2012 Nissan Pathfinder fuses and relays diagram serves as a vital roadmap for understanding the intricate electrical network within this popular SUV. This diagram unveils the secrets behind the vehicle’s essential functions, from powering the headlights to controlling the engine’s performance.
Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a curious car enthusiast, comprehending the fuse and relay system is essential for diagnosing electrical problems and ensuring your Pathfinder runs smoothly.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the 2012 Nissan Pathfinder’s fuse and relay system, providing a clear and concise explanation of its components, functions, and troubleshooting techniques. We’ll explore the location of the fuse and relay boxes, decipher the symbols and labels on the diagrams, and discuss common fuse and relay issues.
By understanding the fundamentals of this critical system, you’ll be equipped to tackle electrical problems with confidence and keep your Pathfinder running at peak performance.
Introduction: 2012 Nissan Pathfinder Fuses And Relays Diagram

The 2012 Nissan Pathfinder is a mid-size SUV known for its spacious interior, capable off-road performance, and reliable engine. Understanding the fuse and relay diagrams for this vehicle is crucial for diagnosing electrical problems and ensuring safe operation.Fuse and relay diagrams are essential tools for anyone working on the electrical system of a vehicle.
They provide a visual representation of the electrical components, their connections, and the fuses and relays that protect them.
The Purpose of Fuses and Relays
Fuses and relays are safety devices that protect the electrical system from damage caused by overloads or short circuits. Fuses are designed to melt and break a circuit when excessive current flows through them. This prevents damage to other components in the circuit.
Relays, on the other hand, are electromagnetic switches that allow a low-current signal to control a high-current circuit. This is often used to control devices like headlights, power windows, and the starter motor.
Location of Fuse and Relay Boxes
The 2012 Nissan Pathfinder features two primary fuse and relay boxes: the main fuse box and the underhood fuse box. Understanding their locations and how to access them safely is crucial for troubleshooting electrical issues and performing maintenance.
Main Fuse Box Location
The main fuse box is located inside the vehicle’s passenger compartment, on the driver’s side of the dashboard. It is typically found below the steering wheel, near the knee bolster.To access the main fuse box, follow these steps:
- Open the driver’s side door and locate the fuse box cover. It is usually a black or gray panel with a label indicating its purpose.
- Carefully remove the fuse box cover by pressing the release clips or tabs on its sides.
- The fuse box will be exposed, allowing you to access the fuses and relays.
Underhood Fuse Box Location
The underhood fuse box is situated in the engine compartment, near the battery. It is usually a black or gray box with a label indicating its purpose.To access the underhood fuse box, follow these steps:
- Open the hood of the vehicle.
- Locate the fuse box cover, which is typically found near the battery.
- Carefully remove the fuse box cover by pressing the release clips or tabs on its sides.
- The fuse box will be exposed, allowing you to access the fuses and relays.
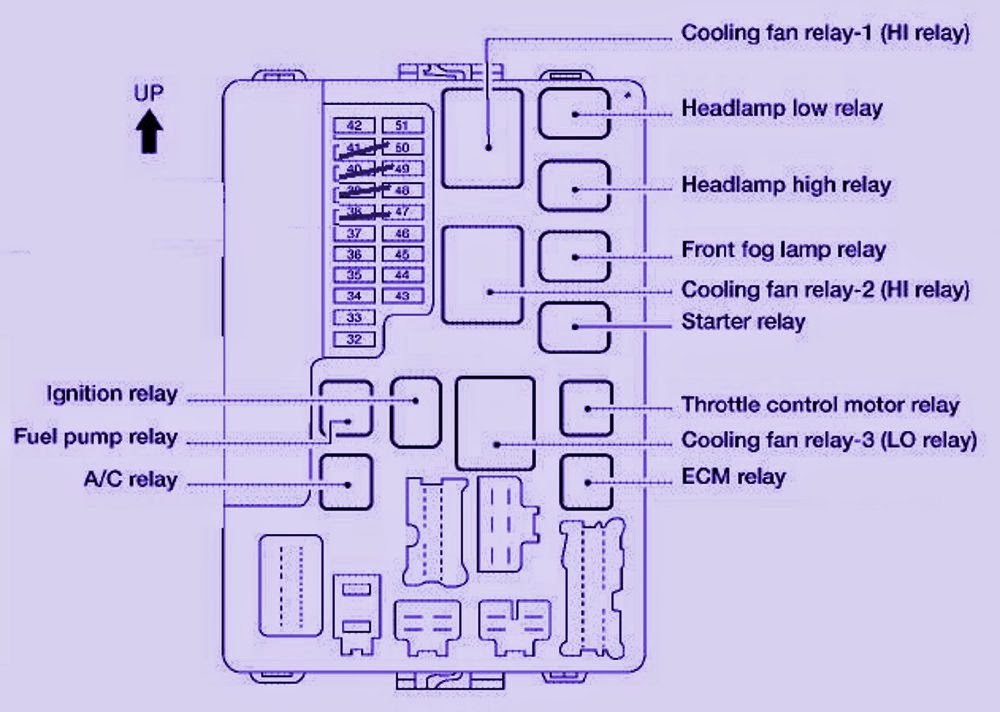
Fuse and Relay Diagram Interpretation
A fuse and relay diagram provides a visual representation of the electrical system’s components, their connections, and the protective devices responsible for their safety. Understanding this diagram is crucial for diagnosing electrical issues, performing repairs, and ensuring the proper functioning of your vehicle.
Fuse and Relay Diagram Structure
Fuse and relay diagrams typically follow a standardized format for easy understanding. They are often organized into sections representing different electrical circuits or systems within the vehicle. Each section usually includes a table listing fuses and relays with their corresponding functions, ratings, and locations.
Symbol Interpretation
Fuse and relay diagrams employ various symbols to represent different components and their relationships. Common symbols include:
- Fuse:A rectangle with a broken line across the middle, representing the fusible link that breaks when excessive current flows.
- Relay:A square with a diagonal line, indicating a switch that is controlled by an electrical signal.
- Wire:A solid line representing a wire connecting different components.
- Ground:A triangle with a horizontal line, indicating a connection to the vehicle’s chassis.
- Battery:A circle with a plus (+) and minus (-) sign, representing the positive and negative terminals of the battery.
Label Interpretation
Labels on the diagram provide essential information about each component, including:
- Fuse Number:A unique identifier for each fuse, allowing easy reference in the diagram and the fuse box.
- Fuse Rating:The maximum current (in amps) that a fuse can safely handle before melting. Exceeding this rating can cause damage to the electrical system.
- Relay Function:A description of the electrical circuit or system that the relay controls, such as headlights, power windows, or air conditioning.
- Associated Components:The specific components that are connected to the fuse or relay, such as the headlights, power window motor, or air conditioning compressor.
Example
Let’s consider an example of a fuse and relay diagram for a 2012 Nissan Pathfinder. The diagram might show a section dedicated to the headlights. This section would include a table listing the fuse responsible for the headlights, its rating (e.g., 15 amps), and the associated components (e.g., left and right headlights).
The diagram would also depict the connections between the fuse, relay, and headlights, along with the symbols representing these components. By analyzing the diagram, you can identify the fuse and relay responsible for the headlights and understand how they are connected to the battery and the headlights themselves.
Common Fuses and Relays
This section details the most common fuses and relays found in the 2012 Nissan Pathfinder. It provides information on the functions of each fuse and relay, including the components they protect or control. Understanding the function of each fuse and relay can be helpful for diagnosing electrical problems and ensuring proper operation of the vehicle’s systems.
Fuse and Relay Locations
The 2012 Nissan Pathfinder has two main fuse and relay boxes: the underhood fuse box and the interior fuse box.The underhood fuse box is located on the driver’s side of the engine compartment, near the battery. It houses the majority of the vehicle’s fuses and relays, including those for the engine, transmission, and other critical systems.The interior fuse box is located in the passenger compartment, typically on the driver’s side, near the steering column.
This box houses fuses and relays for the interior lights, audio system, and other accessories.
Common Fuses and Relays
The following table lists some of the most common fuses and relays found in the 2012 Nissan Pathfinder, along with their descriptions and functions:
| Fuse/Relay Number | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Engine Control Module (ECM) | Protects the ECM, which controls the engine’s operation. |
| 2 | Airbag System | Protects the airbag system, including the sensors and control module. |
| 3 | Power Steering | Protects the power steering pump and motor. |
| 4 | Fuel Pump | Protects the fuel pump, which supplies fuel to the engine. |
| 5 | Radio | Protects the radio and audio system. |
| 6 | Headlights | Protects the headlights and associated wiring. |
| 7 | Taillights | Protects the taillights and associated wiring. |
| 8 | Turn Signals | Protects the turn signal system, including the blinkers and hazard lights. |
| 9 | Horn | Protects the horn and its wiring. |
| 10 | Wiper Motor | Protects the windshield wiper motor. |
| 11 | Heated Mirrors | Protects the heated mirrors and their wiring. |
| 12 | Power Window | Protects the power window motors and mechanisms. |
| 13 | Power Door Locks | Protects the power door lock actuators and wiring. |
| 14 | Climate Control | Protects the climate control system, including the blower motor and air conditioning compressor. |
| 15 | ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) | Protects the ABS system, including the sensors and control module. |
| 16 | TPMS (Tire Pressure Monitoring System) | Protects the TPMS sensors and control module. |
| 17 | Parking Brake | Protects the parking brake system, including the release mechanism. |
| 18 | Rear Defroster | Protects the rear window defroster element and wiring. |
| 19 | Starter Motor | Protects the starter motor and its wiring. |
| 20 | Ignition System | Protects the ignition system, including the ignition coils and spark plugs. |
| 21 | Cigarette Lighter | Protects the cigarette lighter and its wiring. |
| 22 | Rear Window Washer | Protects the rear window washer pump and its wiring. |
| 23 | Instrument Cluster | Protects the instrument cluster and its wiring. |
| 24 | Backup Lights | Protects the backup lights and their wiring. |
| 25 | Fog Lights | Protects the fog lights and their wiring. |
Troubleshooting Fuse and Relay Issues
Troubleshooting fuse and relay problems in your 2012 Nissan Pathfinder is a crucial skill for any owner who wants to maintain their vehicle. Understanding the common symptoms of blown fuses and faulty relays, along with the proper diagnostic steps, can save you time and money in the long run.
This section provides a step-by-step guide to help you identify and resolve these electrical issues.
Diagnosing Fuse and Relay Problems
Diagnosing fuse and relay problems involves a systematic approach to identify the root cause of the electrical malfunction. The process includes examining common symptoms, visually inspecting fuses and relays, and using a multimeter to test their functionality.
- Identifying Common Symptoms:A blown fuse or a faulty relay can manifest in various ways, depending on the circuit it controls. Some common symptoms include:
- Electrical Components Not Working:If a fuse or relay associated with a specific electrical component fails, the component will stop working. For example, a blown fuse for the headlights will cause them to stop functioning.
- Flickering Lights:A faulty relay or a fuse nearing its end can cause flickering lights, indicating an intermittent electrical connection.
- Overheating:A faulty relay can overheat due to excessive resistance, potentially causing damage to surrounding components. This can be identified by touching the relay, which may feel abnormally hot.
- Clicking Sounds:A faulty relay might produce clicking sounds as it tries to engage and disengage, indicating a problem with its internal contacts.
- Visual Inspection:After identifying the possible symptoms, the next step is to visually inspect the fuses and relays. This involves:
- Fuse Box Inspection:Locate the fuse boxes in your 2012 Nissan Pathfinder. There is usually a fuse box under the hood and another one inside the cabin, typically near the driver’s side dashboard. Refer to your owner’s manual for precise locations.
- Fuse Inspection:Carefully examine each fuse. Look for signs of a blown fuse, such as a broken or melted filament inside the fuse. A blown fuse will typically have a visible gap or discoloration. If a fuse appears blown, replace it with a new fuse of the same amperage rating.
- Relay Inspection:Examine the relays. Check for signs of damage, such as cracked or melted plastic, corrosion, or loose connections. If a relay appears damaged, it should be replaced.
- Testing with a Multimeter:If the visual inspection doesn’t reveal any obvious issues, use a multimeter to test the fuses and relays. This is a more precise method to confirm their functionality. Here’s how to test them:
- Fuse Testing:To test a fuse, set your multimeter to the continuity setting. Place one probe on each end of the fuse. A good fuse should show continuity (a low resistance reading on the multimeter), while a blown fuse will show an open circuit (no continuity).
- Relay Testing:To test a relay, set your multimeter to the resistance setting. Connect the probes to the relay’s terminals as per the instructions in your owner’s manual or a reliable repair guide. A working relay should show a certain resistance value, depending on its type and specifications.
Replacing Blown Fuses and Faulty Relays
Once you’ve identified a blown fuse or a faulty relay, replacing it is a relatively simple process. However, it’s crucial to follow safety precautions to avoid any electrical shocks or damage to your vehicle.
- Safety Precautions:Always disconnect the battery before working on electrical components, including fuses and relays. This will prevent any accidental electrical shocks. Ensure you have a fuse puller for removing fuses from the fuse box. When handling fuses and relays, avoid touching the metal contacts, as this can cause a short circuit.
Always use a fuse of the same amperage rating as the one you are replacing. Never use a fuse with a higher amperage rating, as this could lead to overheating and damage to the electrical system.
- Fuse Replacement:Locate the blown fuse in the fuse box. Use a fuse puller to gently remove the blown fuse. Insert a new fuse of the same amperage rating into the empty fuse slot. Ensure the fuse is fully seated in the slot.
- Relay Replacement:Locate the faulty relay in the relay box. Disconnect the electrical connector from the relay. Gently remove the faulty relay from its socket. Insert the new relay into the socket, ensuring it’s fully seated. Reconnect the electrical connector to the new relay.
- Testing After Replacement:After replacing a fuse or relay, reconnect the battery and test the affected electrical component to ensure it is functioning correctly. If the problem persists, there may be another underlying issue in the electrical system that needs further diagnosis.
Safety Precautions
Working with electrical systems, including fuse and relay boxes, requires a high level of caution. Improper handling can lead to serious injury or even death. Always prioritize safety by adhering to the following precautions.
General Safety Precautions
Before accessing the fuse and relay boxes, ensure you disconnect the battery’s negative terminal. This action will prevent any electrical current from flowing through the system while you work, significantly reducing the risk of electric shock.
- Always wear appropriate safety glasses to protect your eyes from potential debris or sparks.
- Ensure you work in a well-lit area to enhance visibility and prevent accidents.
- Keep a fire extinguisher readily available in case of any unexpected electrical fire.
- Avoid wearing loose clothing or jewelry that could get caught in moving parts or create a potential hazard.
- Always use insulated tools to handle electrical components, as this will minimize the risk of electrical shock.
- Avoid touching multiple electrical components simultaneously, as this can create a path for current to flow through your body.
- Never attempt to work on electrical systems if you are wet or standing on a wet surface. Water can conduct electricity, increasing the risk of electric shock.
- If you are unsure about any aspect of the procedure, consult a qualified electrician.
Precautions Specific to Fuse and Relay Boxes
Fuse and relay boxes contain delicate electrical components that require careful handling.
- Always use a fuse puller or pliers with insulated handles to remove and replace fuses. Never use metal objects or your fingers, as this could create a short circuit.
- Before removing a fuse, ensure the circuit is de-energized by disconnecting the battery’s negative terminal.
- Inspect fuses carefully for signs of damage or corrosion before replacing them. If a fuse is blown, it is essential to determine the cause of the failure before replacing it. Replacing a blown fuse without addressing the underlying problem can lead to further damage to the electrical system.
- When replacing fuses, always use fuses with the correct amperage rating. Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards. Using a fuse with a lower amperage rating will blow prematurely and may not protect the circuit properly.
- Relays are electromechanical switches that control the flow of electricity to various components. Ensure you handle relays with care, as they are delicate and can be easily damaged.
- Before removing or replacing a relay, always disconnect the battery’s negative terminal. This will prevent any electrical current from flowing through the system while you work, significantly reducing the risk of electric shock.
- When replacing relays, ensure you use the correct type and make sure it is compatible with the vehicle’s electrical system.
Potential Risks of Improper Handling
Failing to adhere to these safety precautions can lead to various risks, including:
- Electric shock: This can occur when you come into contact with live electrical components, resulting in burns or even death.
- Fire: A short circuit or a faulty fuse can lead to overheating and fire.
- Damage to electrical components: Improper handling can damage fuses, relays, or other electrical components, leading to malfunctions and further problems.
Always prioritize safety when working with electrical systems. Adhering to these precautions can significantly reduce the risk of injury or damage. If you are unsure about any aspect of the procedure, consult a qualified electrician.
Additional Resources
For a comprehensive understanding of the 2012 Nissan Pathfinder’s fuse and relay system, accessing additional resources is highly recommended. These resources can provide detailed information, diagrams, and troubleshooting guides.
Official Nissan Service Manuals
Official Nissan service manuals are the most authoritative source of information regarding your vehicle’s fuse and relay system. These manuals provide detailed diagrams, specifications, and troubleshooting procedures specific to your 2012 Pathfinder.
Understanding the 2012 Nissan Pathfinder fuses and relays diagram is crucial for diagnosing electrical issues. This diagram details the location and function of each fuse and relay, aiding in troubleshooting problems with components like the headlights, radio, and power windows.
For a comprehensive understanding of fuel system functionality, the p 4018 fuel line routing diagram provides a detailed overview of fuel line placement and connections, which can be essential when working on fuel system repairs or modifications. Returning to the 2012 Nissan Pathfinder fuses and relays diagram, it’s important to note that regular maintenance and inspection of these components can prevent future electrical problems.
- You can typically find these manuals online through various automotive websites or by contacting your local Nissan dealership.
- These manuals are often available in digital format, making them easy to access and navigate.
Online Resources
Numerous online resources offer valuable information about fuse and relay systems, including:
- Nissan Owner’s Manual:The owner’s manual for your 2012 Pathfinder may contain a basic fuse and relay diagram and general information about the system.
- Automotive Forums:Online forums dedicated to Nissan vehicles can be a valuable source of information and advice from other owners and enthusiasts. You can search for discussions related to fuse and relay issues or post your questions for assistance.
- Technical Websites:Websites specializing in automotive repair and maintenance often have articles, tutorials, and resources related to fuse and relay systems. These websites can provide helpful insights into common issues and troubleshooting techniques.
Specialized Tools and Equipment
While not always necessary, certain tools and equipment can be helpful for diagnosing and troubleshooting fuse and relay issues:
- Multimeter:A multimeter is essential for testing electrical circuits and verifying the continuity of fuses and relays. It allows you to measure voltage, current, and resistance.
- Fuse Puller:A fuse puller is a specialized tool designed to safely remove and insert fuses without damaging them.
- Relay Tester:A relay tester can help you determine if a relay is functioning correctly. It applies voltage to the relay and tests its switching capabilities.
Example Scenarios
This section presents a series of common fuse and relay problems encountered in the 2012 Nissan Pathfinder, along with detailed explanations and solutions. These scenarios illustrate the practical application of fuse and relay diagram knowledge.
Scenario 1: Headlights Not Working, 2012 nissan pathfinder fuses and relays diagram
The headlights are a critical safety feature, and their failure can be a major concern. If the headlights are not working, the first step is to check the fuse. The headlight fuse is typically located in the fuse box under the hood.
- Identify the Headlight Fuse:Consult the fuse and relay diagram for the specific location of the headlight fuse. The diagram will indicate the fuse number and its corresponding amperage rating.
- Inspect the Fuse:Carefully remove the fuse and visually inspect it. If the fuse is blown, the wire inside will be melted or broken.
- Replace the Fuse:If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the same amperage rating. If the new fuse blows immediately, there is a short circuit in the headlight circuit.
- Check for Short Circuits:To find the short circuit, carefully inspect the wiring and connectors leading to the headlights. Look for any frayed wires, loose connections, or signs of overheating.
Scenario 2: Power Window Malfunction
Power windows are a convenience feature, but their failure can be frustrating. If a power window is not working, the fuse or relay may be the culprit.
- Identify the Power Window Fuse and Relay:The fuse and relay diagram will indicate the location and function of the power window fuse and relay.
- Inspect the Fuse and Relay:Check the fuse for any signs of damage. If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the same amperage rating. Inspect the relay for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Test the Relay:If the fuse is fine, the relay may be faulty. Test the relay using a multimeter or a test light. If the relay is not working, replace it with a new one.
- Check the Window Motor:If the fuse, relay, and wiring are all in good condition, the window motor may be faulty. Test the motor using a multimeter or a test light. If the motor is not working, it will need to be replaced.
Scenario 3: Radio Not Working
The radio is a common source of entertainment in a vehicle, and its failure can be disappointing. If the radio is not working, the fuse may be the culprit.
- Identify the Radio Fuse:Consult the fuse and relay diagram for the specific location of the radio fuse. The diagram will indicate the fuse number and its corresponding amperage rating.
- Inspect the Fuse:Carefully remove the fuse and visually inspect it. If the fuse is blown, the wire inside will be melted or broken.
- Replace the Fuse:If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the same amperage rating. If the new fuse blows immediately, there is a short circuit in the radio circuit.
- Check for Short Circuits:To find the short circuit, carefully inspect the wiring and connectors leading to the radio. Look for any frayed wires, loose connections, or signs of overheating.
Scenario 4: Turn Signals Not Working
Turn signals are a vital safety feature, and their failure can be dangerous. If the turn signals are not working, the fuse or relay may be the culprit.
- Identify the Turn Signal Fuse and Relay:Consult the fuse and relay diagram for the specific location of the turn signal fuse and relay. The diagram will indicate the fuse number and its corresponding amperage rating.
- Inspect the Fuse and Relay:Check the fuse for any signs of damage. If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the same amperage rating. Inspect the relay for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Test the Relay:If the fuse is fine, the relay may be faulty. Test the relay using a multimeter or a test light. If the relay is not working, replace it with a new one.
- Check the Turn Signal Bulbs:If the fuse, relay, and wiring are all in good condition, the turn signal bulbs may be burnt out.
Conclusion
This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of fuse and relay diagrams for the 2012 Nissan Pathfinder, covering key aspects like identifying fuse and relay boxes, interpreting diagrams, recognizing common fuses and relays, troubleshooting issues, and understanding safety precautions. Understanding fuse and relay diagrams is crucial for anyone involved in automotive maintenance and troubleshooting.
By familiarizing yourself with these diagrams, you can quickly diagnose electrical problems, replace faulty fuses and relays, and prevent further damage to your vehicle.
Importance of Understanding Fuse and Relay Diagrams
Understanding fuse and relay diagrams is essential for several reasons:
- Diagnosing Electrical Problems:Fuses and relays are critical components in a vehicle’s electrical system. By understanding their function and location, you can quickly diagnose electrical problems, such as blown fuses, malfunctioning relays, or faulty wiring.
- Troubleshooting Electrical Issues:Fuse and relay diagrams provide a visual representation of the electrical system, allowing you to trace the path of electricity and identify potential points of failure. This helps you pinpoint the root cause of electrical problems and efficiently troubleshoot them.
- Performing Repairs and Maintenance:When replacing fuses or relays, understanding the diagram ensures you select the correct components and install them properly. This prevents further damage to the electrical system and ensures safe operation of your vehicle.
Seeking Professional Assistance
While this guide provides valuable information, it is essential to remember that working with electrical systems can be dangerous. If you are unsure about any aspect of fuse or relay replacement, or if you encounter complex electrical problems, it is always best to seek professional assistance from a qualified automotive technician.
FAQ Insights
What are the fuse and relay box locations in a 2012 Nissan Pathfinder?
The main fuse box is typically located in the engine compartment, while the relay box might be found in the passenger compartment or under the dashboard. Refer to the owner’s manual or online resources for precise locations.
How do I identify the function of a specific fuse or relay?
The fuse and relay diagram usually provides a legend with descriptions and corresponding numbers. Match the fuse or relay number on the diagram with the component it controls.
What should I do if I suspect a blown fuse or faulty relay?
Always disconnect the battery before working with electrical systems. Inspect the fuses for signs of breakage or melting. Replace faulty fuses with ones of the same amperage rating. For relays, check for proper operation and replace if necessary.