The 70 Coronet starter solenoid wiring diagram is a vital component of the car’s electrical system, acting as the intermediary between the ignition switch and the starter motor. It’s a simple but crucial part that ensures the starter motor receives the necessary power to turn the engine over.
Understanding the wiring diagram helps you diagnose and troubleshoot issues with your starter, ensuring a smooth and reliable start every time.
This guide delves into the intricacies of the 70 Coronet starter solenoid wiring diagram, exploring its components, operation, common issues, and troubleshooting techniques. We’ll also cover safety precautions and maintenance tips to keep your starter solenoid in optimal condition.
Starter Solenoid Components
The starter solenoid is a vital component in the starting system of a vehicle, acting as an electrical switch that connects the battery to the starter motor. Understanding the components of the starter solenoid is crucial for diagnosing and troubleshooting starting problems.
Components and Their Functions
The starter solenoid consists of several key components that work together to facilitate the starting process. These components are responsible for receiving the ignition signal, engaging the starter motor, and maintaining a continuous electrical connection until the engine starts.
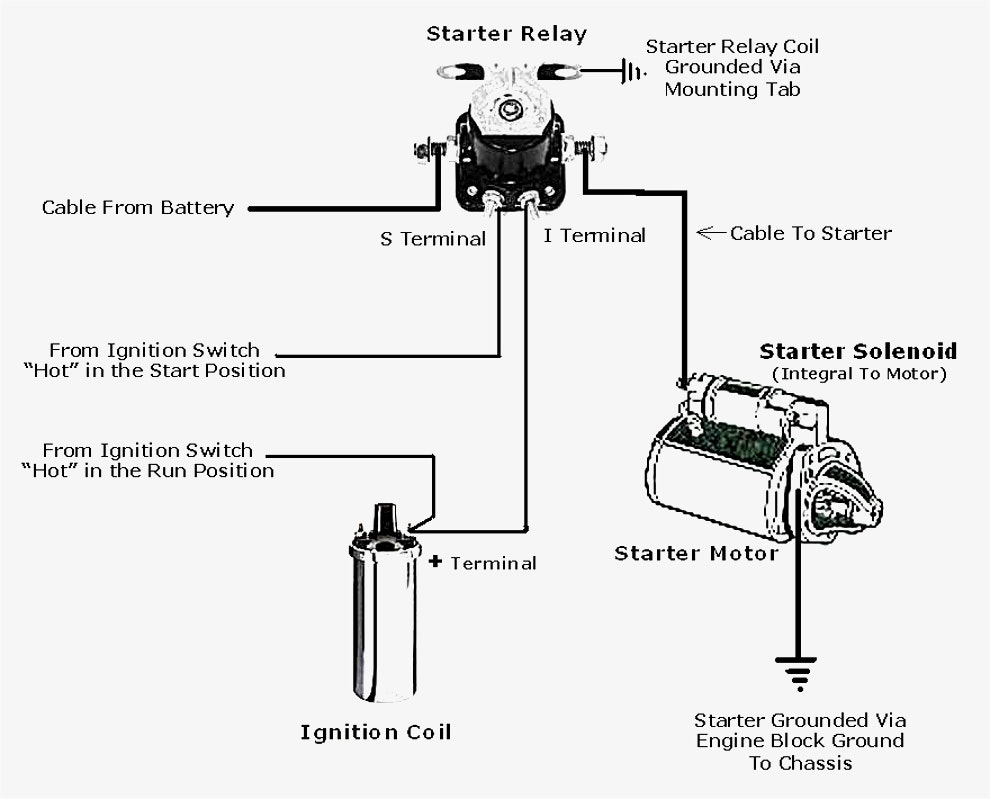
- Terminal Posts:These are the points where the electrical connections are made. The terminal posts are typically labeled with letters or numbers to identify their specific functions. The main terminal posts are the battery terminal (B), the ignition terminal (I), the starter motor terminal (S), and the ground terminal (G).
- Coil:The coil is an electromagnet that creates a magnetic field when energized. When the ignition switch is turned to the “start” position, a current flows through the coil, creating a magnetic field that pulls the armature towards the solenoid’s core.
- Armature:The armature is a movable iron core that is attached to the contacts. When the coil is energized, the armature is drawn towards the core, closing the contacts and completing the circuit to the starter motor.
- Contacts:The contacts are two pieces of metal that are normally open. When the armature is pulled towards the core, the contacts close, creating a direct connection between the battery and the starter motor.
Voltage Ratings
| Component | Function | Typical Voltage Rating |
|---|---|---|
| Coil | Creates magnetic field to pull the armature | 12V |
| Contacts | Connect battery to starter motor | 12V |
Wiring Diagram Overview
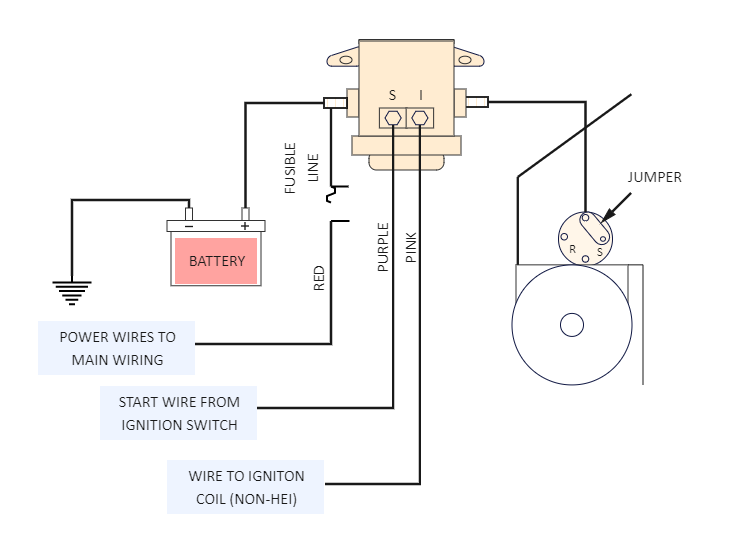
The wiring diagram for a 1970 Coronet starter solenoid illustrates the electrical connections that enable the starter motor to engage and turn the engine. It’s a relatively simple circuit, but understanding the flow of electricity through it is crucial for diagnosing starting problems.The diagram typically depicts the starter solenoid as a rectangular box with several terminals.
Each terminal represents a connection point for a specific wire. These wires carry electrical current from the battery, through the ignition switch, and ultimately to the starter motor.
Starter Solenoid Wiring Diagram Components
The wiring diagram will show the following key components and their connections:
- Battery:The battery is the power source for the starter motor. It provides the high current needed to turn the engine. The battery’s positive (+) terminal connects to the solenoid’s “S” (Start) terminal, and the negative (-) terminal connects to the chassis ground.
- Ignition Switch:The ignition switch acts as a control device, allowing the flow of electricity to the starter solenoid when the key is turned to the “Start” position. The ignition switch’s “Start” terminal connects to the solenoid’s “I” (Ignition) terminal.
- Starter Solenoid:The starter solenoid is an electromagnetic switch that acts as a relay, connecting the high current from the battery to the starter motor. The solenoid has three main terminals:
- “S” (Start):Connects to the battery’s positive terminal.
- “I” (Ignition):Connects to the ignition switch’s “Start” terminal.
- “R” (Run):Connects to the starter motor’s positive terminal.
- Starter Motor:The starter motor is an electric motor that engages the flywheel and turns the engine. It has two terminals:
- Positive Terminal:Connects to the solenoid’s “R” (Run) terminal.
- Negative Terminal:Connects to the chassis ground.
Electricity Flow During Starting
The flow of electricity through the starter solenoid circuit during the starting process is as follows:
1. Key Turned to “Start”
When the ignition key is turned to the “Start” position, the ignition switch closes the circuit between the battery and the solenoid’s “I” terminal.
2. Solenoid Energized
The electrical current flowing through the “I” terminal energizes the solenoid’s electromagnet.
3. Solenoid Contacts Close
The energized electromagnet pulls a metal plunger, closing the heavy-duty contacts inside the solenoid. This connects the battery’s positive terminal (“S”) to the starter motor’s positive terminal (“R”).
4. Starter Motor Engaged
With the high current from the battery now flowing to the starter motor, the motor engages and turns the engine.
5. Key Released
Once the engine starts, the ignition key is released, breaking the circuit at the ignition switch. The solenoid’s electromagnet de-energizes, the plunger retracts, and the contacts open, disconnecting the battery from the starter motor.
The starter solenoid acts as a relay, allowing a small current from the ignition switch to control the flow of a large current from the battery to the starter motor. This prevents the ignition switch from being overloaded by the high current required to start the engine.
Starter Solenoid Operation
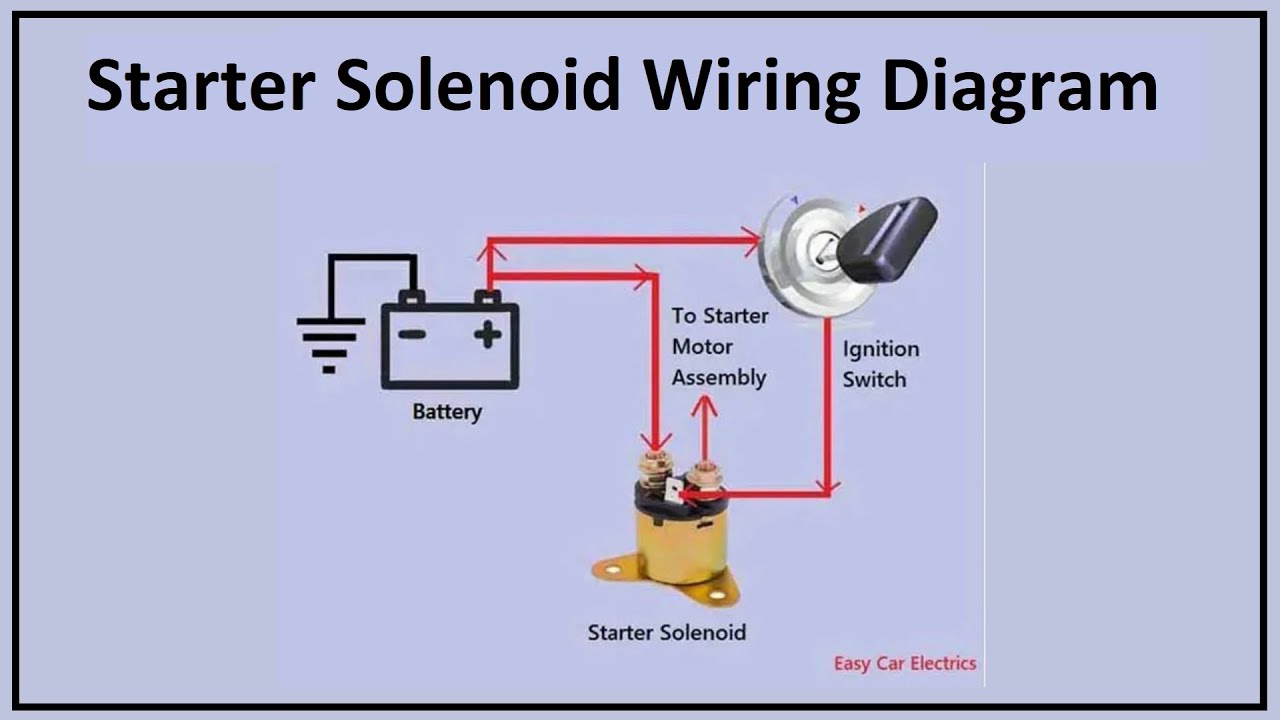
The starter solenoid is a crucial component in the starting system of a vehicle. It acts as an electromagnetic switch, connecting the battery’s power to the starter motor when the ignition key is turned to the start position.The starter solenoid plays a vital role in energizing the starter motor, enabling it to crank the engine and initiate combustion.
It facilitates the flow of high current from the battery to the starter motor, allowing the engine to start.
Current Flow Through the Circuit
The starter solenoid acts as a bridge between the battery and the starter motor. Here’s how the current flows through the circuit:* Ignition Key Turned to Start:When the ignition key is turned to the start position, the starter switch closes, completing the circuit.
Solenoid Energized
The starter switch activates the solenoid’s coil, creating a magnetic field.
Solenoid Contacts Close
The magnetic field draws the solenoid’s armature towards the coil, closing the heavy-duty contacts.
High Current Flow
Once the contacts close, high current flows from the battery, through the solenoid contacts, to the starter motor.
Starter Motor Engages
The starter motor receives the high current and begins to turn the engine’s crankshaft.
Ignition Key Released
When the ignition key is released, the starter switch opens, de-energizing the solenoid coil.
Solenoid Contacts Open
The solenoid’s armature returns to its original position, opening the contacts and interrupting the current flow to the starter motor.
The starter solenoid ensures that the high current required to start the engine flows only when needed, preventing damage to the starter motor and electrical system.
Common Starter Solenoid Issues
A starter solenoid is an essential component of a car’s starting system, and like any electrical component, it can experience problems over time. Understanding common issues and troubleshooting techniques can help you diagnose and resolve problems with your 70 Coronet’s starter solenoid.
Starter Solenoid Clicking
A clicking sound coming from the starter solenoid is a common symptom of a faulty solenoid. This clicking indicates that the solenoid is receiving power but not engaging the starter motor. Several reasons can cause this issue:
- Low Battery Voltage:A weak battery may not provide enough power to energize the solenoid, resulting in a clicking sound.
- Faulty Solenoid:The solenoid itself may be defective, preventing it from engaging the starter motor.
- Corroded or Loose Connections:Corrosion or loose connections at the battery terminals, solenoid terminals, or wiring can interrupt the electrical flow, leading to a clicking sound.
- Faulty Starter Motor:A faulty starter motor can create a high resistance, preventing the solenoid from engaging the starter motor.
Troubleshooting Starter Solenoid Clicking
1. Check the Battery
Use a voltmeter to check the battery voltage. A fully charged battery should read around 12.6 volts. If the voltage is low, recharge or replace the battery.
2. Inspect Connections
Examine the battery terminals, solenoid terminals, and wiring for corrosion or looseness. Clean any corrosion and tighten loose connections.
3. Test the Solenoid
Use a test light or multimeter to check for continuity between the solenoid’s terminals. If there is no continuity, the solenoid is likely faulty.
4. Inspect the Starter Motor
If the solenoid tests good, check the starter motor for any signs of damage or wear. You can test the starter motor by directly applying power to it. If the starter motor doesn’t turn, it needs to be replaced.
Starter Solenoid Not Engaging
If the starter solenoid doesn’t engage at all, there’s no clicking sound, and the car won’t start. This issue could be due to:
- Blown Fuse:A blown fuse in the starter circuit can prevent the solenoid from receiving power.
- Faulty Ignition Switch:A malfunctioning ignition switch may not be sending power to the solenoid.
- Open Circuit:A broken wire or a loose connection in the wiring between the ignition switch and the solenoid can interrupt the electrical flow.
- Faulty Solenoid:As with the clicking issue, a faulty solenoid can also prevent it from engaging the starter motor.
Troubleshooting Starter Solenoid Not Engaging
1. Check the Fuse
Inspect the fuse for the starter circuit, which is usually located in the fuse box under the hood. Replace the fuse if it’s blown.
2. Test the Ignition Switch
Use a test light or multimeter to check for power at the ignition switch. If there’s no power, the ignition switch is likely faulty.
3. Inspect Wiring
Visually inspect the wiring between the ignition switch and the solenoid for any breaks or loose connections. Repair or replace any damaged wiring.
4. Test the Solenoid
As before, test the solenoid for continuity. If the solenoid tests good, check the starter motor for any signs of damage or wear.
Starter Solenoid Overheating
While less common, a starter solenoid can overheat due to excessive current draw or a faulty solenoid. This can lead to damage to the solenoid and may cause the starter to fail.
Troubleshooting Starter Solenoid Overheating
1. Check for High Current Draw
Use a clamp-on ammeter to measure the current draw of the starter motor. If the current draw is significantly higher than the rated current, there might be a problem with the starter motor, such as a seized bearing or a faulty armature.
2. Inspect Solenoid for Damage
Examine the solenoid for any signs of overheating, such as discoloration, melting, or burning. If the solenoid shows signs of damage, it needs to be replaced.
3. Check Battery Connections
Ensure the battery terminals are clean and tight. Loose or corroded connections can cause excessive resistance and heat buildup.
4. Verify Starter Motor Condition
A faulty starter motor can draw excessive current, leading to solenoid overheating. Inspect the starter motor for any signs of damage or wear.
Replacing the Starter Solenoid

Replacing the starter solenoid is a relatively straightforward procedure that can be done by most DIY mechanics. However, it’s crucial to follow safety precautions and work with care when dealing with electrical components. This section Artikels the steps involved in replacing a faulty starter solenoid on a 1970 Coronet.
Disconnecting the Battery, 70 coronet starter solenoid wiring diagram
Before starting any work on the starter solenoid, it’s essential to disconnect the battery to prevent electrical shocks. This step is critical for safety and ensures that you’re not working with live electrical circuits.
- Locate the battery terminals, typically marked with “+” and “-” signs. The positive terminal is usually red, and the negative terminal is black.
- Use a wrench to loosen the battery terminal clamps. Start with the negative terminal (black) first. This helps prevent accidental sparks from the positive terminal when disconnecting.
- Once the negative terminal is disconnected, remove the positive terminal (red) clamp.
Removing the Old Solenoid
Once the battery is disconnected, you can proceed with removing the old starter solenoid. This process may vary slightly depending on the specific location of the solenoid on your 1970 Coronet.
- Locate the starter solenoid, usually mounted on the firewall or near the starter motor. It’s a small, cylindrical device with electrical terminals and a mounting bracket.
- Disconnect the electrical wires connected to the solenoid. Take note of the wire colors and their positions for reconnection later.
- Remove the solenoid mounting bolts using a wrench or socket. Depending on the location, you may need to use an extension to reach the bolts.
- Carefully remove the old solenoid from its mounting bracket.
Installing the New Solenoid
After removing the old solenoid, you can install the new one. This process is essentially the reverse of the removal procedure.
- Align the new solenoid with its mounting bracket. Ensure that the mounting holes on the solenoid match the holes on the bracket.
- Secure the solenoid to the bracket using the mounting bolts. Tighten the bolts securely but avoid overtightening.
- Reconnect the electrical wires to the new solenoid. Match the wire colors and positions to those of the old solenoid.
- Reconnect the battery terminals in reverse order, starting with the positive terminal (red) and then the negative terminal (black). Ensure the connections are tight.
Testing the New Solenoid
After installing the new solenoid, test its functionality by attempting to start the engine. If the starter motor engages and the engine starts, the new solenoid is working correctly.
Starter Solenoid Testing

Testing a starter solenoid involves using a multimeter to check for continuity and voltage. This helps determine if the solenoid is functioning correctly or if it needs replacement.
Testing the Starter Solenoid with a Multimeter
The following steps Artikel the procedure for testing a starter solenoid using a multimeter:
- Disconnect the Battery:Before you start testing, disconnect the negative battery terminal to prevent any accidental electrical shocks.
- Locate the Starter Solenoid:The starter solenoid is typically mounted on the firewall or near the starter motor. It will have a series of wires connected to it.
- Identify the Terminals:The starter solenoid will have several terminals. The main terminals are:
- Battery Terminal (B):This is the terminal connected to the positive battery cable.
- Starter Terminal (S):This terminal is connected to the starter motor.
- Ignition Terminal (I):This terminal is connected to the ignition switch.
- Ground Terminal (G):This terminal is connected to the vehicle’s chassis.
- Continuity Test:
- Set the multimeter to the continuity setting (usually represented by a diode symbol or Ω).
- Touch the positive lead of the multimeter to the battery terminal (B) and the negative lead to the starter terminal (S).
- If the solenoid is good, the multimeter should show a reading of continuity (usually a low resistance reading, often near zero ohms).
- Repeat this test between the battery terminal (B) and the ignition terminal (I).
- If the solenoid is good, the multimeter should show a reading of continuity between these terminals as well.
- Voltage Test:
- Set the multimeter to the voltage setting (usually represented by a V symbol).
- Connect the positive lead of the multimeter to the battery terminal (B) and the negative lead to the ground terminal (G).
- Turn the ignition key to the “start” position.
- If the solenoid is good, the multimeter should show a voltage reading close to the battery voltage (usually around 12 volts).
- Interpreting the Results:
- If the multimeter does not show continuity between the battery terminal (B) and the starter terminal (S) or the battery terminal (B) and the ignition terminal (I), the solenoid is likely faulty.
- If the multimeter does not show a voltage reading close to the battery voltage when the ignition key is turned to the “start” position, the solenoid is likely faulty.
- Reconnect the Battery:After completing the tests, reconnect the negative battery terminal.
Starter Solenoid Maintenance: 70 Coronet Starter Solenoid Wiring Diagram
Although the starter solenoid is a relatively simple and robust component, regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring its long-term reliability and preventing unexpected breakdowns. By performing routine inspections and cleaning, you can help extend the life of your starter solenoid and avoid potential problems down the road.
Inspecting the Solenoid for Wear or Damage
Regularly inspecting the starter solenoid for signs of wear or damage is essential for identifying potential issues before they become major problems. A visual inspection can reveal signs of corrosion, loose connections, or damaged components.
- Corrosion:Corrosion can build up on the solenoid’s contacts, terminals, and housing, hindering proper electrical conductivity. This can lead to a weak starting signal or complete failure. Inspect the solenoid for any signs of rust or white powdery residue, which indicates corrosion.
- Loose Connections:Over time, the connections between the solenoid’s terminals and wires can become loose due to vibration or heat. This can result in intermittent or complete loss of power to the starter motor. Ensure that all connections are tight and secure.
Decoding the intricacies of a 70 Coronet starter solenoid wiring diagram can feel like deciphering an ancient language, but fear not! Understanding the flow of electricity is crucial for keeping your classic car running smoothly. Sometimes, a little inspiration from other vintage machines can be helpful, like the lighting schematic diagram for a 1980 gs750 suzuki spec.
It might seem unrelated, but seeing how a motorcycle’s electrical system works can provide valuable insights into the principles behind your Coronet’s starter solenoid wiring. With a little patience and a good diagram, you’ll be turning those keys and hitting the road in no time!
- Damaged Components:Physical damage to the solenoid’s housing, contacts, or internal components can also lead to malfunction. Look for any cracks, dents, or other signs of physical damage.
Cleaning and Lubricating the Solenoid Contacts
Cleaning and lubricating the solenoid contacts can help to improve electrical conductivity and prevent corrosion.
- Cleaning:Use a wire brush or a small piece of sandpaper to clean the contacts and terminals. Remove any dirt, debris, or corrosion buildup. Avoid using harsh chemicals or solvents that could damage the solenoid.
- Lubrication:After cleaning, apply a thin layer of dielectric grease to the contacts. Dielectric grease is a specialized lubricant that prevents corrosion and improves electrical conductivity. It is available at most automotive parts stores.
Alternative Starter Solenoids
While the original starter solenoid is a reliable option, you may find yourself needing a replacement or considering an upgrade. Thankfully, several aftermarket options are available for your 1970 Coronet. These alternative solenoids offer varying advantages in terms of price, performance, and reliability.
Understanding the differences can help you choose the best option for your specific needs and budget.
Types of Starter Solenoids
Different types of starter solenoids are available, each with its own set of pros and cons. Here are some of the most common types:
- Standard Starter Solenoids:These are the most basic type of solenoid, typically found in OEM applications. They are relatively inexpensive and offer good performance for standard applications. However, they may not be as durable as some other options.
- Heavy-Duty Starter Solenoids:Designed for high-performance applications, these solenoids are built to handle higher amperage and more frequent use. They are typically more expensive than standard solenoids but offer increased reliability and longevity.
- High-Torque Starter Solenoids:These solenoids are designed to provide more torque to the starter motor, resulting in faster and more powerful starting. They are often used in applications with high compression engines or modified engines. They are usually more expensive than standard solenoids.
- Electronic Starter Solenoids:These solenoids use electronic components to control the starter motor, offering increased precision and efficiency. They are typically more expensive than standard solenoids but can offer advantages in fuel economy and emissions.
Choosing the Right Starter Solenoid
Several factors need to be considered when choosing a replacement starter solenoid for your 1970 Coronet.
- Engine Size and Performance:If you have a stock engine, a standard starter solenoid will likely suffice. However, if you have a high-performance engine or modified engine, a heavy-duty or high-torque solenoid might be a better choice.
- Budget:Standard starter solenoids are the most affordable option. If you are on a tight budget, a standard solenoid may be the best choice. However, if you are willing to spend a bit more, a heavy-duty or high-torque solenoid can provide increased reliability and performance.
- Reliability:If you want the most reliable option, a heavy-duty starter solenoid is the best choice. These solenoids are built to handle higher amperage and more frequent use, making them ideal for demanding applications.
- Compatibility:Make sure the solenoid you choose is compatible with your 1970 Coronet’s starter motor. Some solenoids are designed for specific applications and may not be compatible with all starter motors.
Recommendations
When choosing a replacement starter solenoid for your 1970 Coronet, it’s essential to consider your specific needs and budget. If you have a stock engine and are on a tight budget, a standard starter solenoid is a good option. However, if you have a high-performance engine or are looking for increased reliability, a heavy-duty or high-torque solenoid might be a better choice.
Question Bank
What is the purpose of a starter solenoid?
The starter solenoid acts as a switch that receives a signal from the ignition switch and sends a large amount of current to the starter motor, turning the engine over.
How do I know if my starter solenoid is bad?
Common signs of a bad starter solenoid include a clicking sound when you turn the key, a slow cranking engine, or a complete failure to start.
Can I test the starter solenoid myself?
Yes, you can test the starter solenoid using a multimeter. You can find detailed instructions online or in your owner’s manual.