The 2011 Ford F150 fuse box diagram is your essential roadmap to understanding and troubleshooting the vehicle’s electrical system. This diagram serves as a visual representation of the intricate network of fuses and relays that safeguard and control the flow of electricity throughout your truck.
Understanding the layout and functionality of this diagram empowers you to diagnose electrical problems, replace blown fuses, and ensure the smooth operation of your F150.
From identifying the location of the fuse box to deciphering the symbols and navigating the table of fuses and relays, this comprehensive guide provides a step-by-step journey through the intricacies of the 2011 Ford F150 fuse box diagram. We’ll explore the importance of each component, the potential hazards associated with electrical systems, and the proper procedures for addressing electrical issues with confidence.
Introduction to the 2011 Ford F150 Fuse Box
The fuse box is a crucial component of your 2011 Ford F150’s electrical system, acting as a protective barrier against electrical overloads. When a circuit experiences an overload, the fuse melts, interrupting the flow of electricity and preventing damage to your vehicle’s wiring and components.
Understanding the fuse box layout and knowing how to identify and replace fuses is essential for maintaining the functionality and safety of your vehicle.The 2011 Ford F150 has two main fuse box compartments: the underhood fuse box and the passenger compartment fuse box.
Each compartment houses a specific set of fuses that control various electrical circuits in your vehicle.
Underhood Fuse Box Location and Purpose
The underhood fuse box is located in the engine compartment, typically on the driver’s side, near the battery. It houses fuses that protect circuits related to the engine, lighting, and other essential systems.
Passenger Compartment Fuse Box Location and Purpose
The passenger compartment fuse box is located on the driver’s side of the dashboard, typically beneath the steering wheel or in the glove box. It houses fuses that protect circuits related to interior lights, power accessories, and the audio system.
Fuse Box Diagrams
The fuse box diagrams provide a visual representation of the fuse box layout and the circuits that each fuse protects. The diagrams are usually located on the inside of the fuse box lid or in the owner’s manual. By referencing the diagram, you can easily identify the fuse responsible for a particular circuit and replace it if necessary.
Fuse Replacement
To replace a blown fuse, follow these steps:
1. Locate the blown fuse
Use the fuse box diagram to identify the fuse that corresponds to the malfunctioning circuit.
2. Remove the blown fuse
The 2011 Ford F150 fuse box diagram is a critical resource for diagnosing electrical issues and replacing blown fuses. Understanding the layout of the fuse box allows for quick and efficient troubleshooting. Similarly, locating the appropriate fuse for the dashboard gauge cluster in a 2008 Volvo S60 can be simplified by consulting a 2008 Volvo S60 dashboard gauge cluster fuse diagram.
By referencing these diagrams, owners can confidently address electrical problems in their vehicles.
Use a fuse puller or pliers to carefully remove the blown fuse.
3. Inspect the fuse
Check the fuse for a broken or melted filament. If the filament is intact, the fuse may not be blown.
4. Install a new fuse
Install a new fuse of the same amperage as the blown fuse.
5. Test the circuit
After installing the new fuse, test the circuit to ensure it is working properly.
It is crucial to use fuses with the correct amperage. Using a fuse with a higher amperage can result in damage to your vehicle’s electrical system.
Understanding Fuse Box Diagram Components: 2011 Ford F150 Fuse Box Diagram
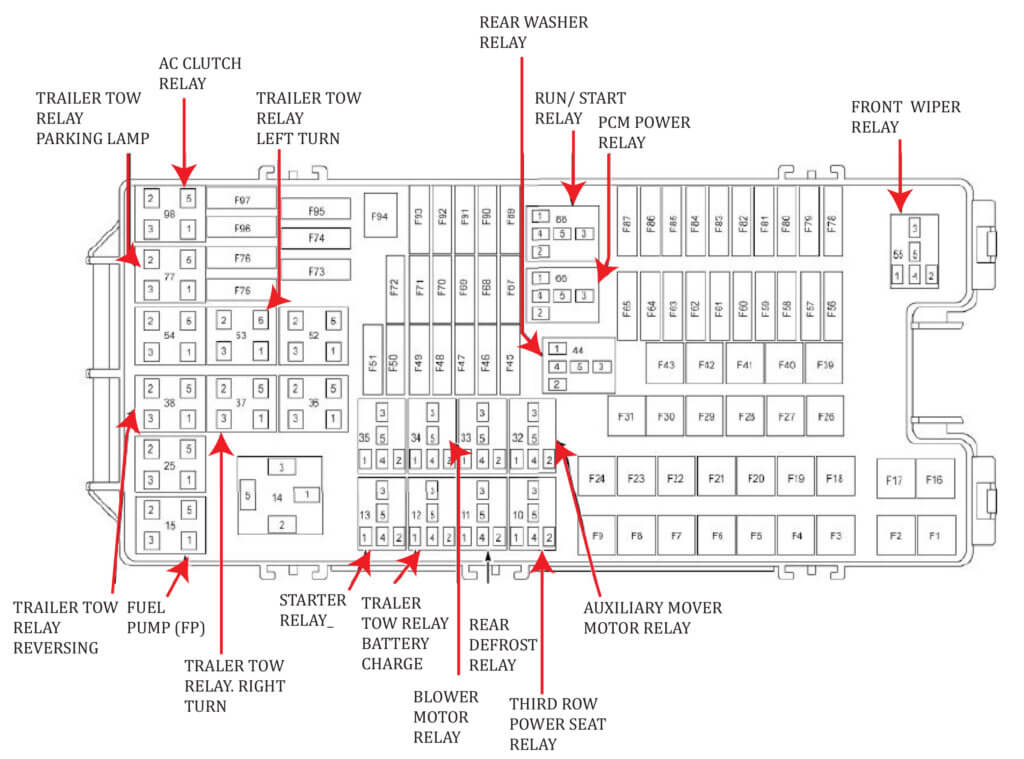
The fuse box diagram for your 2011 Ford F150 is a visual guide that helps you locate and identify fuses and relays. It uses a variety of symbols to represent different components and their functions. Understanding these symbols is crucial for effectively using the diagram and troubleshooting electrical issues.
Symbol Legend
The symbols on the fuse box diagram are designed to be easily recognizable and provide information about each fuse and relay. Here is a comprehensive legend explaining the meaning of common symbols:
- Fuse Size: The fuse size is indicated by a number representing the amperage rating of the fuse. For example, a fuse labeled “10A” can handle up to 10 amps of current before blowing.
- Circuit Function: Each fuse is assigned a specific circuit function, which is usually labeled on the diagram. This tells you which electrical component or system the fuse protects. For instance, a fuse labeled “Headlights” protects the headlights circuit.
- Relay Location: Relays are often depicted on the diagram with a unique symbol, such as a square with a diagonal line. The symbol may be accompanied by a label indicating the relay’s function or location. For example, a relay labeled “Power Seat” controls the power seat function.
- Fuse Block Location: The diagram may indicate the location of different fuse blocks within the vehicle. This helps you quickly identify the correct fuse block for the circuit you are working on. For instance, a label might say “Underhood Fuse Box” or “Passenger Compartment Fuse Box”.
- Fuse Block Layout: The diagram often shows the physical layout of the fuses and relays within each fuse block. This helps you visually locate the specific fuse or relay you need. The diagram may use color coding or numbered positions to represent the individual fuses and relays.
Troubleshooting Electrical Issues
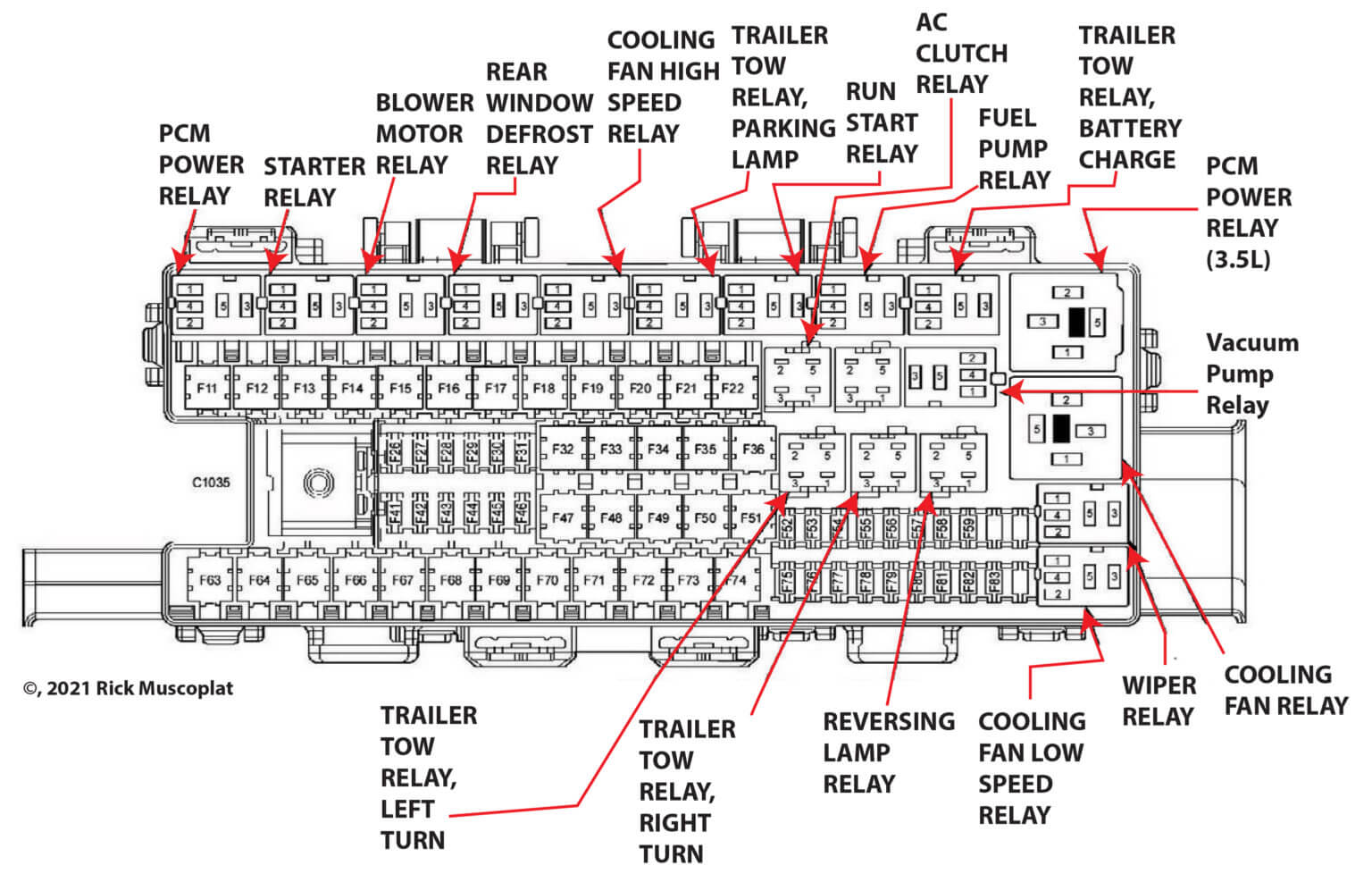
The fuse box diagram is an invaluable tool for diagnosing and resolving electrical problems in your 2011 Ford F150. It provides a visual representation of the fuse and relay locations, along with the circuits they protect. By understanding how to interpret this diagram, you can efficiently pinpoint the source of electrical issues and implement appropriate solutions.
Checking Fuses and Relays
Checking fuses and relays is a fundamental step in troubleshooting electrical problems. These components act as safety devices, protecting circuits from overloads and short circuits. A blown fuse or faulty relay can interrupt the flow of electricity, causing various electrical malfunctions.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to check fuses and relays:
- Locate the Fuse Box:The 2011 Ford F150 has multiple fuse boxes, typically located under the hood and in the passenger compartment. Refer to your owner’s manual or the fuse box diagram to identify the correct location.
- Identify the Relevant Fuse or Relay:Use the fuse box diagram to determine the fuse or relay responsible for the circuit experiencing the problem. The diagram will indicate the fuse or relay number, as well as the circuit it protects.
- Remove the Fuse or Relay:Carefully remove the fuse or relay using a fuse puller or pliers. Avoid touching the metal contacts.
- Inspect for Damage:Examine the fuse for any signs of damage, such as a broken filament or a melted casing. A blown fuse will have a broken filament, typically visible as a gap in the metal strip. For relays, visually inspect for any signs of overheating or damage.
- Test the Fuse or Relay (if necessary):You can use a multimeter to test the continuity of a fuse. If the fuse is blown, it will not conduct electricity. For relays, you can use a test light or multimeter to check for proper operation.
- Replace the Fuse or Relay:If the fuse or relay is faulty, replace it with a new one of the same amperage rating. Ensure the new fuse or relay is properly inserted into the fuse box.
Important:Always use the correct amperage rating for replacement fuses. Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating can damage electrical components and potentially cause a fire.
Identifying and Addressing Common Electrical Issues
The fuse box diagram can help you diagnose and address common electrical issues, such as:
- Headlights Not Working:If your headlights are not working, check the fuses associated with the headlight circuit. The diagram will indicate the fuse numbers and locations.
- Power Windows Not Functioning:If your power windows are not operating, check the fuses related to the power window circuit. The diagram will guide you to the appropriate fuses.
- Radio Not Turning On:If your radio is not turning on, check the fuses responsible for the radio circuit. The diagram will provide the necessary information.
- Tail Lights Not Working:If your tail lights are not working, check the fuses that protect the tail light circuit. The diagram will specify the fuse numbers and locations.
Fuse Replacement Procedures
Replacing a blown fuse is a common maintenance task for any vehicle owner. This section Artikels the correct procedures for removing and replacing fuses in your 2011 Ford F150, ensuring safety and optimal performance.
Fuse Removal and Replacement
Replacing a blown fuse is a straightforward process, but it’s essential to follow the correct steps to avoid damaging the fuse box or causing electrical issues. Here’s a detailed explanation:
- Locate the Fuse Box:The fuse box in your 2011 Ford F150 is typically located in the passenger compartment, under the dashboard, or in the engine compartment. Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the precise location.
- Identify the Blown Fuse:Open the fuse box cover and consult the fuse diagram on the inside of the cover. This diagram will show the location and amperage rating of each fuse. Identify the fuse corresponding to the malfunctioning electrical component.
- Remove the Blown Fuse:Using fuse puller tool (usually provided with the fuse box), gently pull the blown fuse out of its slot.
- Inspect the Fuse:Examine the fuse to confirm if it is blown. A blown fuse will have a broken wire or melted metal inside.
- Install the Replacement Fuse:Insert the new fuse, with the correct amperage rating, into the empty slot. Ensure it is securely seated.
- Test the Electrical Component:After replacing the fuse, test the electrical component that was malfunctioning to ensure it is now working properly.
Importance of Using the Correct Fuse Size and Type
Using the correct fuse size and type is crucial for ensuring the safety and optimal performance of your vehicle’s electrical system.
- Fuse Amperage Rating:Each fuse is designed to handle a specific amount of electrical current. If the fuse is rated too low, it will blow frequently, interrupting the electrical circuit. Conversely, a fuse rated too high will not protect the circuit from overloads, potentially causing damage to electrical components or even a fire.
- Fuse Type:Fuses come in various types, including blade fuses, mini fuses, and maxi fuses. Each type has a specific design and size. Using the wrong type of fuse can result in a loose fit, poor contact, and potentially lead to overheating or even a fire.
Consequences of Using an Incorrect Fuse
Using an incorrect fuse can have serious consequences for your vehicle’s electrical system and overall safety.
- Circuit Overload:If you use a fuse with a higher amperage rating than the circuit requires, it will not protect the circuit from overloads. This can lead to overheating, melting of wires, and potentially a fire.
- Electrical Component Damage:A fuse is designed to protect the electrical components in a circuit. If the fuse is not the correct size, it may not blow when it should, allowing excessive current to flow through the circuit and potentially damage the components.
- Safety Hazard:Using an incorrect fuse can create a safety hazard, as it can lead to electrical fires or malfunctions in critical systems such as the brakes or airbags.
Relay Replacement Procedures
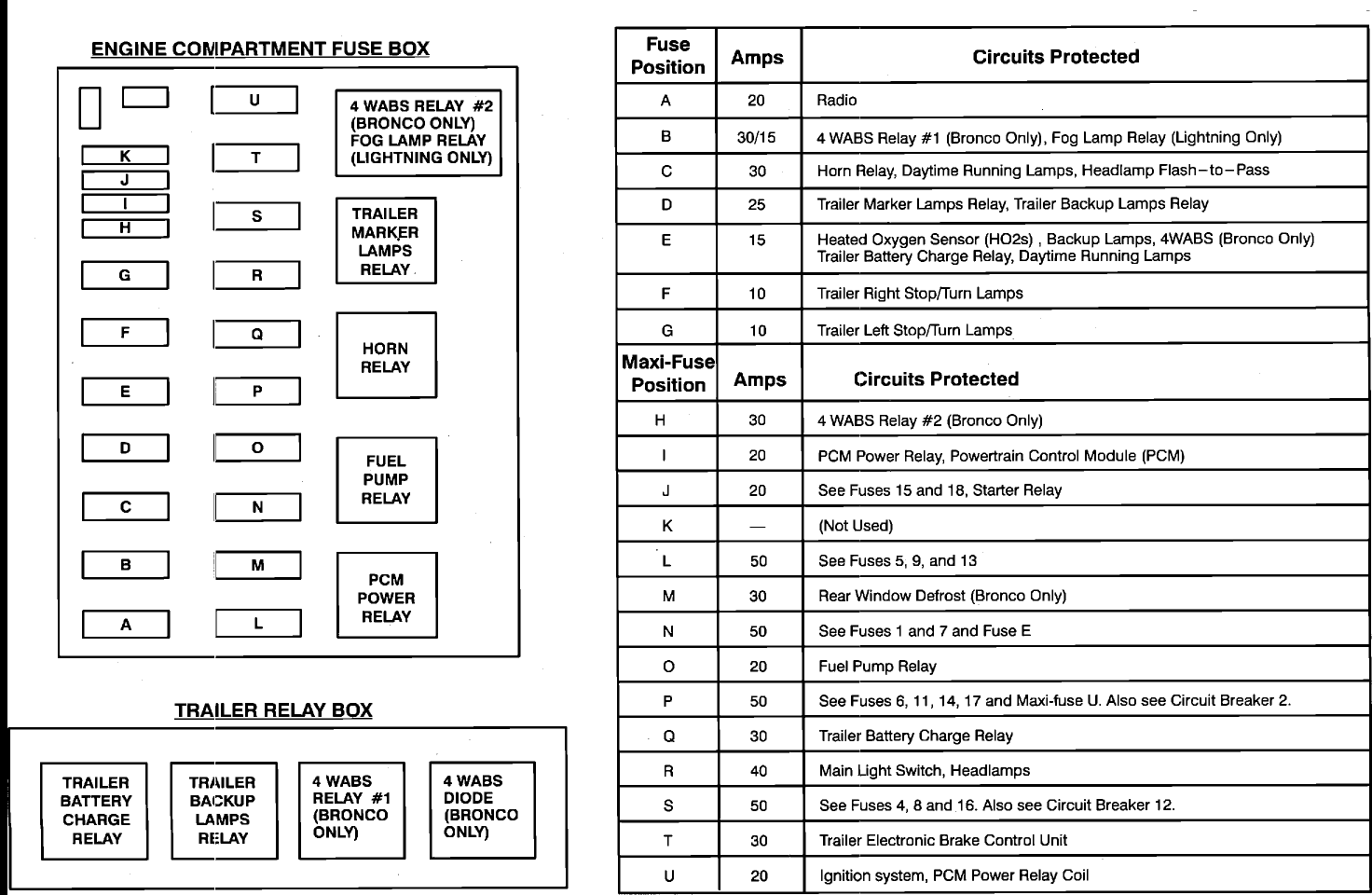
Relays are essential components in the electrical system of your 2011 Ford F150, acting as switches that control various circuits. Understanding how to identify, test, and replace a faulty relay is crucial for maintaining your vehicle’s electrical functionality.
Identifying and Replacing Faulty Relays
Identifying a faulty relay often involves troubleshooting electrical issues and pinpointing the specific circuit affected.
- Consult the fuse box diagram to locate the relay associated with the malfunctioning component.
- Visually inspect the relay for any signs of damage, such as burnt contacts or a cracked casing.
- If the relay appears intact, use a multimeter to test its functionality (explained in the next section).
- If the relay is faulty, replace it with a new one of the same type and amperage rating.
- Ensure the new relay is securely installed in its designated slot within the fuse box.
Understanding Relay Function and Role
Relays act as electromagnetic switches, controlled by a small electrical current that activates a larger current flow to a specific circuit.
- They are designed to protect sensitive components, such as the starter motor, from the high current demands of the circuit.
- Relays also enable the use of smaller gauge wires for controlling larger loads, improving wiring efficiency and reducing the risk of overheating.
- Some common applications for relays in the 2011 Ford F150 include:
- Headlights and taillights
- Power windows and locks
- Fuel pump
- Starter motor
Testing Relays with a Multimeter
A multimeter is an essential tool for testing relays. It allows you to measure voltage, current, and resistance, enabling you to determine if a relay is functioning correctly.
- Before testing, disconnect the relay from the electrical system to avoid potential damage or injury.
- Set the multimeter to the continuity setting (usually represented by a symbol resembling a diode).
- Place the multimeter probes on the relay’s terminals, as indicated in the diagram.
- If the relay is working properly, the multimeter should register a low resistance reading, indicating a closed circuit.
- If the reading is high or shows no continuity, the relay is likely faulty and needs replacement.
Safety Precautions
Working on the fuse box of your 2011 Ford F150 involves dealing with electrical components and circuits. It is crucial to prioritize safety to avoid potential hazards and ensure a smooth repair process.
Disconnecting the Battery, 2011 ford f150 fuse box diagram
Before working on the fuse box, it is essential to disconnect the battery. This step prevents electrical shock and short circuits. To disconnect the battery, locate the negative terminal (usually marked with a minus sign or a black cable) and carefully remove the terminal clamp.
Ensure the clamp is fully removed to break the circuit. After disconnecting the battery, wait for a few minutes to allow any residual electrical charge to dissipate before working on the fuse box.
Safety Guidelines for Working on Electrical Systems
- Always wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from potential debris or sparks.
- Avoid wearing loose clothing or jewelry that could get caught in moving parts.
- Work in a well-lit area to ensure proper visibility of components.
- Use insulated tools to minimize the risk of electrical shock.
- Never touch any electrical components with wet hands or while standing on a wet surface.
- If you are unsure about any aspect of the repair process, consult a qualified mechanic.
Potential Hazards Associated with Electrical Components and Circuits
- Electrical shock: Contact with live electrical components can result in severe electric shock, which can be fatal.
- Short circuits: A short circuit occurs when electricity flows through an unintended path, often due to faulty wiring or loose connections. This can cause overheating, damage to electrical components, and even fire.
- Overloading: If too much electrical current flows through a circuit, it can overload and cause damage to the wiring or components.
- Battery acid: Battery acid is corrosive and can cause burns if it comes into contact with skin or eyes.
Additional Resources
This section provides you with valuable resources to further enhance your understanding of the 2011 Ford F150 fuse box and its components. These resources can be helpful for both general knowledge and specific troubleshooting needs.
Online Resources for Fuse Box Diagrams
The internet offers a wealth of information regarding the 2011 Ford F150 fuse box diagrams. Here are some reputable sources:
- Ford’s Official Website:Ford’s website provides access to owner’s manuals, repair guides, and other technical information. You can find specific fuse box diagrams by entering your vehicle’s VIN (Vehicle Identification Number) or selecting your model year and trim level.
- Automotive Forums:Many automotive forums, such as F150 Forum, provide a platform for owners and enthusiasts to share information and discuss technical topics. These forums often have threads dedicated to fuse box diagrams and troubleshooting guides.
- Online Repair Manuals:Online repair manuals, such as Chilton’s or Haynes, offer detailed information on various aspects of vehicle maintenance and repair, including fuse box diagrams. These manuals are a great resource for those who prefer a comprehensive approach to troubleshooting.
Owner’s Manuals and Repair Guides
The owner’s manual for your 2011 Ford F150 provides essential information about your vehicle, including the fuse box layout and a fuse chart. It also includes details about the vehicle’s electrical system, troubleshooting tips, and safety precautions.
- Ford’s Official Website:You can download a digital copy of your owner’s manual from Ford’s website using your VIN.
- Local Dealerships:Ford dealerships often have a stock of owner’s manuals and repair guides available for purchase.
- Online Retailers:Websites like Amazon and eBay sell both physical and digital copies of owner’s manuals and repair guides for various vehicle models.
Seeking Professional Assistance
While DIY repairs can be satisfying, there are situations where professional assistance is necessary.
- Complex Electrical Issues:If you encounter complex electrical issues, such as intermittent problems, wiring malfunctions, or faulty electrical components, it’s best to consult a qualified mechanic.
- Safety Concerns:If you’re unsure about any electrical repairs or have concerns about safety, always seek professional help.
- Specialized Equipment:Some repairs may require specialized equipment or tools that are not readily available to the average individual. In such cases, a professional mechanic can provide the necessary expertise and equipment.
Common Fuse Box Diagram Variations
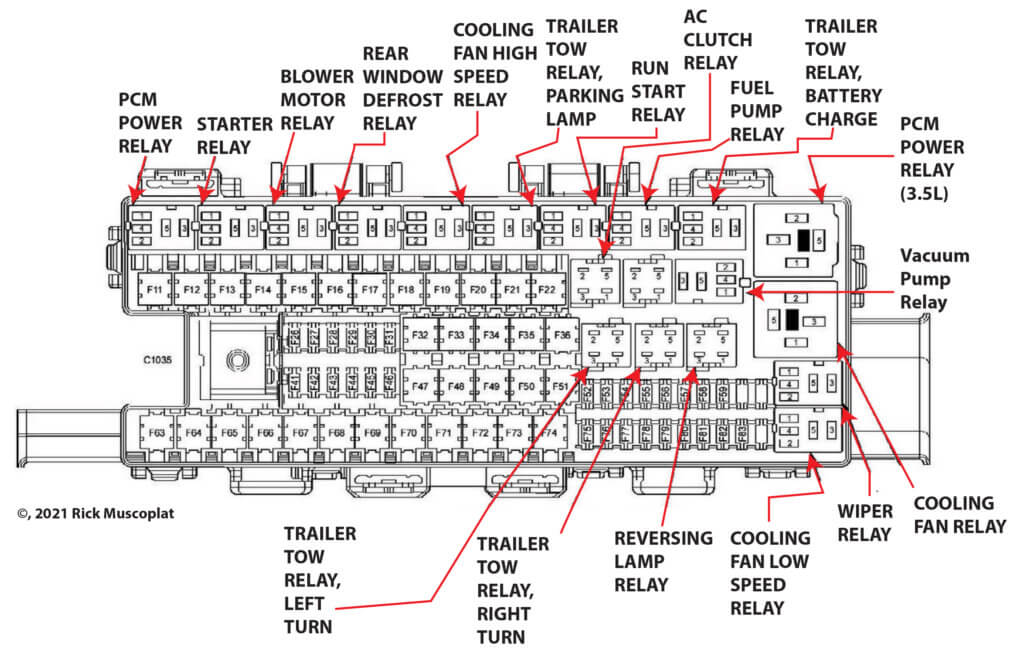
While the 2011 Ford F150 shares a common fuse box layout, minor variations may exist across different trim levels and configurations. These differences primarily relate to the inclusion or exclusion of specific fuses and relays, reflecting the unique features and options equipped in each vehicle.
Understanding these variations is crucial for accurately identifying the fuse or relay responsible for a particular circuit.
Identifying Fuse Box Diagram Variations
The most significant differences in fuse box diagrams typically occur due to the presence or absence of specific options and features. For example, a 2011 Ford F150 equipped with a navigation system might have additional fuses dedicated to the navigation unit and its associated components, while a standard model without navigation might lack these fuses.
Similarly, vehicles with different engine configurations or drivetrain options may have variations in the fuse box diagram.
Locating the Correct Fuse Box Diagram
To ensure you’re using the correct fuse box diagram for your specific 2011 Ford F150, it’s essential to identify the vehicle’s trim level and configuration. This information can typically be found on the vehicle’s identification plate, located on the driver’s side doorjamb.
Once you have identified the trim level and configuration, you can use the owner’s manual or an online resource to locate the appropriate fuse box diagram. Alternatively, you can consult a local Ford dealership or a reputable automotive repair shop for assistance in identifying the correct diagram.
Future Considerations
The automotive industry is constantly evolving, with technological advancements influencing every aspect of vehicle design, including the fuse box. As vehicles become more sophisticated, the fuse box will likely undergo significant changes in layout, functionality, and complexity.
Impact of Evolving Vehicle Technologies
The integration of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), infotainment systems, and connected car technologies will necessitate a more comprehensive fuse box design. ADAS features like lane departure warning, adaptive cruise control, and automated emergency braking rely on numerous sensors and electronic control units (ECUs), each requiring dedicated fuses and circuits.
The increasing complexity of these systems will lead to a higher concentration of fuses and relays within the fuse box.
FAQ Corner
Where is the fuse box located in a 2011 Ford F150?
The fuse box in a 2011 Ford F150 is typically located under the hood, on the driver’s side, near the battery. It might be housed in a black plastic box with a hinged cover.
What does a blown fuse look like?
A blown fuse will have a broken filament inside, which can be seen as a thin, melted wire. It might also appear discolored or charred.
What are the potential consequences of using an incorrect fuse?
Using a fuse with an amperage rating that is too low can cause the fuse to blow frequently, potentially damaging electrical components. Using a fuse with an amperage rating that is too high can result in overheating and fire hazards.
What is a relay and what is its function?
A relay is an electromagnetic switch that controls the flow of electricity to a specific circuit. It acts as an intermediary between the electrical system and the component it controls, allowing for higher current flow than a fuse can handle.
How do I find the right fuse box diagram for my 2011 Ford F150?
You can find the correct fuse box diagram for your specific 2011 Ford F150 model by checking your owner’s manual or by searching online for a diagram specific to your trim level and configuration.