2013 gmc terrain 3.6 litre idler pulley diagram – 2013 GMC Terrain 3.6L idler pulley diagram is your key to understanding the engine’s heart and soul, my friend. Imagine a tropical sunset, the sky ablaze with vibrant colors, and the sound of gentle waves lapping at the shore.
That’s how smooth your engine should run with a healthy idler pulley! This little guy plays a big role in keeping everything moving smoothly.
The idler pulley, part of the accessory drive system, keeps the serpentine belt properly tensioned. This ensures that all your essential engine accessories like the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioner compressor get the power they need. Think of it as the engine’s personal assistant, making sure everything runs like a well-oiled machine.
Introduction
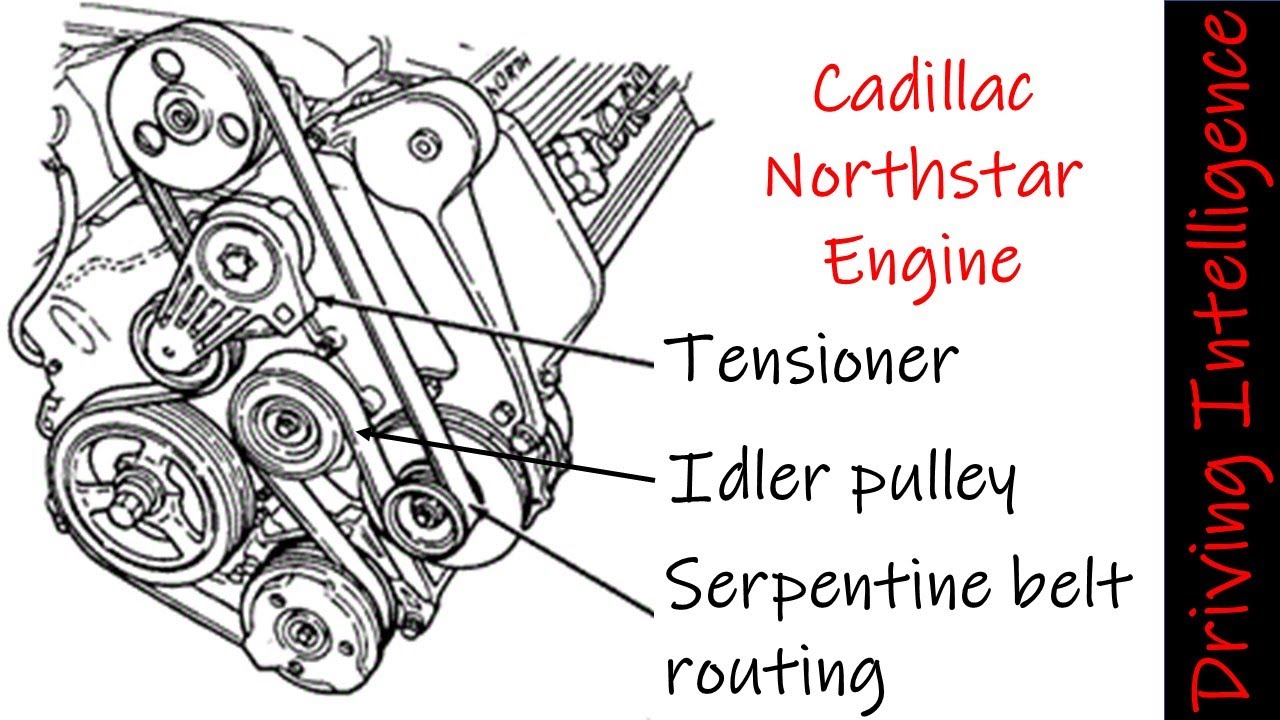
The 2013 GMC Terrain, equipped with a 3.6L V6 engine, is a popular SUV known for its performance and reliability. At the heart of its accessory drive system is the idler pulley, a seemingly simple yet crucial component. This guide delves into the idler pulley diagram, shedding light on its role and significance in maintaining the smooth operation of your Terrain’s engine.
Idler Pulley’s Role in the Accessory Drive System
The idler pulley, positioned within the accessory drive system, plays a vital role in ensuring the proper tension and alignment of the serpentine belt. This belt powers essential components like the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. The idler pulley acts as a guide, preventing the belt from slipping or wearing prematurely.
By maintaining the correct tension, the idler pulley ensures efficient energy transfer from the engine to the accessories. Understanding the idler pulley diagram is essential for proper maintenance and repair, allowing you to identify and address potential issues before they escalate.
Idler Pulley Diagram
The idler pulley diagram for the 2013 GMC Terrain 3.6L engine is a visual representation of the components that help drive the engine’s auxiliary systems. This diagram provides valuable insights into the belt routing, tensioning system, and the location of critical components like the idler pulleys themselves.
Understanding the diagram is crucial for diagnosing belt-related issues, performing maintenance, and ensuring the smooth operation of the engine.
Idler Pulley Components and Their Functions
The idler pulley diagram for the 2013 GMC Terrain 3.6L engine showcases several components, each playing a specific role in the engine’s operation.
- Idler Pulley:This component is a wheel with a groove that guides the serpentine belt around the engine. It helps maintain proper belt tension and ensures smooth operation of the auxiliary systems. There are typically multiple idler pulleys in the system, each positioned strategically to direct the belt and optimize its function.
- Tensioner Pulley:This pulley is responsible for adjusting the belt tension. It utilizes a spring or hydraulic mechanism to keep the belt taut, ensuring optimal performance and preventing slippage. The tensioner pulley is typically located near the idler pulleys, allowing for easy access and adjustment.
- Alternator:This component generates electrical power for the vehicle’s systems, including the battery, lights, and other electrical components. It is driven by the serpentine belt and is typically located near the front of the engine.
- Power Steering Pump:This pump provides hydraulic pressure to assist the steering system, making it easier to turn the wheel. It is also driven by the serpentine belt and is usually located near the alternator.
- Air Conditioning Compressor:This compressor is responsible for cooling the vehicle’s cabin. It is driven by the serpentine belt and is typically located near the power steering pump.
- Water Pump:This pump circulates coolant through the engine, keeping it at the optimal temperature. It is also driven by the serpentine belt and is typically located near the front of the engine.
Belt Routing and Tensioning System
The serpentine belt, also known as the drive belt, is a single belt that drives multiple accessories in the engine. The belt routing is carefully designed to ensure that each component receives the necessary power. The belt’s path is determined by the placement of the idler pulleys and the tensioner pulley.
The tensioner pulley plays a crucial role in maintaining the correct belt tension. It uses a spring or hydraulic mechanism to adjust the belt’s tightness, preventing slippage and ensuring optimal performance.
The tensioning system is vital for the proper operation of the serpentine belt. If the belt is too loose, it can slip, leading to reduced power output from the accessories and potential damage to the belt. Conversely, if the belt is too tight, it can put excessive strain on the bearings and other components, leading to premature wear and failure.
Idler Pulley Components

The idler pulley assembly in a 2013 GMC Terrain 3.6L engine is a critical component in the accessory drive system, ensuring proper belt tension and smooth operation of various engine accessories.
Components of the Idler Pulley Assembly
The idler pulley assembly consists of several key components:
- Pulley Wheel:The pulley wheel is a grooved wheel made of durable materials like steel or aluminum. It is designed to guide the serpentine belt around the accessory drive system.
- Bearing:The bearing is the heart of the idler pulley, providing smooth rotation and minimizing friction. Bearings can be ball bearings or roller bearings, depending on the specific application.
- Housing:The housing encloses the bearing and pulley wheel, providing structural support and protection. It is typically made of metal or plastic.
- Mounting Bracket:The mounting bracket secures the idler pulley assembly to the engine block or other components. It is often made of steel and features holes for attaching bolts.
- Tensioner Mechanism (Optional):Some idler pulleys are integrated with a tensioner mechanism, which allows for adjustment of belt tension. This mechanism typically involves a spring or hydraulic system.
Materials Used in the Construction of the Pulley and Bearing
The materials used for the idler pulley and bearing are crucial for ensuring durability and performance:
- Pulley Wheel:Steel and aluminum are commonly used for pulley wheels. Steel offers high strength and durability, while aluminum provides a lightweight option. The choice of material depends on factors such as load capacity, operating temperature, and cost.
- Bearing:Bearings are typically made of hardened steel, which offers excellent wear resistance and load capacity. The bearing raceways and balls or rollers are carefully manufactured to ensure smooth and efficient operation. The material choice for the bearing cage can vary, with materials like nylon or steel being common.
Lubrication and Sealing Methods
Proper lubrication and sealing are essential for extending the life of the idler pulley and bearing:
- Lubrication:The bearing within the idler pulley is typically lubricated with grease, which is sealed within the housing. Grease provides a lubricating film between the bearing components, reducing friction and wear. The type of grease used is crucial and must be compatible with the operating temperature and load conditions.
- Sealing:The idler pulley assembly employs seals to prevent contaminants such as dirt, water, and debris from entering the bearing and causing damage. These seals are typically made of rubber or synthetic materials and are designed to withstand the harsh operating environment.
Idler Pulley Function
The idler pulley is a vital component in the accessory drive system of your 2013 GMC Terrain, playing a crucial role in ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of various engine accessories. This pulley acts as a guide and tensioner for the serpentine belt, which powers essential components like the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor.
Impact of a Faulty Idler Pulley on Engine Performance, 2013 gmc terrain 3.6 litre idler pulley diagram
A faulty idler pulley can significantly impact engine performance, leading to a range of problems. The most common issue is belt slippage, which can cause the accessories to malfunction or fail to operate at all. This can result in:* Dimming headlights:The alternator, responsible for charging the battery, may not function correctly, causing the battery to drain and the headlights to dim.
Power steering failure
The power steering pump may not receive enough power, making steering difficult and potentially dangerous.
Air conditioning issues
The air conditioning compressor may not function properly, leading to a loss of cool air.
Engine overheating
The water pump, which circulates coolant to prevent engine overheating, might not operate efficiently.
Common Symptoms of an Idler Pulley Failure
Several symptoms can indicate an idler pulley failure. These include:* Squealing or whining noise:A worn or damaged idler pulley can produce a distinct squealing or whining sound, particularly when the engine is accelerating.
Vibrations
A loose or damaged idler pulley can cause vibrations, especially at high speeds.
Locating a diagram for the 2013 GMC Terrain 3.6 liter idler pulley can be crucial for understanding its function and potential replacement needs. Similar to the need for a clear visual representation of the parts within a 1980 Suzuki GS 750 gas tank parts diagram , a diagram of the idler pulley can assist in identifying the component’s location, its connection points, and its role in the overall engine operation.
Belt wear and tear
An idler pulley that is not functioning properly can lead to premature wear and tear on the serpentine belt.
Belt slippage
A loose or damaged idler pulley can cause the serpentine belt to slip, resulting in reduced accessory performance.
Maintenance and Replacement: 2013 Gmc Terrain 3.6 Litre Idler Pulley Diagram
The idler pulley, a vital component in your GMC Terrain’s engine, requires regular inspection and maintenance to ensure smooth and reliable operation. Ignoring these crucial steps can lead to premature wear, damage, and potential engine problems.
Inspecting the Idler Pulley
Regularly inspecting the idler pulley is essential for identifying any signs of wear or damage. A worn or damaged idler pulley can lead to a range of issues, including belt slippage, premature belt wear, and even engine damage.
- Visual Inspection:Visually inspect the idler pulley for any cracks, chips, or other signs of damage. Look for excessive wear on the pulley’s groove or bearing.
- Bearing Check:Check the bearing for any signs of roughness or noise. Spin the pulley by hand and listen for any unusual sounds. A smooth, quiet rotation indicates a healthy bearing.
- Belt Tension:Inspect the belt tension. If the belt is too loose or too tight, it can put extra strain on the idler pulley, leading to premature wear. Consult your owner’s manual for the correct belt tension specifications.
Replacing the Idler Pulley
If your inspection reveals signs of wear or damage, it’s time to replace the idler pulley. A worn or damaged idler pulley can lead to a range of issues, including belt slippage, premature belt wear, and even engine damage.
- Gather the Necessary Tools and Parts:Before starting the replacement process, ensure you have the correct tools, including a wrench set, socket set, and a torque wrench. You’ll also need a new idler pulley that matches your vehicle’s specifications. It’s best to purchase an OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) part for optimal compatibility and longevity.
- Remove the Old Idler Pulley:Refer to your vehicle’s repair manual for specific instructions on removing the old idler pulley. Typically, this involves loosening the mounting bolts and removing the pulley.
- Install the New Idler Pulley:Once the old pulley is removed, install the new one in its place. Ensure that the pulley is properly aligned and that the mounting bolts are tightened to the specified torque. Refer to your owner’s manual for the correct torque specifications.
- Reinstall the Belt:Once the new idler pulley is installed, re-install the belt. Ensure the belt is properly routed around the other pulleys and that it’s tensioned correctly. Refer to your owner’s manual for the correct belt tension specifications.
Choosing the Right Replacement Part
When choosing a replacement idler pulley, it’s crucial to select a high-quality part that meets your vehicle’s specifications. A high-quality idler pulley will ensure smooth operation, reduce wear and tear, and prolong the lifespan of your engine.
- OEM Parts:Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) parts are designed specifically for your vehicle and offer the best fit and performance. They are typically more expensive but provide the highest quality and reliability.
- Aftermarket Parts:Aftermarket parts are produced by companies other than the vehicle manufacturer. They can be a more affordable option but may not offer the same level of quality or durability as OEM parts. When choosing an aftermarket part, research the manufacturer’s reputation and ensure the part meets your vehicle’s specifications.
- Bearing Quality:Pay close attention to the quality of the bearing. A high-quality bearing will ensure smooth operation and prevent premature wear. Look for bearings with a high-quality seal to prevent contamination and premature failure.
Related Components
The idler pulley, while seemingly simple, plays a crucial role in the smooth operation of your GMC Terrain’s accessory drive system. Its interaction with other components like the tensioner, belt, and other pulleys ensures proper power transmission and system stability.
The Idler Pulley’s Relationship with Other Components
The idler pulley’s primary role is to maintain the correct belt tension. It works in conjunction with the tensioner, a component that adjusts the belt’s tightness. When the tensioner applies pressure to the belt, the idler pulley helps to maintain the tension by providing a fixed point of contact.
This interaction ensures that the belt doesn’t slip or become too loose, preventing power loss and potential damage to the components it drives.The idler pulley also interacts with other pulleys in the system, which are responsible for driving various accessories like the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor.
These pulleys, along with the idler pulley, ensure that the belt runs smoothly and efficiently, transmitting power to all connected components.
Potential Issues from Malfunctioning Related Components
A malfunctioning tensioner can lead to excessive belt tension, causing premature wear on the belt and other pulleys. Conversely, a faulty tensioner can result in insufficient tension, leading to belt slippage and reduced power delivery to accessories. This can cause issues with the alternator’s charging ability, leading to a dead battery or a malfunctioning power steering system.A worn or damaged belt can cause slippage and loss of power, affecting the performance of the accessories.
This can lead to a variety of issues, including a dimming or flickering headlight, a sluggish power steering system, or a malfunctioning air conditioning system.A malfunctioning pulley, including the idler pulley, can cause the belt to misalign or even come off, leading to significant damage to the engine and accessory drive system.
It’s important to remember that the idler pulley, tensioner, belt, and other pulleys all work together to ensure the proper functioning of your GMC Terrain’s accessory drive system. Any malfunction in one of these components can affect the entire system, leading to a variety of issues.
Troubleshooting
A malfunctioning idler pulley can disrupt the smooth operation of your GMC Terrain’s engine, leading to various problems. Recognizing the symptoms and implementing the right troubleshooting steps can help you pinpoint the issue and address it promptly.
Identifying Common Idler Pulley Problems
A failing idler pulley can manifest in several ways. Here are some common signs that might indicate a problem:
- Loud Noises:A worn-out idler pulley can produce a distinct squeaking, grinding, or rattling sound, especially when the engine is accelerating or decelerating. This noise usually originates from the accessory drive belt rubbing against the damaged pulley.
- Vibrations:A damaged idler pulley can cause vibrations throughout the engine compartment, particularly noticeable at idle or during acceleration. This is due to the uneven rotation of the pulley.
- Belt Slippage:A worn-out idler pulley can cause the accessory drive belt to slip, leading to reduced power output, difficulty starting the engine, and a warning light on the dashboard.
- Accessory Malfunctions:A failing idler pulley can affect the operation of accessories powered by the accessory drive belt, such as the alternator, power steering pump, or air conditioning compressor.
Diagnosing Idler Pulley Failure
If you suspect an idler pulley problem, it’s crucial to diagnose the issue accurately. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
- Visual Inspection:Start by visually inspecting the idler pulley for signs of wear, cracks, or damage. Look for any loose or missing bolts. If the pulley is damaged or worn, it needs replacement.
- Belt Tension Check:Check the tension of the accessory drive belt. A loose belt can indicate a worn-out idler pulley. Use a belt tension gauge to measure the belt tension and compare it to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Bearing Inspection:If you suspect a bearing failure, carefully inspect the idler pulley bearing for any signs of wear, damage, or excessive play. You can try to spin the pulley by hand to feel for any resistance or roughness. If you feel any unusual resistance or play, the bearing needs replacement.
Resolving Idler Pulley Issues
Once you’ve diagnosed the idler pulley problem, you can take steps to resolve it. Here are some tips:
- Replacement:If the idler pulley is worn out or damaged, it needs to be replaced. Use a high-quality replacement pulley from a reputable manufacturer to ensure longevity and optimal performance.
- Belt Replacement:If the accessory drive belt is also worn out or damaged, replace it along with the idler pulley. This ensures proper belt tension and prevents premature wear on the new pulley.
- Accessory Drive System Inspection:After replacing the idler pulley, inspect the entire accessory drive system for any other potential problems. This includes checking the tensioner, alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. Addressing any issues in the accessory drive system will help prevent future problems.
Safety Considerations
Replacing the idler pulley on your 2013 GMC Terrain 3.6L engine requires careful attention to safety. Working on any engine component can be dangerous if proper precautions aren’t taken. This section highlights potential hazards and offers recommendations for safe practices.
Potential Hazards
Replacing the idler pulley involves working in close proximity to moving engine components. This poses several potential hazards, including:
- Burns:The engine and its components can become extremely hot during operation. Touching these surfaces can result in severe burns.
- Crush Injuries:Moving engine components can trap fingers or other body parts, causing serious injuries.
- Eye Injuries:Flying debris or particles can cause eye injuries.
- Chemical Exposure:Engine fluids, such as coolant or oil, can be harmful if they come into contact with skin or eyes.
Safe Practices
To minimize the risk of injury, follow these safety precautions:
- Allow the engine to cool completelybefore starting any work.
- Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety glasses, gloves, and closed-toe shoes.
- Be aware of your surroundingsand ensure that no one is in the way of moving engine parts.
- Use proper lifting techniquesto avoid strain or injury.
- Never work under a vehicle that is supported only by a jack. Use jack stands for secure support.
- Avoid wearing loose clothing or jewelrythat could get caught in moving parts.
- Work in a well-ventilated areato avoid exposure to harmful fumes.
- If you are unsure about any procedure, consult a qualified mechanic.
Tool Safety
Proper handling of tools is essential for safety.
- Use the correct tools for the joband ensure they are in good condition.
- Keep tools clean and free of grease or oilto prevent slipping.
- Store tools properlywhen not in use to prevent accidents.
- Never use a tool that is damaged or worn.
Component Handling
When handling engine components, such as the idler pulley, it’s crucial to take precautions.
- Avoid dropping components, as this can damage them or create sharp edges.
- Use gloves to protect your handsfrom sharp edges or contaminated surfaces.
- Be mindful of the weight of componentsand use proper lifting techniques.
- If you need to dispose of any components, do so in an environmentally responsible manner.
Resources

To further enhance your understanding of the 2013 GMC Terrain 3.6L idler pulley, accessing additional resources is highly recommended. These resources can provide valuable insights into the idler pulley’s intricacies, maintenance procedures, and potential issues. They also offer access to repair guides, manufacturer’s manuals, and online forums, facilitating informed decision-making and troubleshooting.
Manufacturer’s Manuals
The manufacturer’s manuals provide comprehensive information about the vehicle, including details on the idler pulley. They typically include diagrams, specifications, and troubleshooting guides.
- The official GMC website offers access to downloadable manuals for various models, including the 2013 Terrain.
- You can also find manuals at local dealerships or online retailers specializing in automotive literature.
Repair Guides
Repair guides provide step-by-step instructions for various repair procedures, including idler pulley replacement. They often include detailed diagrams, component descriptions, and troubleshooting tips.
- Online platforms like Chilton, Haynes, and AllData offer repair guides specifically tailored to the 2013 GMC Terrain 3.6L engine.
- These guides are valuable resources for DIY enthusiasts and professional mechanics alike.
Online Forums
Online forums dedicated to automotive enthusiasts and professionals can be excellent sources of information and support. They provide a platform for sharing experiences, asking questions, and seeking advice on specific issues related to the idler pulley.
- Forums like GM-Trucks.com, TerrainForum.net, and CarTalk.com often have dedicated sections for the 2013 GMC Terrain.
- Engaging with the community can provide insights into common idler pulley problems, repair strategies, and recommended parts.
Authorized Service Centers
Authorized GMC service centers offer expertise and genuine parts for your vehicle. They can diagnose idler pulley issues, perform repairs, and provide maintenance recommendations.
- To locate an authorized GMC service center near you, visit the official GMC website or use an online directory like Yelp or Google Maps.
- Contacting the dealership where you purchased the vehicle can also provide information about authorized service centers in your area.
Parts Suppliers
Parts suppliers offer a wide range of idler pulleys and other components for the 2013 GMC Terrain 3.6L engine. They can provide genuine OEM parts, aftermarket alternatives, and competitive pricing.
- Online retailers like Amazon, AutoZone, and Advance Auto Parts offer a variety of idler pulleys for the 2013 Terrain.
- Local auto parts stores can also provide idler pulleys and other components.
Conclusion
The idler pulley, a seemingly simple component, plays a vital role in the smooth operation of your 2013 GMC Terrain’s engine. Understanding the idler pulley diagram is crucial for ensuring proper maintenance and timely repairs. This diagram provides a visual representation of the pulley’s location, its connection to other components, and its function within the engine’s belt system.
By familiarizing yourself with the idler pulley diagram, you can identify potential issues, perform routine inspections, and understand the importance of regular maintenance. This knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions about your vehicle’s care, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
FAQ Explained
What are the signs of a failing idler pulley?
You might hear a squealing or groaning sound coming from the engine, especially when starting or accelerating. The belt might also be loose or have visible wear and tear.
How often should I check my idler pulley?
It’s a good idea to inspect it during your regular engine maintenance, which is typically every 3,000-5,000 miles.
Can I replace the idler pulley myself?
While it’s possible, it’s best to leave it to a professional mechanic, especially if you’re not comfortable working on your engine. They have the tools and experience to ensure a safe and proper replacement.