse-related issues.
- Chilton Repair Manuals:Chilton manuals offer step-by-step instructions, diagrams, and specifications for various automotive repairs, including fuse box troubleshooting.
- Haynes Repair Manuals:Haynes manuals provide comprehensive information on vehicle maintenance and repair, including detailed explanations of fuse box diagrams and common fuse problems.
Reputable Automotive Forums
Engaging with online automotive forums dedicated to Dodge vehicles can provide valuable insights and support from experienced enthusiasts and technicians. These forums offer a platform for sharing information, troubleshooting tips, and seeking assistance.
- Dodge Forums:Dedicated forums for Dodge vehicles, such as Charger forums, often have sections or threads specifically focused on electrical issues, including fuse box problems. These forums can provide a wealth of information and practical advice from fellow owners and technicians.
- General Automotive Forums:General automotive forums, such as those focused on car repair or DIY mechanics, can also be helpful for finding information on fuse box issues. These forums often have experienced members who can provide guidance and troubleshooting tips for various vehicle models.
Conclusion
Understanding the fuse box diagram for your 2006 Dodge Charger RT is crucial for maintaining the electrical health of your vehicle. It allows you to quickly identify and address any electrical issues, preventing further damage to your car’s systems.Fuses act as safety devices, protecting your vehicle’s electrical system from overloads and short circuits.
By interrupting the flow of electricity when a circuit is overloaded, they prevent damage to sensitive components and ensure the safety of your vehicle.
Importance of Understanding the Fuse Box Diagram
The fuse box diagram provides a visual representation of the electrical system, making it easier to locate and troubleshoot specific circuits. It also helps you understand the relationship between different electrical components and how they interact with each other.
Role of Fuses in Protecting the Electrical System
Fuses are essential for safeguarding your vehicle’s electrical system. When a circuit experiences an overload or short circuit, the fuse melts and breaks the circuit, preventing further damage to components. This protects your car’s electrical system from overheating, fires, and other potential hazards.
Consulting a Qualified Mechanic for Complex Electrical Issues
While the fuse box diagram can be a valuable tool for basic troubleshooting, it’s important to consult a qualified mechanic for complex electrical issues. A mechanic can diagnose the problem accurately, repair any damaged components, and ensure the safety of your vehicle.
FAQ Insights
What are the most common fuse problems in a 2006 Dodge Charger RT?
Common fuse problems include blown fuses due to overloads, faulty wiring, or corrosion. These can affect various systems like headlights, power windows, and even the ignition.
How do I know if a fuse is blown?
A blown fuse will typically have a broken filament, which can be visually identified as a gap or a blackened area within the fuse. You can also use a multimeter to test for continuity.
What are relays and what is their role in the fuse box?
Relays are electrical switches that control the flow of electricity to specific circuits. They are often used to protect sensitive components from high currents and to manage the power flow to various systems.