73 – ’87 Chevy Truck Fuse Box Diagram is your key to understanding and tackling electrical issues in your classic truck. This comprehensive guide will unravel the mysteries of your fuse box, helping you diagnose problems and restore your truck’s electrical system to its former glory.
From locating the fuse box to deciphering its diagram, we’ll break down the intricacies of this essential component. We’ll explore the role of fuses in protecting your circuits, provide a detailed overview of common fuses and their functions, and guide you through the process of troubleshooting electrical problems.
Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, this guide will empower you to tackle electrical issues with confidence.
Introduction
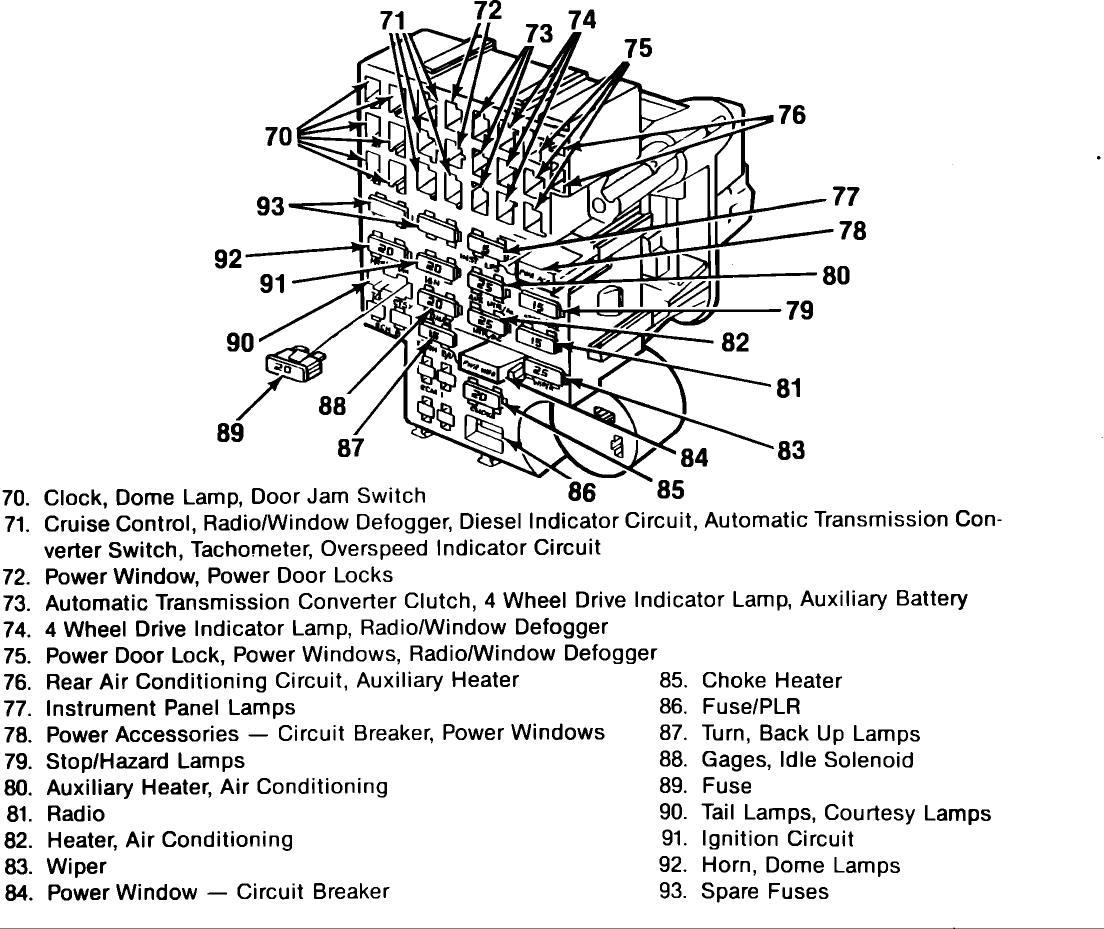
The fuse box in your 1973-1987 Chevrolet truck is a crucial component of the vehicle’s electrical system. It houses a network of fuses that protect individual circuits from damage caused by electrical overloads. Understanding the layout and function of your fuse box is essential for diagnosing and resolving electrical problems.
Importance of the Fuse Box Diagram
The fuse box diagram provides a visual representation of the location and function of each fuse in the box. It helps you identify the fuse responsible for a particular circuit, allowing you to quickly and safely replace a blown fuse.
By using the diagram, you can avoid unnecessary troubleshooting and potential damage to your truck’s electrical system.
Role of Fuses
Fuses are safety devices designed to protect electrical circuits from damage caused by excessive current flow. They are typically made of a thin wire that melts and breaks the circuit when the current exceeds a predetermined limit. This prevents the circuit from overheating and potentially causing a fire.
Fuse Box Location

The fuse box in 1973-1987 Chevrolet trucks is typically located under the hood, on the driver’s side, near the firewall. Its position can vary depending on the model year and trim level.
Fuse Box Appearance
The fuse box is typically a rectangular or square-shaped box with a black or gray plastic cover. It has multiple rows of fuses, each labeled with a number or description. The cover may have a diagram or chart that identifies the purpose of each fuse.
Troubleshooting Electrical Issues
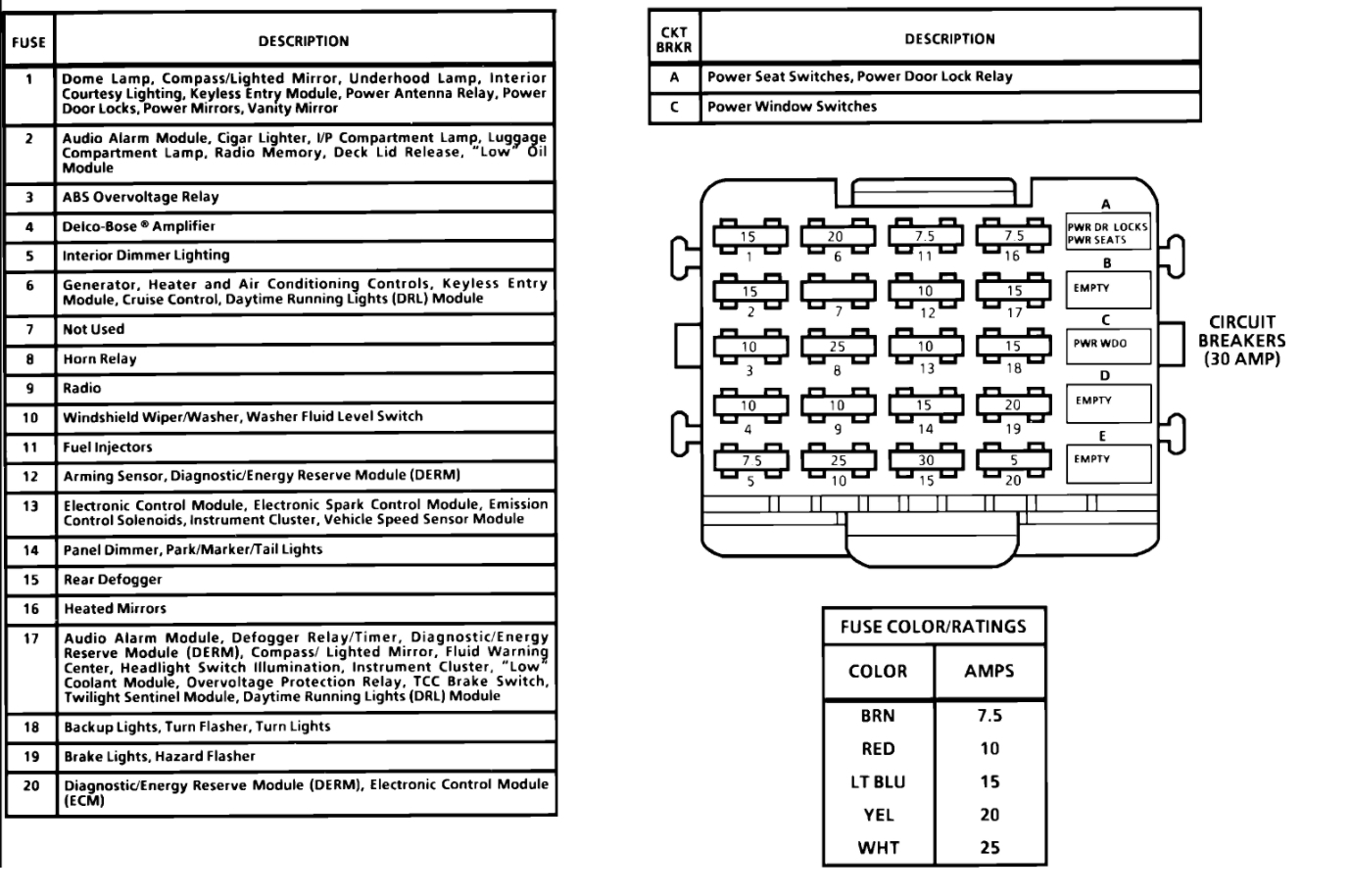
The fuse box diagram is your guide to diagnosing and fixing electrical problems in your 73-87 Chevy truck. It shows the location of each fuse and the circuits they protect, allowing you to quickly identify the source of an electrical malfunction.
Common Symptoms of Blown Fuses
Blown fuses are a common electrical problem in vehicles. They can cause a variety of symptoms, depending on the circuit that has been affected. Here are some common symptoms:
- Lights not working: This could be headlights, taillights, interior lights, or any other lights on your truck.
- Electrical accessories not working: This could include power windows, power locks, radio, or other accessories.
- Engine starting problems: A blown fuse in the ignition system can prevent your engine from starting.
- Electrical system overload: If multiple fuses blow at once, it could indicate a larger electrical problem.
Potential Causes of Blown Fuses
There are several reasons why a fuse might blow. Here are some common causes:
- Short circuit: A short circuit occurs when electricity flows through an unintended path, often due to damaged wiring or a faulty component.
- Overload: A circuit can be overloaded if too many electrical devices are connected to it. This can happen if you use a high-wattage accessory or if there is a problem with the wiring.
- Faulty component: A faulty component, such as a light bulb, motor, or switch, can draw too much current and blow a fuse.
- Corrosion: Corrosion on fuse terminals or wiring can create a high resistance, leading to overheating and fuse failure.
Checking and Replacing Fuses
It is important to safely check and replace fuses. Follow these steps:
- Disconnect the battery: Before working on any electrical system, always disconnect the negative battery terminal to prevent electrical shock.
- Locate the fuse box: Refer to your owner’s manual or the fuse box diagram to locate the fuse box in your truck.
- Identify the blown fuse: Inspect the fuses in the box for any that are blown. A blown fuse will have a broken filament, which will appear as a gap or a melted section.
- Remove the blown fuse: Use a fuse puller or pliers to carefully remove the blown fuse.
- Check the fuse rating: The fuse rating is printed on the fuse. Make sure you replace the blown fuse with one of the same rating.
- Insert the new fuse: Carefully insert the new fuse into the empty fuse holder.
- Reconnect the battery: Once the new fuse is in place, reconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Test the circuit: After reconnecting the battery, test the circuit to make sure the fuse is working properly.
Important Note:Always use fuses with the correct amperage rating. Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating can cause damage to your electrical system.
Fuse Box Maintenance
Proper maintenance of the fuse box is crucial for ensuring the safe and reliable operation of your 1973-1987 Chevrolet truck’s electrical system. Neglecting this essential component can lead to various electrical problems, potentially causing damage to your vehicle and compromising your safety.
Inspecting Fuses
Regularly inspecting the fuses for signs of damage is essential for maintaining the integrity of your electrical system. Damaged fuses can cause electrical malfunctions, leading to potential hazards.
- Look for blown fuses:Blown fuses have a melted or broken filament, indicating that they have been overloaded and need replacement. A blown fuse can be identified by a visible gap in the metal strip within the fuse.
- Check for corrosion:Corrosion can occur on fuse terminals, impairing electrical conductivity. This can lead to overheating and potential electrical failures. Look for signs of green or white powder on the terminals, which indicate corrosion.
- Inspect for loose connections:Loose connections in the fuse box can cause intermittent electrical problems. Ensure that all fuses are securely seated in their slots. If a fuse is loose, it may need to be replaced.
Using the Correct Fuse Type
Using the wrong fuse type can have serious consequences, potentially damaging your vehicle’s electrical system and creating safety hazards.
- Amperage rating:Each fuse is designed for a specific amperage rating. Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating than required can lead to overheating and potential electrical fires. Conversely, using a fuse with a lower amperage rating can cause the fuse to blow frequently, disrupting electrical circuits.
- Fuse type:There are different types of fuses, each designed for specific applications. Using the wrong type of fuse can lead to improper operation or even damage to the fuse box itself. For example, using a blade-type fuse in a cartridge-type fuse holder can result in a loose connection and potential electrical hazards.
Safety Precautions
Working on the fuse box of your 73-87 Chevy truck involves dealing with electrical systems, which can be dangerous if not handled properly. It’s crucial to prioritize safety to avoid electrical shocks, fires, or other potential hazards.
Disconnecting the Battery
Before working on any electrical components, including the fuse box, it’s essential to disconnect the battery. This step is crucial to prevent electrical shocks, as the battery provides a constant source of power even when the engine is off.
- Locate the battery terminals, typically marked with “+” (positive) and “-” (negative).
- Using a wrench or socket, loosen the nut on the negative (-) terminal first.
- Remove the negative cable from the terminal.
- Once the negative cable is disconnected, you can then loosen and remove the positive (+) cable.
Working with Electrical Systems
Always exercise caution when working with electrical systems. Even with the battery disconnected, there may still be residual electrical charge in the system.
- Avoid touching any exposed wires or electrical components with bare hands.
- Use insulated tools, such as screwdrivers, pliers, and wire cutters, to prevent electrical shocks.
- Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from potential sparks or debris.
Handling Fuses and Electrical Components
Fuses are designed to protect electrical circuits from overloads. When a fuse blows, it interrupts the flow of electricity to prevent damage to the circuit.
- Always replace blown fuses with the correct amperage rating. Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating can damage the wiring or cause a fire.
- When handling fuses, use insulated pliers or tweezers to avoid contact with the metal contacts.
- Be careful not to touch the fuse terminals with your bare hands, as this can create a path for electricity to flow through your body.
Additional Resources
This section provides valuable resources that can help you further understand the fuse box diagrams and troubleshoot electrical issues in your 1973-1987 Chevrolet truck. These resources can offer in-depth information, detailed diagrams, and troubleshooting tips, empowering you to confidently address any electrical problems.
Online Manuals and Repair Guides
The internet offers a wealth of information on automotive repair and maintenance. Several websites specialize in providing online manuals and repair guides for various vehicle models, including Chevrolet trucks. These resources often include detailed fuse box diagrams, wiring schematics, and step-by-step instructions for diagnosing and repairing electrical problems.
- Chilton Library:Chilton offers comprehensive repair manuals for a wide range of vehicles, including Chevrolet trucks. Their manuals often include detailed fuse box diagrams, wiring schematics, and troubleshooting guides.
- Haynes Manuals:Haynes manuals are another popular resource for automotive repair information. They provide detailed instructions, diagrams, and troubleshooting tips, including fuse box diagrams and electrical system information.
- AllData:AllData is a subscription-based service that provides access to a vast database of technical information for various vehicle models, including Chevrolet trucks. Their database includes detailed fuse box diagrams, wiring schematics, and troubleshooting guides.
- AutoZone:AutoZone offers a free online repair guide that includes fuse box diagrams, wiring schematics, and troubleshooting tips for a wide range of vehicles.
Searching for Specific Information
When searching for specific information about fuse box diagrams, use relevant s and phrases. For example, you can search for “1973 Chevrolet truck fuse box diagram,” “1987 Chevrolet truck fuse box location,” or “Chevrolet truck fuse box troubleshooting.” Be specific in your search terms to get the most relevant results.
Use quotation marks around specific phrases to ensure that the search engine finds exact matches.
Understanding the 73 – ’87 Chevy truck fuse box diagram is crucial for diagnosing electrical issues. Similar to the complexities of a tt-30r to l14-3r wiring diagram , the fuse box layout often requires detailed analysis to identify the correct fuse for a specific circuit.
Familiarity with the fuse box diagram can save time and frustration when troubleshooting electrical problems in these classic trucks.
You can also use advanced search operators to refine your search results. For example, you can use the “site:” operator to limit your search to a specific website, such as “site:chilton.com 1973 Chevrolet truck fuse box diagram.”
Fuse Box Variations by Model Year: 73 – ’87 Chevy Truck Fuse Box Diagram
Chevrolet trucks from 1973 to 1987 saw several changes in their fuse box layouts, making it essential to understand the differences for accurate troubleshooting and maintenance. This section will guide you through the variations in fuse box locations and diagrams across these model years.
Fuse Box Variations by Model Year
The fuse box location and appearance can vary depending on the model year of your Chevrolet truck. Here is a breakdown of the key differences:
| Model Year | Fuse Box Location | Fuse Box Diagram Variations | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1973-1979 | Under the dash, on the driver’s side, near the steering column. | The fuse box layout is generally similar across these years, but some minor differences may exist depending on the specific trim level and options. | The fuse box is typically a rectangular box with a metal cover. It has a series of fuses arranged in rows and columns. |
| 1980-1987 | Under the dash, on the driver’s side, near the steering column. | The fuse box layout is more standardized in these years, with a larger number of fuses and relays. | The fuse box is similar in appearance to the 1973-1979 models but may be slightly larger to accommodate the increased number of fuses. |
Fuse Box Diagram Examples
This section provides examples of fuse box diagrams for specific model years of Chevrolet trucks from 1973 to 1987. These diagrams illustrate the layout and arrangement of fuses, relays, and other components within the fuse box. Understanding these diagrams is crucial for effectively troubleshooting electrical issues and performing repairs.
Fuse Box Diagram Variations by Model Year
The layout and components within the fuse box can vary depending on the model year of the Chevrolet truck. These variations can impact troubleshooting and repair procedures, so it is essential to use the correct diagram for your specific model year.
- 1973-1977 Chevrolet Trucks: These models typically feature a fuse box located under the hood, near the driver’s side fender. The fuse box diagram for these models will show a relatively simple layout, with a limited number of fuses and relays.
- 1978-1980 Chevrolet Trucks: These trucks may have a fuse box with a more complex layout, with additional fuses and relays to accommodate the introduction of new features and electrical systems.
- 1981-1987 Chevrolet Trucks: These models may have a fuse box with a more modern layout, with a higher density of fuses and relays. The diagram will reflect these changes, including the addition of fuses for features like electronic fuel injection and air conditioning.
Visual Comparison of Fuse Box Diagrams, 73 – ’87 chevy truck fuse box diagram
To illustrate the differences between fuse box diagrams for various model years, consider the following visual comparison:
- 1973 Chevrolet C10: The fuse box diagram for this model year will show a relatively simple layout with a limited number of fuses and relays. The fuses are typically arranged in rows, with each fuse labeled with its corresponding circuit.
- 1980 Chevrolet Silverado: The fuse box diagram for this model year will show a more complex layout, with additional fuses and relays for new features. The diagram may also include a legend that explains the symbols used to represent different components.
- 1987 Chevrolet Suburban: The fuse box diagram for this model year will show a modern layout with a high density of fuses and relays. The diagram may also include a color-coded system to identify different circuits.
Impact of Fuse Box Diagram Differences on Troubleshooting and Repair
The differences in fuse box diagrams between model years can have a significant impact on troubleshooting and repair procedures. For example, a fuse for a specific circuit in a 1973 Chevrolet truck may be located in a different position in a 1987 Chevrolet truck.
Similarly, the function of a particular relay may have changed over time.
- Incorrect Diagram: Using the wrong fuse box diagram can lead to misdiagnosis and improper repairs, potentially causing further damage to the electrical system.
- Component Identification: The accurate identification of fuses and relays is essential for troubleshooting and repair. The correct diagram will provide clear labeling and symbols for each component.
- Circuit Tracing: Fuse box diagrams help trace the flow of electricity through various circuits, enabling technicians to pinpoint the source of electrical problems.
Troubleshooting Common Electrical Issues
The fuse box diagram is a crucial tool for diagnosing and resolving electrical problems in your Chevrolet truck. It provides a visual representation of the fuses and their corresponding circuits, enabling you to quickly identify the source of an electrical malfunction.
Identifying Electrical Problems
The fuse box diagram is invaluable for pinpointing the cause of electrical issues. It helps you determine which fuse is responsible for a particular circuit. When a fuse blows, it’s an indication that there’s a problem within that circuit. By examining the fuse box diagram, you can identify the components connected to the blown fuse, such as headlights, taillights, radio, or power windows.
Troubleshooting Steps
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to troubleshoot common electrical problems using the fuse box diagram:
1. Identify the Symptoms
Begin by identifying the electrical issue you’re experiencing. This could be a malfunctioning light, a non-functioning radio, or a dead battery.
2. Locate the Relevant Fuse
Consult the fuse box diagram to find the fuse that corresponds to the affected circuit.
3. Inspect the Fuse
Carefully examine the fuse. If the fuse is blown, it will have a broken filament, appearing as a gap or a melted area.
4. Replace the Fuse
If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the same amperage.
5. Test the Circuit
After replacing the fuse, test the circuit to see if the problem is resolved. If the new fuse blows immediately, it indicates a persistent short circuit within the circuit.
6. Inspect the Wiring
If the new fuse blows, it’s time to inspect the wiring associated with the affected circuit. Look for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires, loose connections, or corrosion.
7. Repair or Replace Damaged Wiring
If you find damaged wiring, repair or replace it as necessary.
8. Test the Circuit Again
Once you’ve addressed any wiring issues, test the circuit again to ensure the problem is fixed.
Common Electrical Problems and Solutions
- Dead Battery:A blown fuse in the battery charging circuit can prevent the battery from charging properly. Check the fuse labeled “Battery” or “Charging System” on the fuse box diagram.
- Headlights Not Working:A blown fuse in the headlight circuit will prevent the headlights from illuminating. Consult the fuse box diagram to locate the fuse responsible for the headlights.
- Taillights Not Working:Similar to headlights, a blown fuse in the taillight circuit will disable the taillights. Identify the taillight fuse using the fuse box diagram.
- Radio Not Working:A blown fuse in the radio circuit will prevent the radio from receiving power. Locate the radio fuse on the fuse box diagram.
- Power Windows Not Working:A blown fuse in the power window circuit will disable the power windows. Use the fuse box diagram to find the fuse responsible for the power windows.
- Power Seats Not Working:If the power seats are not functioning, check the fuse associated with the power seat circuit, which is typically labeled “Power Seats” or “Seat Motors” on the fuse box diagram.
Top FAQs
Where is the fuse box located in a 1973-1987 Chevy truck?
The fuse box is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side, near the steering column. However, its exact location can vary depending on the model year and trim level. Consult your owner’s manual or a repair guide for specific details.
What are the common symptoms of a blown fuse?
Common symptoms of a blown fuse include:
- Lights not working
- Electrical accessories not functioning
- Engine stalling or not starting
- Overheating electrical components
How can I tell if a fuse is blown?
A blown fuse will typically have a broken filament, which will appear as a gap or a dark spot in the metal strip. You can also check for a melted or discolored fuse.
What are the potential consequences of using the wrong fuse type?
Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating than the circuit requires can cause overheating and damage to electrical components. Using a fuse with a lower amperage rating can cause the fuse to blow frequently, disrupting the electrical system.