BMW 3 Wires AUC Sensor Pinout Diagram: A guide to unraveling the mysteries of this vital component, a key player in emissions control, and a crucial part of your BMW’s engine health. This diagram is your roadmap to understanding the three wires, their functions, and how they work together to ensure your car runs smoothly and efficiently.
It’s a world of color-coded connections and signal types, waiting to be deciphered. Prepare to embark on a journey into the heart of your BMW’s engine management system, where we’ll explore the AUC sensor’s role in keeping your car running at its peak performance.
The AUC sensor, or Air-to-Fuel Ratio Sensor, is a critical component in your BMW’s emissions control system. This sensor plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal fuel efficiency and minimizing harmful emissions. The three wires connected to the AUC sensor each have a specific function, transmitting vital information to the engine control unit (ECU) to ensure the engine operates at peak efficiency.
This pinout diagram serves as a visual guide, mapping out each wire’s function and color, enabling you to understand the sensor’s role in the engine’s intricate dance of fuel and air.
Replacing the AUC Sensor: Bmw 3 Wires Auc Sensor Pinout Diagram
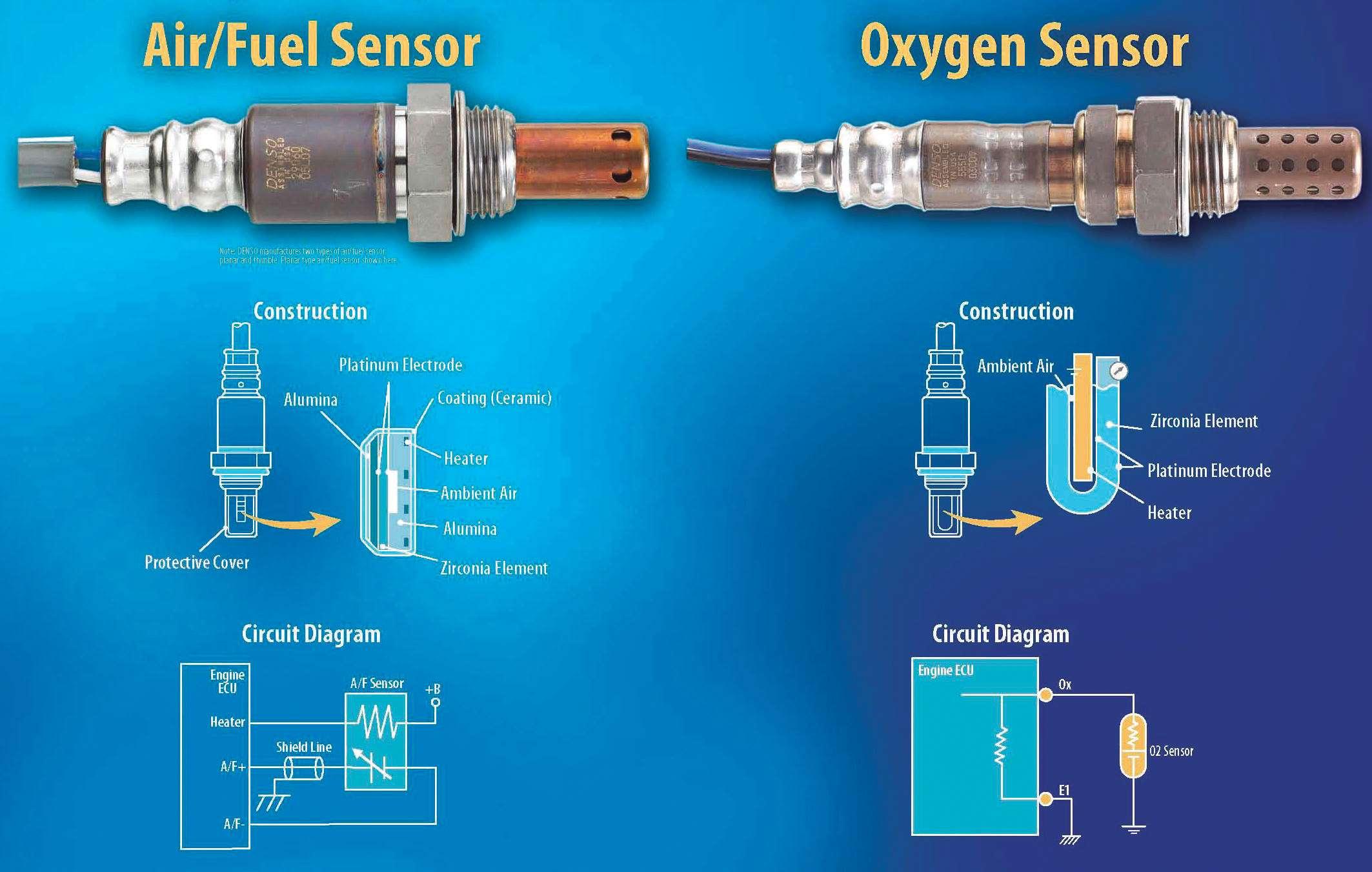
Replacing the AUC sensor in a BMW 3-series vehicle is a straightforward procedure that can be accomplished with basic tools and a bit of patience. This sensor plays a crucial role in monitoring the air-fuel ratio, ensuring optimal engine performance and emissions control.
Tools and Equipment
A set of basic tools is required for this task, ensuring a safe and efficient replacement process.
- Socket wrench set: For loosening and tightening bolts and nuts.
- Torx screwdriver set: For removing and installing screws with star-shaped heads.
- Flat-head screwdriver: For prying open clips and connectors.
- New AUC sensor: Ensure it is compatible with your specific BMW model and engine.
- Protective gloves: To prevent skin irritation or contact with engine fluids.
- Eye protection: To safeguard your eyes from potential debris or splashes.
- Shop towels: For cleaning up any spills or residue.
Safety Precautions
Prioritize safety throughout the replacement process, minimizing the risk of accidents or injuries.
- Park the vehicle on a level surface and engage the parking brake.
- Disconnect the negative battery terminal before starting any work on the electrical system.
- Be cautious when working near hot engine components.
- Avoid touching any exposed electrical wires or connections.
- Wear appropriate protective gear, including gloves and eye protection.
Step-by-Step Replacement Procedure
The following steps Artikel the process for replacing the AUC sensor, ensuring a smooth and successful procedure.
- Locate the AUC sensor. It is typically positioned on the exhaust manifold or near the catalytic converter.
- Disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor. Gently pull on the connector’s release tab to detach it.
- Remove the sensor mounting bolts. Use the appropriate socket wrench to loosen and remove the bolts securing the sensor.
- Carefully remove the old sensor. Once the bolts are removed, gently pull the sensor out of its mounting location.
- Install the new sensor. Insert the new sensor into the mounting location, aligning it with the mounting holes.
- Tighten the mounting bolts. Use the socket wrench to tighten the bolts to the specified torque, ensuring a secure connection.
- Reconnect the electrical connector. Plug the connector back into the new sensor, ensuring a secure connection.
- Reconnect the negative battery terminal. Once the sensor is installed, reconnect the battery terminal to restore power to the vehicle.
- Clear any fault codes. After installing the new sensor, use an OBD-II scanner to clear any fault codes related to the AUC sensor.
- Test drive the vehicle. After clearing any fault codes, take the vehicle for a test drive to ensure proper operation.
Important Notes
- Refer to the BMW service manual for specific instructions and torque specifications for your vehicle model.
- Ensure the new sensor is compatible with your vehicle’s engine and emissions system.
- If you are not comfortable performing this procedure, consult a qualified mechanic.
AUC Sensor Testing and Calibration
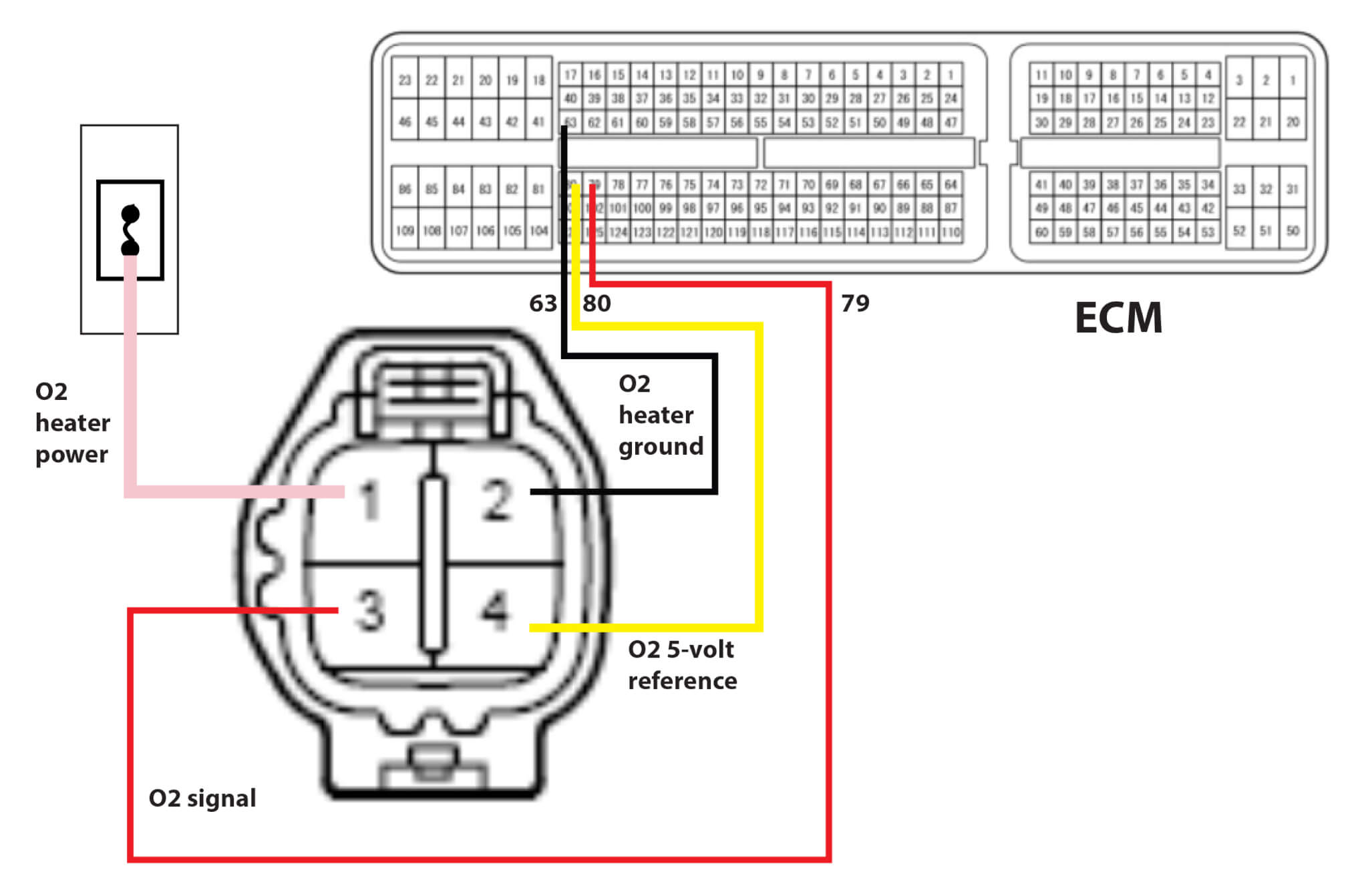
After replacing the AUC sensor, it’s crucial to ensure it’s functioning correctly and properly calibrated. This process involves testing the sensor’s output and adjusting its readings to match the actual air-fuel ratio in the engine.
AUC Sensor Testing
Testing the AUC sensor involves verifying its electrical signals and comparing them to expected values. This can be done using a diagnostic tool or a multimeter. Here’s a breakdown of common testing methods:
- Voltage Measurement:With the engine running, check the voltage output of the AUC sensor using a multimeter. The voltage should fluctuate within a specific range, typically between 0.1 and 4.9 volts, depending on the air-fuel ratio.
- Resistance Measurement:Measure the resistance of the AUC sensor using a multimeter.
The resistance should vary depending on the temperature of the sensor.
- Diagnostic Tool Scan:Use a diagnostic tool to retrieve sensor data from the engine control unit (ECU). The tool can display the sensor’s voltage, resistance, and other relevant information, allowing for comparison with expected values.
AUC Sensor Calibration, Bmw 3 wires auc sensor pinout diagram
Calibrating the AUC sensor is essential to ensure accurate air-fuel ratio readings. The calibration process involves adjusting the sensor’s output to match the actual air-fuel ratio in the engine. This can be done using a diagnostic tool.
- Diagnostic Tool Calibration:Connect a diagnostic tool to the vehicle’s OBD-II port. Access the calibration function for the AUC sensor within the tool’s menu. The tool will typically guide you through the calibration process, which may involve setting the sensor’s baseline voltage or adjusting its output based on a series of readings.
Impact of a Faulty AUC Sensor

A faulty AUC sensor can significantly impact engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions. The sensor plays a crucial role in determining the amount of air entering the engine, and any malfunction can lead to inaccurate readings, affecting the engine’s ability to operate optimally.
Consequences for Engine Performance
A malfunctioning AUC sensor can cause various issues with engine performance. The sensor provides the engine control unit (ECU) with data about the amount of air entering the engine. If the sensor is faulty, the ECU may receive inaccurate information, leading to problems like:
- Rough idling:The engine may idle erratically or stall due to incorrect air-fuel mixture calculations.
- Hesitation or stalling:The engine may hesitate or stall when accelerating, as the ECU struggles to adjust the fuel mixture based on faulty air readings.
- Reduced power:The engine may experience a loss of power, as the ECU compensates for the inaccurate air readings, leading to a leaner air-fuel mixture.
- Backfiring:In extreme cases, the engine may backfire due to an excessively lean air-fuel mixture caused by a faulty AUC sensor.
Impact on Fuel Efficiency and Emissions
A faulty AUC sensor can also impact fuel efficiency and emissions. The sensor’s inaccurate readings can cause the ECU to miscalculate the air-fuel mixture, resulting in:
- Increased fuel consumption:The engine may consume more fuel than usual, as the ECU compensates for the inaccurate air readings by adding more fuel.
- Higher emissions:A faulty sensor can lead to higher emissions, as the engine may run richer or leaner than optimal, resulting in increased levels of pollutants like carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides.
Warning Signs of a Failing AUC Sensor
Several warning signs can indicate a failing AUC sensor. These signs may include:
- Check engine light:The most common warning sign is the check engine light illuminating on the dashboard, indicating a fault detected by the ECU.
- Rough idling:The engine may idle erratically or stall, indicating a problem with the air-fuel mixture.
- Hesitation or stalling:The engine may hesitate or stall when accelerating, as the ECU struggles to adjust the fuel mixture based on faulty air readings.
- Reduced power:The engine may experience a loss of power, as the ECU compensates for the inaccurate air readings, leading to a leaner air-fuel mixture.
- Backfiring:In extreme cases, the engine may backfire due to an excessively lean air-fuel mixture caused by a faulty AUC sensor.
- Increased fuel consumption:The engine may consume more fuel than usual, as the ECU compensates for the inaccurate air readings by adding more fuel.
- Excessive smoke:The engine may emit excessive smoke, indicating an imbalance in the air-fuel mixture.
Alternative AUC Sensor Solutions

While the standard AUC sensor remains a reliable component in BMW vehicles, alternative technologies and solutions are emerging, offering potential advantages and addressing specific needs. These alternatives cater to various factors, including cost, performance, and compatibility with different vehicle models.
Alternative Sensor Technologies
The search for improved AUC sensor technologies has led to the development of alternative sensor types. These sensors offer unique characteristics and may be more suitable for certain applications.
- Hall Effect Sensors:These sensors rely on the Hall effect, a phenomenon where a magnetic field influences the flow of electric current. Hall effect sensors are known for their robustness, durability, and high accuracy in measuring speed and position. They can be a suitable alternative to traditional AUC sensors in certain BMW models.
- Optical Sensors:Optical sensors utilize light to detect changes in speed or position. These sensors offer high precision and are less susceptible to interference from magnetic fields or other environmental factors. However, their cost can be higher than traditional AUC sensors.
- Capacitive Sensors:Capacitive sensors measure changes in capacitance, which can be influenced by proximity or displacement. These sensors are highly sensitive and can provide accurate measurements even in challenging environments. They are often used in applications where precise measurements are required, such as in automotive engine management systems.
Aftermarket AUC Sensors
The aftermarket offers a wide range of AUC sensors compatible with BMW vehicles. These sensors can be a cost-effective alternative to OEM parts, but it’s crucial to ensure their quality and reliability.
- Compatibility:When choosing an aftermarket AUC sensor, it’s essential to ensure it’s compatible with your specific BMW model and engine type. Incorrect compatibility can lead to performance issues and damage to your vehicle.
- Quality:Look for reputable aftermarket brands that offer sensors manufactured to meet or exceed OEM standards. Check for certifications and reviews to gauge the quality and reliability of the sensor.
- Warranty:A good aftermarket AUC sensor should come with a warranty that covers defects in materials and workmanship. This provides peace of mind and protection against potential issues.
Advanced Diagnostics and Data Analysis
Delving deeper into the intricacies of the AUC sensor requires advanced diagnostic techniques and data analysis. These methods go beyond basic readings and provide valuable insights into the sensor’s health and performance. By analyzing data patterns and trends, technicians can identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
It’s frustrating when you’re trying to fix a car and you’re staring at a jumble of wires, not knowing where they go. You need a diagram, a map to guide you through the maze. That’s where a pinout diagram comes in handy, like the one for a BMW 3-wire AUC sensor.
It’s like a decoder ring for your car’s electrical system. And just like you need a diagram for your car, you’ll need one for a John Deere 111 moo111s242340, and you can find that diagram on this website.
It’s a similar concept – knowing which wire goes where can make the difference between a frustrating repair and a smooth one. So, whether you’re dealing with a BMW or a John Deere, a good wiring diagram is your best friend.
Analyzing AUC Sensor Data
Analyzing AUC sensor data involves examining its output signals to determine the sensor’s accuracy and functionality. This includes evaluating the sensor’s response to various stimuli, such as changes in air quality, temperature, and pressure. By analyzing the data patterns, technicians can identify potential issues, such as drift, noise, or faulty readings.
Interpreting Sensor Readings
Interpreting sensor readings requires understanding the sensor’s operating principles and calibration parameters. The readings must be compared against established benchmarks and standards to determine if they fall within acceptable ranges. Deviations from expected values can indicate potential problems.
Specialized Software and Tools
Specialized software and tools are crucial for efficient data analysis. These tools can automate the process of collecting, storing, and analyzing sensor data. They can also provide visual representations of the data, making it easier to identify trends and anomalies.
Examples include diagnostic software packages specifically designed for BMW vehicles and data analysis tools like MATLAB or Python.
Real-World Case Studies and Applications

The pinout diagram and troubleshooting information for the AUC sensor are invaluable tools for technicians and professionals working on BMW vehicles. They have been instrumental in resolving various real-world cases, showcasing the practical application of this knowledge. This section will delve into some of these case studies, highlighting how the pinout diagram and troubleshooting techniques have been used to diagnose and fix issues related to the AUC sensor.
Case Studies from Experienced Technicians
The pinout diagram and troubleshooting information are crucial for technicians in diagnosing and resolving issues related to the AUC sensor. Here are some real-world case studies that highlight their importance:
- A BMW 3 Series owner was experiencing intermittent engine misfires. The technician used the pinout diagram to identify the correct wiring for the AUC sensor and performed a continuity test on the sensor’s wiring. The test revealed a broken wire, which was repaired, resolving the misfire issue.
- A BMW X5 owner was experiencing a rough idle and a lack of power. The technician suspected a faulty AUC sensor and used the pinout diagram to check the sensor’s voltage readings. The readings were significantly lower than expected, confirming the sensor’s malfunction.
The sensor was replaced, resolving the idle and power issues.
FAQ Section
What is the purpose of the AUC sensor in a BMW?
The AUC sensor, or Air-to-Fuel Ratio Sensor, measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases, providing the engine control unit (ECU) with crucial information about the air-fuel mixture. This data helps the ECU adjust fuel delivery for optimal combustion, ensuring efficient engine performance and minimizing emissions.
Can I replace the AUC sensor myself?
While replacing the AUC sensor is a relatively straightforward process, it’s recommended to consult your owner’s manual or a qualified mechanic for specific instructions. Incorrect installation can lead to further issues, so it’s best to ensure proper procedures are followed.
What are some warning signs of a faulty AUC sensor?
A faulty AUC sensor can manifest in several ways, including reduced fuel efficiency, engine misfires, rough idling, and a check engine light. If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to have the sensor inspected and potentially replaced.
How often should I replace the AUC sensor?
The lifespan of an AUC sensor can vary depending on factors like driving conditions and maintenance. Generally, they can last for several years, but it’s best to consult your owner’s manual or a mechanic for specific recommendations.
Can I use an aftermarket AUC sensor for my BMW?
While aftermarket AUC sensors are available, it’s crucial to ensure compatibility with your specific BMW model. Using a sensor that isn’t compatible can lead to issues with the engine’s performance and emissions control system. It’s always best to consult a mechanic or a reputable parts supplier to ensure compatibility.