The 6.7 Powerstroke belt diagram is a crucial tool for anyone looking to understand and maintain the intricate workings of this powerful engine. The belt system plays a vital role in powering essential components like the alternator, water pump, and power steering pump, ensuring smooth and efficient operation.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the 6.7 Powerstroke belt system, providing a detailed understanding of its components, functions, and maintenance requirements.
From deciphering the belt diagram to navigating the intricacies of belt replacement, tensioning, and troubleshooting, this guide empowers you with the knowledge needed to keep your 6.7 Powerstroke engine running at peak performance. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a curious enthusiast, this exploration into the heart of the 6.7 Powerstroke belt system will equip you with the confidence to tackle any maintenance challenge.
Introduction to the 6.7 Powerstroke Engine

The Ford 6.7 Powerstroke engine, introduced in 2011, is a powerful and durable diesel engine designed for heavy-duty trucks and commercial vehicles. It is a significant advancement over its predecessors, featuring a host of technological innovations aimed at maximizing performance, efficiency, and reliability.
The engine’s belt system plays a crucial role in its operation, ensuring the proper functioning of various ancillary components that contribute to the engine’s overall performance.
The Significance of the Belt System, 6.7 powerstroke belt diagram
The belt system in the 6.7 Powerstroke engine is responsible for driving a range of essential components, including the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and water pump. These components rely on the belt’s consistent rotation to perform their functions, which are vital for the engine’s operation and the vehicle’s overall performance.
Components of the 6.7 Powerstroke Belt System: 6.7 Powerstroke Belt Diagram
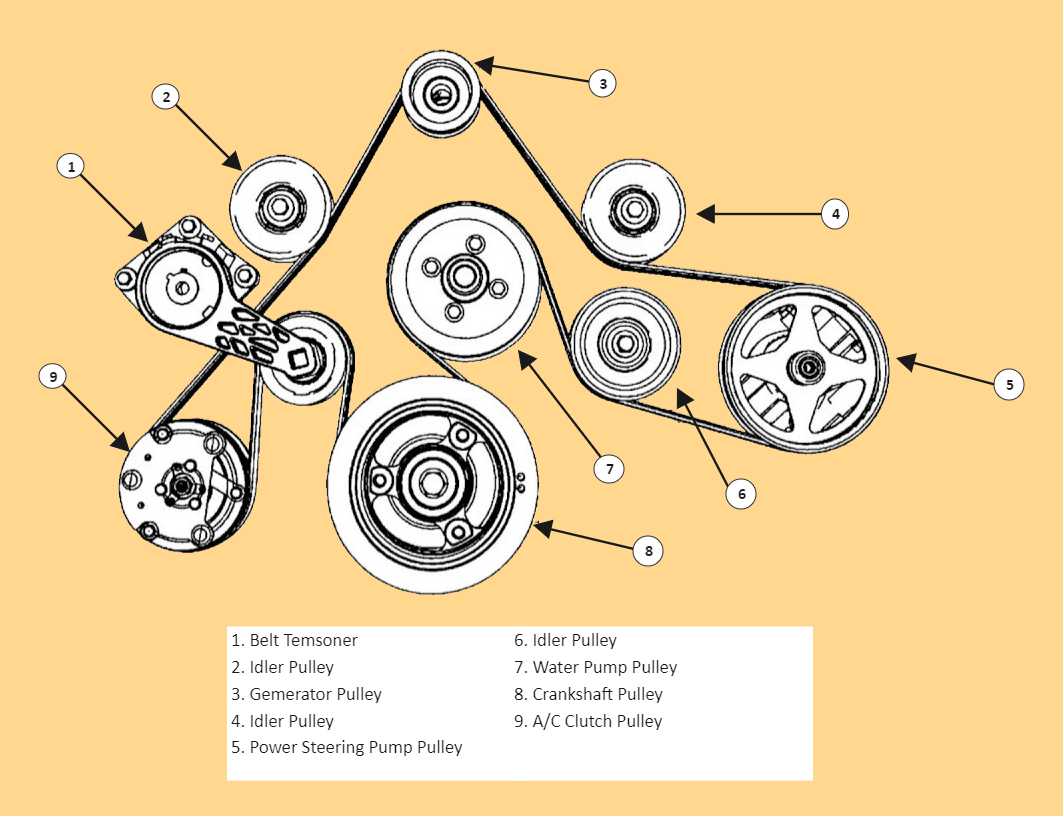
The 6.7 Powerstroke engine utilizes a serpentine belt system to drive various essential components. This system is designed for efficiency and reliability, ensuring smooth operation of the engine and its auxiliary systems. Understanding the components of this belt system is crucial for proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
Components of the 6.7 Powerstroke Belt System
The 6.7 Powerstroke belt system consists of several key components, each playing a vital role in the engine’s operation. These components include the belt itself, tensioner, idler pulleys, and driven accessories.
| Component | Function | Location | Typical Maintenance Schedule |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serpentine Belt | Drives the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and other accessories. | Wraps around the crankshaft pulley, tensioner, idler pulleys, and driven accessories. | Inspect for wear, cracks, or glazing every 50,000 miles or as recommended by the manufacturer. Replace if necessary. |
| Tensioner | Maintains proper belt tension, ensuring smooth operation and preventing belt slippage. | Located near the belt’s path, typically on the driver’s side of the engine. | Inspect for wear, damage, or excessive noise. Replace if necessary, typically every 100,000 miles or as recommended by the manufacturer. |
| Idler Pulleys | Guide the belt around the engine and provide support for the belt’s path. | Located at various points along the belt’s path. | Inspect for wear, damage, or excessive noise. Replace if necessary, typically every 100,000 miles or as recommended by the manufacturer. |
| Driven Accessories | Components that are driven by the belt, such as the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and water pump. | Located at various points along the belt’s path. | Inspect for wear, damage, or leaks. Replace or repair as necessary, following the manufacturer’s recommendations. |
Belt Tensioning and Adjustment
Maintaining the correct belt tension is crucial for the proper operation of the 6.7 Powerstroke engine. A belt that is too loose can slip, causing a loss of power, overheating, and premature wear on the belt and driven components. Conversely, a belt that is too tight can put excessive strain on the bearings and other components, leading to premature failure.
Navigating the intricate web of belts on a 6.7 Powerstroke engine can be a daunting task, akin to deciphering the hieroglyphics on an ancient Egyptian tomb. However, fear not, for there are resources available to guide you through this serpentine journey.
For instance, if you’re ever feeling lost and need to replace a windshield nozzle on your trusty ’98 Chevy S10, you can consult a 98 Chevy S10 windshield nozzle diagram. With a little patience and the right diagrams, you’ll be back on the road in no time, and your 6.7 Powerstroke will be purring like a well-oiled kitten.
Belt Tension Measurement Methods
The correct belt tension can be measured using a variety of methods. The two most common methods are:
- Using a Tension Gauge:This method involves using a specialized tool that measures the belt’s deflection when a specific amount of force is applied. The tension gauge provides a numerical reading that can be compared to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Observing Belt Deflection:This method involves manually pressing down on the belt at a specific point and measuring the amount of deflection. The deflection should fall within the range specified by the manufacturer.
Belt Tension Adjustment
Adjusting the belt tension involves altering the position of the belt tensioner. The tensioner is typically a spring-loaded mechanism that can be adjusted by rotating a bolt or nut.
To adjust the belt tension, follow the manufacturer’s instructions for your specific engine model.
Adjusting the belt tension can be a delicate process, as over-tightening or under-tightening can have detrimental effects on the engine’s performance and longevity.
Consequences of Incorrect Belt Tension
- Over-tensioning:Excessive belt tension can cause premature wear on the belt, bearings, and other components. This can lead to increased noise, vibration, and ultimately, component failure.
- Under-tensioning:A loose belt can slip, causing a loss of power, overheating, and damage to the driven components, such as the alternator, water pump, and power steering pump.
Common Belt Problems and Troubleshooting
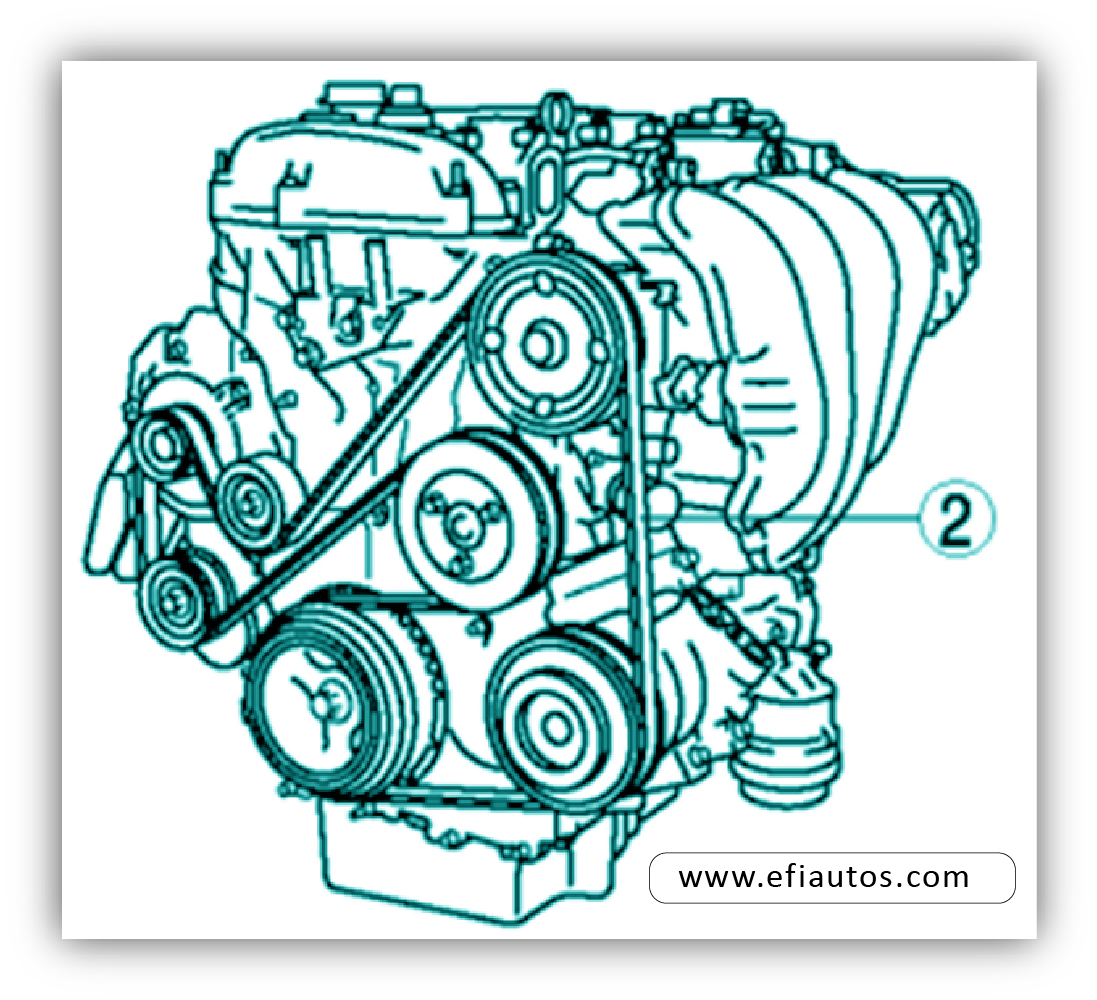
The 6.7 Powerstroke belt system, while robust, can experience issues that affect engine performance. Identifying these problems early and understanding their root causes is essential for maintaining optimal engine function.
Belt Wear and Slippage
Belt wear is a common issue, resulting from friction, heat, and exposure to the elements. Worn belts can slip, leading to reduced power output, accessory failure, and potential damage to the engine.
- Visual Inspection:Regularly inspect the belt for cracks, fraying, glazing, or excessive wear. A worn belt will often exhibit a glazed or shiny appearance.
- Belt Tension:Use a belt tension gauge to check the belt tension. A properly tensioned belt should deflect a specific amount when pressed. Consult your owner’s manual or a repair manual for the correct specifications.
- Component Alignment:Ensure all pulleys and components are properly aligned. Misalignment can cause uneven wear and belt slippage.
Belt Component Failure
Components within the belt system, such as pulleys, tensioners, and idlers, can fail, leading to belt problems.
- Pulley Wear:Examine pulleys for cracks, wear, or damage. Worn or damaged pulleys can cause premature belt wear and slippage.
- Tensioner and Idler Failure:Inspect tensioners and idlers for signs of wear, noise, or excessive play. A failed tensioner or idler can result in improper belt tension and premature wear.
- Bearing Failure:Bearings within pulleys, tensioners, and idlers can fail, leading to noise, vibration, and belt slippage.
Preventing Belt Problems
Regular maintenance and preventative measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of belt issues.
- Regular Inspections:Conduct visual inspections of the belt and components at least every 3,000 miles or more frequently in harsh conditions.
- Belt Replacement:Replace the belt according to the manufacturer’s recommended intervals, typically every 50,000-75,000 miles.
- Proper Tension:Ensure the belt is properly tensioned using a belt tension gauge. Over-tensioning can damage components, while under-tensioning can lead to slippage.
- Cleanliness:Keep the belt and components clean and free of debris. Dirt and grime can accelerate wear and tear.
Maintenance and Inspection
Proactive maintenance of the 6.7 Powerstroke belt system is crucial for preventing unexpected breakdowns and ensuring optimal engine performance. Adhering to a recommended maintenance schedule helps identify potential issues early and minimize downtime.
Recommended Maintenance Schedule
A regular inspection of the belt system is essential to identify any signs of wear or damage. The recommended inspection interval for the 6.7 Powerstroke belt system is every 50,000 miles or 12 months, whichever comes first.
- Belt Condition:Inspect the belt for signs of cracking, fraying, glazing, or excessive wear. Replace the belt if any of these issues are observed.
- Tensioner Operation:Check the tensioner for smooth operation and ensure it is properly tensioning the belt. Replace the tensioner if it exhibits any signs of wear, damage, or excessive noise.
- Pulley Wear:Inspect all pulleys for signs of wear, damage, or excessive play. Replace any damaged or worn pulleys.
Key Areas to Inspect
During routine maintenance, carefully inspect the following components of the 6.7 Powerstroke belt system:
- Belt:Visually examine the belt for signs of cracking, fraying, glazing, or excessive wear. These are indicators of belt deterioration and require immediate replacement.
- Tensioner:Check the tensioner for smooth operation and ensure it is properly tensioning the belt. A worn or damaged tensioner can lead to improper belt tension, resulting in premature belt failure.
- Pulleys:Inspect all pulleys for signs of wear, damage, or excessive play. Worn or damaged pulleys can cause premature belt wear and failure.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance of the 6.7 Powerstroke belt system is essential for preventing belt failures and ensuring optimal engine performance.
- Preventing Belt Failures:Regular inspections and timely replacements help prevent catastrophic belt failures, which can lead to engine damage and costly repairs.
- Optimizing Engine Performance:A properly functioning belt system ensures that all engine accessories are receiving the necessary power, contributing to optimal engine performance.
Belt System Upgrades and Modifications
While the stock 6.7 Powerstroke belt system is generally reliable, some enthusiasts opt for upgrades or modifications to enhance performance, durability, or aesthetics. These modifications often involve replacing components with higher-quality alternatives or utilizing different belt materials.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Belt System Upgrades
Upgrading the belt system can offer several advantages, including increased belt lifespan, improved performance, and enhanced reliability. However, these modifications also come with certain drawbacks, such as increased cost and potential risks.
- Increased Belt Lifespan:Upgrading to a higher-quality belt material, such as aramid fiber or carbon fiber, can significantly extend the belt’s lifespan. This reduces the frequency of replacements, saving both time and money.
- Improved Performance:Some belt materials, like aramid fiber, offer lower stretch and higher tensile strength, resulting in more efficient power transfer and potentially improved engine performance.
- Enhanced Reliability:Using high-quality components, including a stronger belt and improved tensioner, can reduce the risk of belt failure, ensuring a more reliable engine operation.
- Increased Cost:Upgrading to premium belt materials and components typically comes at a higher cost compared to stock parts.
- Potential Risks:Improper installation or the use of incompatible components can lead to belt slippage, premature wear, or even engine damage.
Common Belt System Upgrades
Several popular upgrades and modifications are commonly employed by 6.7 Powerstroke enthusiasts.
- High-Performance Belts:Replacing the stock belt with a high-performance belt made from aramid fiber or carbon fiber can improve belt lifespan, reduce stretch, and potentially enhance engine performance. These belts are typically more expensive than standard belts but offer superior durability and resistance to wear.
- Upgraded Tensioner:Replacing the stock tensioner with a higher-quality, heavier-duty tensioner can ensure proper belt tension and reduce the risk of belt slippage. This can improve belt lifespan and overall engine performance.
- Belt Idler Pulley Upgrades:Replacing the stock idler pulleys with upgraded versions made from higher-quality materials can reduce friction and improve belt longevity. This can also contribute to a smoother engine operation and potentially improve fuel efficiency.
Belt System Modification Considerations
When considering upgrades or modifications to the 6.7 Powerstroke belt system, it is crucial to carefully evaluate the potential benefits and drawbacks.
- Compatibility:Ensure that any replacement components are compatible with the specific engine model and year. Consult with a reputable parts supplier or mechanic to confirm compatibility.
- Installation:Proper installation is essential for optimal performance and safety. If you are not comfortable performing the installation yourself, seek the assistance of a qualified mechanic.
- Maintenance:Regular maintenance and inspection of the belt system are crucial, even after upgrading components. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for belt replacement and tension adjustment.
Resources and Additional Information
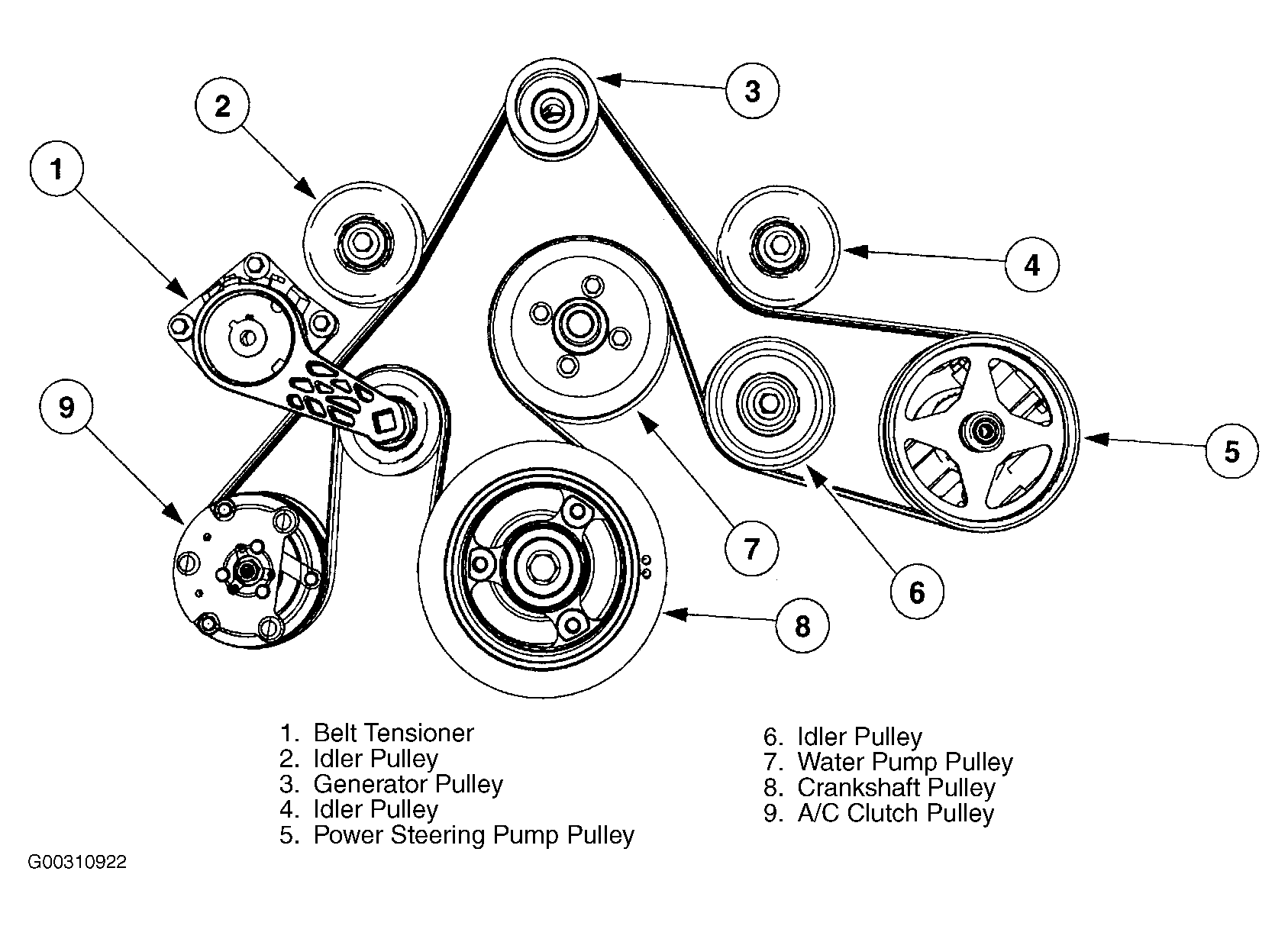
This section provides links to reputable sources for further information on the 6.7 Powerstroke belt system, including online forums, repair manuals, and manufacturer websites. It also shares additional resources that may be helpful to readers, such as videos, articles, or diagrams.
Online Forums
Online forums offer a valuable platform for connecting with other owners and enthusiasts of the 6.7 Powerstroke engine. These forums provide a space for sharing experiences, troubleshooting tips, and seeking advice from experienced mechanics.
- Ford Powerstroke Diesel Forum:This forum is dedicated to all things Powerstroke, including the 6.7L engine. You can find discussions on belt system issues, maintenance tips, and modifications.
- TheDieselStop.com:This forum is another popular destination for Powerstroke owners. It offers a wide range of information on the 6.7L engine, including detailed discussions on the belt system.
Repair Manuals
Repair manuals provide comprehensive information on the 6.7 Powerstroke engine, including detailed diagrams and instructions for diagnosing and repairing belt system issues.
- Chilton Repair Manuals:Chilton offers a range of repair manuals for Ford vehicles, including the 6.7 Powerstroke. These manuals provide detailed information on the belt system, including component descriptions, troubleshooting guides, and repair procedures.
- Haynes Repair Manuals:Haynes also provides repair manuals for Ford vehicles, covering the 6.7 Powerstroke engine.
These manuals offer similar information to Chilton manuals, with detailed diagrams and step-by-step instructions for belt system repairs.
Manufacturer Websites
Manufacturer websites provide official information on the 6.7 Powerstroke engine, including technical specifications, maintenance schedules, and troubleshooting guides.
- Ford Motor Company:Ford’s website offers a wealth of information on the 6.7 Powerstroke engine, including owner’s manuals, service bulletins, and technical specifications.
Additional Resources
Beyond online forums, repair manuals, and manufacturer websites, additional resources can further enhance your understanding of the 6.7 Powerstroke belt system.
- YouTube Videos:Numerous YouTube channels offer informative videos on the 6.7 Powerstroke belt system, covering topics such as belt replacement, tensioning, and troubleshooting common issues.
- Technical Articles:Online automotive publications and websites often feature technical articles that provide in-depth information on the 6.7 Powerstroke belt system, including component descriptions, operation principles, and common problems.
Expert Answers
What are the signs of a worn or damaged belt?
Signs of a worn or damaged belt include cracking, fraying, or excessive wear on the belt surface. You may also notice squeaking or squealing noises coming from the engine, indicating belt slippage.
How often should I replace the 6.7 Powerstroke belt?
The recommended replacement interval for the 6.7 Powerstroke belt varies depending on driving conditions and maintenance practices. Consult your owner’s manual for specific recommendations, but generally, replacement is recommended every 60,000 to 100,000 miles.
What tools do I need to replace the 6.7 Powerstroke belt?
To replace the belt, you’ll need basic tools such as wrenches, sockets, and a belt tension gauge. It’s essential to have the correct tools for the job and consult your owner’s manual or a repair guide for specific instructions.
Can I use a different type of belt on my 6.7 Powerstroke engine?
It’s crucial to use the correct type of belt specified by the manufacturer. Using a different type of belt could result in improper tension, slippage, and potential damage to the engine. Always consult your owner’s manual or a reputable parts supplier for the correct belt specifications.