30 amp schematic keystone rv wiring diagrams led lighting sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with melancholic poem style and brimming with originality from the outset. Navigating the intricate world of RV electrical systems can be daunting, especially when it comes to understanding the nuances of wiring diagrams and the benefits of LED lighting.
This guide will serve as a beacon, illuminating the path to understanding and mastering the complexities of your RV’s electrical system.
From the basics of 30 amp RV electrical systems to the intricacies of LED lighting installation, this guide will unravel the mysteries of your RV’s electrical heart. We’ll delve into the world of wiring diagrams, decipher their cryptic symbols, and equip you with the knowledge to troubleshoot common electrical issues.
By the end of this journey, you’ll be equipped with the confidence to navigate the electrical landscape of your RV with ease, ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience on the open road.
Understanding 30 Amp RV Electrical Systems
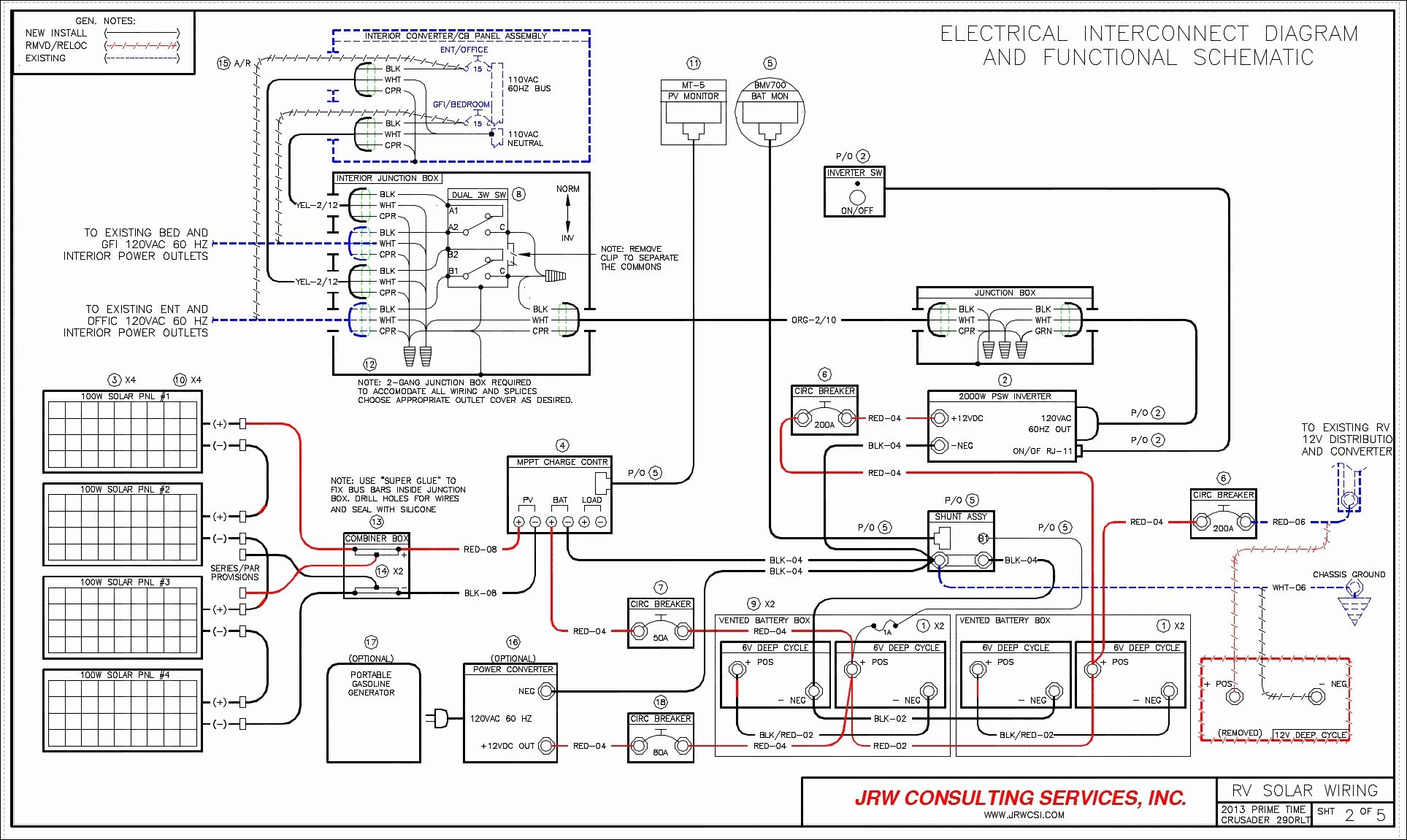
RV electrical systems are essential for powering various appliances and amenities within a recreational vehicle. Understanding the basics of a 30-amp system, including voltage, amperage, and common components, is crucial for safe and efficient operation. This section will delve into the intricacies of these systems, providing insights into their functionality and the key components that make them work.
Voltage and Amperage
The primary electrical supply for most RVs is a 30-amp system, operating on a 120-volt AC power source. The voltage refers to the electrical potential difference, while the amperage represents the rate of electrical current flow. In a 30-amp system, the maximum current that can flow through the circuit is 30 amps.
Common Components
A 30-amp RV electrical system consists of several essential components, each playing a crucial role in the safe and efficient distribution of power. These components include:
- Shore Power Cord:This cord connects the RV to an external power source, typically a campground’s electrical pedestal.
- Transfer Switch:This switch allows you to select between shore power or generator power as the primary power source.
- Circuit Breakers:These devices protect the electrical system from overloads by interrupting the flow of electricity when a fault occurs.
- Outlets:These are the points where electrical appliances and devices are plugged in.
- Wiring:The electrical wiring within the RV carries power from the source to the outlets and appliances.
- Battery Charger:This component charges the RV’s battery bank, ensuring that the batteries are fully charged and ready to provide power when needed.
- Inverter:An inverter converts DC power from the battery bank to AC power, allowing you to run AC appliances even when not connected to shore power or using a generator.
Types of Wiring
RV electrical systems utilize different types of wiring, each designed for specific applications and to meet safety standards. Some common types include:
- THHN (Thermoplastic High Heat-Resistant Nylon):This type of wiring is commonly used for 120-volt AC circuits in RVs due to its high heat resistance and durability.
- THWN (Thermoplastic High Heat-Resistant Nylon with Water Resistance):This type of wiring is similar to THHN but offers additional protection against moisture, making it suitable for applications where exposure to water is likely.
- UF (Underground Feeder):This type of wiring is designed for direct burial applications and is often used for connections between the RV’s electrical system and an external power source.
- Romex:This type of wiring is a popular choice for residential applications and is sometimes used in RVs for 120-volt AC circuits.
Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers are essential safety devices that protect the electrical system from overloads. They are designed to interrupt the flow of electricity when the current exceeds a predetermined limit. RV circuit breakers typically have a rating of 15 or 20 amps, depending on the circuit’s load capacity.
When a circuit breaker trips, it indicates that a fault has occurred, and the circuit needs to be reset. To reset a tripped circuit breaker, simply switch it to the “off” position and then back to the “on” position. If the circuit breaker trips again immediately, it indicates a persistent problem, and you should consult with a qualified electrician.
So, you’re trying to figure out how to wire those fancy LED lights in your RV, right? You’ve got a 30-amp schematic and a Keystone wiring diagram, but it’s all Greek to you. Don’t worry, I’ve been there! Maybe if you can figure out how to install a Pioneer AVIC in a 2004 Corvette using this wiring diagram , you’ll have a better shot at understanding your RV’s electrical system.
After all, those Corvettes are like tiny RVs on wheels, right? Just don’t try to plug your RV into the Corvette’s power outlet – that’s asking for trouble!
Outlets
RV outlets are typically 15-amp or 20-amp receptacles, designed to accommodate standard household appliances and devices. They are available in various configurations, including standard 3-prong outlets, GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) outlets, and RV-specific outlets with twist-lock connectors.
Wiring Connections, 30 amp schematic keystone rv wiring diagrams led lighting
RV wiring connections are typically made using wire nuts, terminal blocks, or crimp connectors. These connections must be made securely to ensure a reliable and safe electrical connection. It is crucial to use the correct type of connectors for each application and to follow proper installation procedures.
Keystone RV Wiring Diagrams
Keystone RV wiring diagrams are essential tools for understanding the intricate electrical systems of your RV. These diagrams provide a visual representation of the electrical components, their connections, and the flow of electricity throughout your RV. Understanding these diagrams is crucial for troubleshooting electrical issues, performing maintenance, and even upgrading your RV’s electrical system.
Key Elements of a Keystone RV Wiring Diagram
Keystone RV wiring diagrams typically include a variety of elements that help you understand the electrical system of your RV. Here are some of the key elements you can expect to find on a Keystone RV wiring diagram:
- Electrical Components:The diagram will show the location and connection points of all the major electrical components in your RV, such as batteries, fuses, breakers, switches, lights, appliances, and outlets.
- Wiring Paths:The diagram will illustrate the pathways of the wiring connecting the different components. This includes the size and type of wire used, as well as the color coding of the wires.
- Circuit Diagrams:Keystone RV wiring diagrams often include circuit diagrams that show how different electrical components are connected in a circuit. This can help you understand how electricity flows through the system and identify potential issues.
- Symbols and Legends:Wiring diagrams use standardized symbols to represent different electrical components and connections. These symbols are explained in a legend that is usually included on the diagram.
- Fuse and Breaker Panels:The diagram will often show the location and layout of the fuse and breaker panels, indicating which fuses or breakers are connected to specific circuits and components.
- Grounding:The diagram will depict the grounding system, including the ground wire connections and the ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs).
Reading and Interpreting a Keystone RV Wiring Diagram
Reading and interpreting a Keystone RV wiring diagram can be a valuable skill for any RV owner. Here’s a breakdown of how to approach this task:
- Start with the Legend:Begin by familiarizing yourself with the symbols and abbreviations used in the diagram. The legend will provide a key to understanding the different components and connections.
- Identify the Main Components:Locate the main electrical components, such as the batteries, fuse panel, and main breaker.
- Trace the Wiring Paths:Follow the lines on the diagram to understand how the wires connect the different components.
- Pay Attention to Color Codes:Color codes are used to distinguish different types of wires, such as positive, negative, and ground wires. Familiarize yourself with the standard color codes used in your RV.
- Check for Circuit Diagrams:If included, study the circuit diagrams to understand how different components are connected in a circuit.
- Locate the Grounding System:Identify the grounding system on the diagram to understand how the electrical system is grounded.
Understanding Color Codes
Color codes are essential for identifying different types of wires in an RV electrical system. Here are some common color codes used in Keystone RV wiring diagrams:
- Red:Positive (Hot) wire, typically carrying power from the battery or generator to the electrical components.
- Black:Positive (Hot) wire, often used in circuits with multiple components.
- White:Neutral wire, carrying the return current from the electrical components back to the battery or generator.
- Green:Ground wire, providing a path for current to flow to the ground in case of a fault.
- Blue:Often used for a second neutral wire in a circuit, especially in systems with higher power demands.
- Yellow:Sometimes used for a second ground wire, providing additional safety.
It’s important to note that color codes can vary slightly depending on the manufacturer and year of your RV. Consult your RV’s owner’s manual or the specific wiring diagram for your model to confirm the color codes used.
LED Lighting in RVs
LED lighting has become increasingly popular in RVs due to its numerous benefits, including energy efficiency, longevity, and versatility. Unlike traditional incandescent bulbs, LEDs consume significantly less power, leading to lower energy bills and extended battery life. Their durability and resistance to vibrations make them ideal for the often-bumpy RV lifestyle.
Moreover, LED lighting offers a wide range of color temperatures and brightness levels, allowing for customized ambiance and functionality.
Types of LED Lighting
LED lighting in RVs comes in various forms, each with its unique characteristics and applications.
- Strip Lights:These flexible strips are commonly used for under-cabinet lighting, accent lighting, and even as mood lighting. They are available in various lengths and colors, offering customization options. Strip lights are often self-adhesive, making installation quick and easy.
- Puck Lights:These small, round lights are ideal for accent lighting, reading lights, and even replacing traditional overhead lights. They are often equipped with magnetic bases for easy installation and repositioning. Puck lights are available in various colors and brightness levels.
- Panel Lights:Panel lights provide a more diffused and even light distribution, making them suitable for overhead lighting, bathroom lighting, and general illumination. They are typically rectangular or square and offer a modern aesthetic.
- Bulb Lights:Traditional bulb-shaped LED lights are readily available in various sizes and wattages, making them suitable for replacing existing incandescent bulbs in fixtures. They offer a familiar look and feel while providing the benefits of LED technology.
LED Lighting Installation
Installing LED lighting in an RV typically involves connecting the lights to the RV’s 12-volt DC power system. The installation process may vary depending on the type of LED lights and the existing wiring.
- Wiring Connections:LED lights are typically wired using a positive (+) and negative (-) connection. The positive wire is connected to the RV’s 12-volt power source, while the negative wire is connected to ground. Some LED lights may have a built-in resistor or driver that regulates the voltage and current flow.
- Considerations:When installing LED lighting, it is crucial to consider the following factors:
- Amperage:Ensure that the LED lights’ amperage rating does not exceed the capacity of the RV’s wiring. Overloading the wiring can cause overheating and potential damage.
- Polarity:Always connect the positive (+) and negative (-) wires correctly. Incorrect wiring can damage the LED lights or the RV’s electrical system.
- Heat Dissipation:Some LED lights, especially high-power models, may generate heat. Ensure adequate ventilation to prevent overheating and potential fire hazards.
- Water Resistance:In areas prone to moisture, such as bathrooms or outdoor spaces, use water-resistant LED lights.
30 Amp Schematic for LED Lighting
A 30-amp RV electrical system is designed to handle a limited amount of power. LED lighting is energy-efficient and requires less power compared to traditional incandescent bulbs, making them ideal for RV applications. This section will provide a comprehensive guide on designing a 30-amp RV electrical system with LED lighting, covering the schematic diagram, component specifications, wiring guide, and safety considerations.
Components and Wire Sizes
The components and wire sizes for the LED lighting circuit are crucial for a safe and efficient system. The following table lists the essential components and their corresponding wire sizes:
| Component | Wire Size | Connection |
|---|---|---|
| LED Lights | 18 AWG | Connected in parallel to the power source |
| Power Source (Battery or Inverter) | 10 AWG | Connected to the main power distribution panel |
| Circuit Breaker | 15 Amp | Protects the LED lighting circuit from overloads |
| Switch | 18 AWG | Controls the flow of electricity to the LED lights |
| Wire Connectors | Appropriate size for the wire gauge | Securely connect wires together |
Wiring Guide
This step-by-step guide provides instructions for wiring LED lighting in a 30-amp RV electrical system:
- Plan the Circuit:Determine the number and location of LED lights in the RV. This will help you determine the total wattage required and the appropriate wire size.
- Install the Circuit Breaker:Install a 15-amp circuit breaker in the main power distribution panel. This will protect the LED lighting circuit from overloads.
- Run the Power Wire:Run a 10 AWG wire from the circuit breaker to the location where the LED lights will be installed.
- Connect the Switch:Install a switch on the power wire and connect it to the circuit breaker. The switch will control the flow of electricity to the LED lights.
- Connect the LED Lights:Connect the LED lights in parallel to the power wire. Ensure that the positive (+) and negative (-) terminals of the LED lights are correctly connected to the positive and negative terminals of the power wire.
- Secure the Connections:Use wire connectors to securely connect all the wires together. Ensure that the connections are properly insulated to prevent short circuits.
- Test the Circuit:Turn on the circuit breaker and test the LED lights to ensure that they are working correctly.
Safety Considerations for RV Electrical Systems
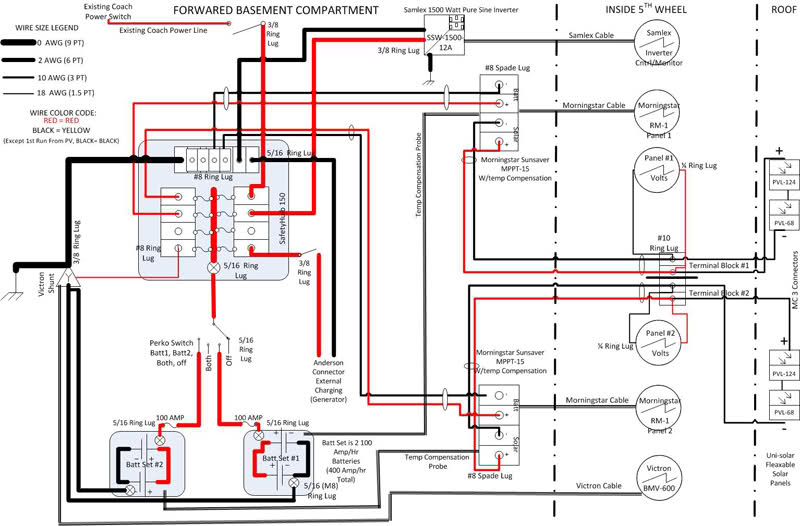
RV electrical systems, like any other electrical system, require careful attention to safety. Ensuring proper grounding and implementing safety measures are crucial to prevent electrical hazards and protect yourself and your RV.
Understanding Grounding in RV Electrical Systems
Grounding is a fundamental safety feature in RV electrical systems. It provides a path for electrical current to flow to the ground in case of a fault. This prevents electrical shock and reduces the risk of electrical fires. In an RV, the ground wire is typically connected to the RV’s chassis, which acts as a ground plane.
This connection ensures that any stray current is safely directed to the ground.
Common Safety Hazards Associated with RV Electrical Wiring
- Overloaded Circuits:Overloading an electrical circuit by connecting too many appliances or using high-wattage devices can cause overheating, leading to wire melting, electrical fires, and potential damage to appliances.
- Loose Connections:Loose connections in electrical wiring can create resistance, generating heat and potentially causing fires. This is especially important to consider in areas subject to vibration, such as the RV’s chassis.
- Damaged Wiring:Damaged or frayed wiring can expose live wires, increasing the risk of electrical shock and fires. Regularly inspect wiring for signs of wear and tear and replace any damaged components promptly.
- Improper Grounding:A faulty ground connection can compromise the safety of the entire electrical system. Ensure that all electrical components are properly grounded and that the ground wire is connected to the RV’s chassis.
- Water Intrusion:Water can conduct electricity, so it’s crucial to prevent water from entering electrical components or wiring. Inspect for leaks and ensure that electrical outlets and appliances are installed in dry locations.
Tips for Preventing Electrical Fires and Other Safety Issues
- Regular Inspections:Regularly inspect your RV’s electrical system for signs of damage or wear. This includes checking wiring, connections, outlets, and appliances. Pay attention to any signs of overheating, burning smells, or loose connections.
- Use Surge Protectors:Surge protectors help protect your RV’s electrical system from voltage surges that can damage appliances and electronics. Install a surge protector at the power source and consider using smaller surge protectors for individual appliances.
- Avoid Overloading Circuits:Be mindful of the amperage rating of your RV’s circuits and avoid overloading them by connecting too many appliances or using high-wattage devices. Use a power meter to monitor your power consumption and distribute loads accordingly.
- Properly Ground All Appliances:Ensure that all appliances are properly grounded to prevent electrical shock. Check for three-prong plugs and ensure that the ground wire is connected to the RV’s chassis.
- Use Certified Electricians:For any significant electrical work, consult a certified RV electrician. They have the expertise and knowledge to ensure that your electrical system is safe and compliant with industry standards.
Troubleshooting Common RV Electrical Problems
RV electrical systems are complex and can sometimes malfunction. Understanding common problems and troubleshooting techniques can help you resolve issues quickly and safely.
Identifying Common RV Electrical Problems
Common electrical problems in RVs include:
- Blown fuses:Fuses are designed to protect electrical circuits from overloads. If a fuse blows, it indicates that there is a problem with the circuit, such as a short circuit or an overloaded appliance.
- Faulty wiring:Damaged or corroded wiring can cause electrical problems, including shorts, open circuits, and power loss.
- Malfunctioning components:Electrical components, such as switches, outlets, and appliances, can fail and cause electrical problems.
- Loose connections:Loose connections can cause intermittent power loss or even complete power outages.
- Overloaded circuits:Using too many appliances on a single circuit can overload it and cause fuses to blow or wires to overheat.
Troubleshooting Steps for Diagnosing Electrical Problems
Here are some steps you can take to diagnose and resolve common RV electrical problems:
- Check the fuses:Start by checking the fuses in your RV’s fuse box. If a fuse is blown, replace it with a fuse of the same amperage. If the new fuse blows immediately, there is a problem with the circuit.
- Inspect the wiring:Carefully inspect the wiring in your RV for signs of damage or corrosion.
Look for frayed wires, exposed wires, or corrosion on the terminals.
- Test electrical components:Use a multimeter to test electrical components, such as switches, outlets, and appliances. This will help you determine if the component is functioning properly.
- Check for loose connections:Inspect all electrical connections in your RV for looseness.
Tighten any loose connections.
- Identify overloaded circuits:If you are experiencing frequent blown fuses, you may have an overloaded circuit. Try using fewer appliances on the affected circuit.
Tips for Preventing Future Electrical Problems
Here are some tips to help you prevent future electrical problems in your RV:
- Use surge protectors:Surge protectors can help protect your RV’s electrical system from power surges.
- Avoid overloading circuits:Be mindful of the amperage rating of your RV’s circuits and avoid overloading them.
- Inspect wiring regularly:Regularly inspect your RV’s wiring for signs of damage or corrosion.
- Maintain electrical components:Regularly inspect and maintain electrical components, such as switches, outlets, and appliances.
- Use qualified electricians:If you are not comfortable working with electrical systems, consult a qualified RV electrician for repairs or maintenance.
Upgrading RV Electrical Systems: 30 Amp Schematic Keystone Rv Wiring Diagrams Led Lighting
Upgrading an RV’s electrical system can be a significant investment, but it can also enhance your RVing experience by providing more power and functionality. This section will delve into the advantages and disadvantages of upgrading an RV’s electrical system, guide you on choosing the right components for an upgrade, and provide a step-by-step guide for upgrading an RV’s electrical system, including safety precautions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Upgrading an RV’s Electrical System
Upgrading an RV’s electrical system can offer numerous advantages, but it’s crucial to weigh these against the potential disadvantages before making a decision.
- Increased Power Capacity: Upgrading to a larger generator or installing additional batteries can provide more power for appliances and devices, enabling you to use more high-power appliances without overloading the system.
- Enhanced Functionality: Upgrading the electrical system can allow you to add features like solar panels, inverters, and more advanced electrical outlets, expanding your RV’s functionality and comfort.
- Improved Reliability: Upgrading components like wiring and breakers can improve the reliability of the electrical system, reducing the risk of malfunctions and power outages.
- Increased Resale Value: A well-maintained and upgraded electrical system can enhance your RV’s resale value, making it more appealing to potential buyers.
- Cost: Upgrading an RV’s electrical system can be expensive, especially if you’re installing new components like a larger generator or solar panels.
- Complexity: Upgrading an RV’s electrical system can be complex and require specialized knowledge and skills, particularly if you’re dealing with advanced components like inverters or solar panels.
- Potential for Damage: Improper installation or modifications to the electrical system can lead to damage to the RV’s wiring, appliances, or even create safety hazards.
- Warranty Considerations: Upgrading the electrical system might void the manufacturer’s warranty on the RV, so it’s essential to consult with the manufacturer before making any significant changes.
Choosing the Right Components for an Electrical Upgrade
Selecting the right components for an RV electrical upgrade is crucial for ensuring the upgrade is effective and safe. Here are some factors to consider:
- Power Requirements: Determine the total power requirements of your RV, considering the appliances and devices you intend to use. This will help you choose a generator or battery bank with sufficient capacity.
- Type of Upgrade: Decide whether you’re upgrading the entire electrical system or focusing on specific components like the generator, battery bank, or wiring. This will help you narrow down the components you need.
- Budget: Set a realistic budget for the upgrade, considering the cost of components, labor, and any necessary permits or inspections.
- RV Model and Year: Consult your RV’s owner’s manual or contact the manufacturer to determine the electrical system’s specifications and compatibility with various components.
Upgrading an RV’s Electrical System: A Step-by-Step Guide
Upgrading an RV’s electrical system can be a challenging task, but following these steps can help you ensure a safe and successful upgrade:
- Plan the Upgrade: Start by planning the upgrade thoroughly, considering your power requirements, budget, and the components you want to install. Consult your RV’s owner’s manual or contact the manufacturer for guidance.
- Gather Necessary Components: Purchase all the necessary components, including a generator, battery bank, inverter, solar panels, wiring, breakers, and any other required items. Ensure the components are compatible with your RV’s electrical system.
- Safety Precautions: Always prioritize safety during the upgrade process. Disconnect the RV’s battery, wear appropriate protective gear, and work in a well-ventilated area. Follow all manufacturer instructions and consult with a qualified electrician if needed.
- Install the Components: Install the new components according to the manufacturer’s instructions. This may involve running new wiring, connecting components to the existing electrical system, and configuring settings.
- Test and Inspect: After installation, thoroughly test the upgraded electrical system to ensure all components are functioning correctly. It’s also recommended to have a qualified electrician inspect the system for safety and compliance with local codes.
RV Electrical Codes and Standards
RV electrical systems are designed to operate safely and efficiently within the confines of a recreational vehicle. These systems are subject to strict codes and standards, ensuring the safety of both the occupants and the RV itself.
Importance of RV Electrical Codes and Standards
RV electrical codes and standards are crucial for several reasons. They serve as a comprehensive set of guidelines that dictate the design, installation, and maintenance of electrical systems in RVs, ensuring the following:
- Safety:The primary goal of these codes is to prevent electrical hazards such as shocks, fires, and malfunctions. By adhering to these standards, RV manufacturers and owners can mitigate risks and create a safe environment for everyone onboard.
- Reliability:Codes and standards ensure the reliability of electrical systems, reducing the likelihood of failures and breakdowns. This is especially important when traveling long distances or camping in remote areas.
- Compatibility:RV electrical systems are designed to be compatible with various power sources, including campgrounds and RV parks. Codes and standards ensure that these systems can connect safely and efficiently to these external power sources.
- Compliance:Adhering to codes and standards ensures that RVs meet legal requirements and are approved for use on public roads and in campgrounds.
Key Codes and Standards for RV Electrical Systems
Several key codes and standards are relevant to RV electrical systems. These include:
- National Electrical Code (NEC):The NEC is a comprehensive set of electrical safety standards developed by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA). It provides guidelines for the installation and maintenance of electrical systems in buildings, including RVs. The NEC is adopted and enforced by local jurisdictions throughout the United States.
- American National Standards Institute (ANSI):ANSI develops and publishes standards for various industries, including recreational vehicles. ANSI standards cover aspects such as RV electrical systems, appliances, and wiring.
- Recreational Vehicle Industry Association (RVIA):The RVIA is a trade association that represents manufacturers of RVs and related products. The RVIA develops and publishes standards specific to the RV industry, including electrical systems. These standards ensure that RVs meet specific safety and performance requirements.
- Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE):The SAE is a global association of engineers that develops standards for various industries, including the automotive industry. SAE standards cover aspects such as RV electrical connectors and wiring harnesses.
Ensuring Compliance with RV Electrical Codes and Standards
To ensure compliance with RV electrical codes and standards, several steps are essential:
- Consult with Qualified Electricians:When installing or modifying electrical systems in an RV, it is crucial to consult with a qualified electrician who is familiar with RV electrical codes and standards. This ensures that the work is done correctly and safely.
- Review the RV’s Electrical Manual:Every RV comes with an electrical manual that Artikels the specific electrical system design and components. Carefully reviewing this manual can provide valuable information about the RV’s electrical system and how to maintain it safely.
- Regular Inspections:Regularly inspecting the RV’s electrical system for any signs of damage or wear is crucial. This includes checking wires, connectors, and appliances for signs of overheating, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Stay Updated on Code Changes:Electrical codes and standards are periodically updated to reflect advancements in technology and safety practices. It is important to stay informed about any changes or updates to these codes to ensure compliance.
Understanding RV Electrical Codes and Standards
RV electrical codes and standards are comprehensive sets of guidelines that ensure the safe and reliable operation of RV electrical systems. Understanding these codes is essential for RV owners and anyone working on RV electrical systems.
FAQ Summary
What are the different types of LED lighting used in RVs?
Common types include strip lights, bulb replacements, and dedicated LED fixtures, each offering unique benefits for different applications.
How do I choose the right wire size for my LED lighting circuit?
Consult a wiring chart to determine the appropriate wire size based on the amperage of the LED lights and the length of the wiring run.
What are some common safety hazards associated with RV electrical wiring?
Common hazards include loose connections, frayed wires, overloaded circuits, and improper grounding, all of which can lead to electrical fires or shocks.
How can I prevent future electrical problems in my RV?
Regular maintenance, inspecting wiring for damage, and avoiding overloading circuits are crucial for preventing future electrical issues.