The 2005 Yamaha Rhino 660 relay diagram is your roadmap to understanding the intricate electrical system of this popular ATV. This diagram acts as a blueprint, detailing the connections between relays, fuses, and wiring, allowing you to diagnose and troubleshoot electrical issues with confidence.
Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, deciphering the relay diagram is essential for keeping your Rhino running smoothly.
This guide delves into the world of the 2005 Yamaha Rhino 660 relay diagram, explaining its purpose, components, and how to use it to solve common electrical problems. We’ll cover everything from identifying relays to replacing faulty ones, equipping you with the knowledge to tackle electrical challenges head-on.
Understanding the Relay Diagram: 2005 Yamaha Rhino 660 Relay Diagram

The relay diagram for a 2005 Yamaha Rhino 660 is a crucial tool for understanding the vehicle’s electrical system. It provides a visual representation of the various components, their connections, and the flow of electrical current throughout the system. This diagram serves as a roadmap for diagnosing electrical problems, troubleshooting malfunctions, and performing repairs.
Relays and Their Functions
Relays are electromagnetic switches that control the flow of electrical current in specific circuits. They are typically used to protect sensitive components, handle high currents, and provide remote control of electrical devices. The relay diagram identifies each relay by its location, purpose, and the circuits it controls.
Relays are like miniature electricians, acting as intermediaries to control the flow of electricity.
- Starter Relay:This relay controls the flow of current to the starter motor, enabling the engine to crank and start. When the ignition key is turned to the start position, the starter relay receives a signal and closes its contacts, allowing current to flow to the starter motor.
- Headlight Relay:This relay controls the flow of current to the vehicle’s headlights. When the headlight switch is turned on, the headlight relay receives a signal and closes its contacts, allowing current to flow to the headlights.
- Fuel Pump Relay:This relay controls the flow of current to the fuel pump, which delivers fuel to the engine. When the ignition key is turned on, the fuel pump relay receives a signal and closes its contacts, allowing current to flow to the fuel pump.
Understanding the intricate network of relays within a 2005 Yamaha Rhino 660 is crucial for ensuring its smooth operation. Just as a detailed 2012 Smart Car lower components diagram reveals the interconnectedness of its suspension and steering systems, a comprehensive relay diagram for the Rhino 660 empowers you to troubleshoot electrical issues and keep your off-road adventures going strong.
Fuses and Their Roles
Fuses are safety devices that protect electrical circuits from damage caused by excessive current flow. They are designed to melt and break the circuit if the current exceeds a predetermined limit, preventing overheating and potential fires. The relay diagram indicates the location and amperage rating of each fuse.
Fuses are like sacrificial lambs, protecting other electrical components from excessive current flow.
- Headlight Fuse:This fuse protects the headlight circuit from excessive current flow. If a short circuit or overload occurs in the headlight circuit, the headlight fuse will melt and break the circuit, preventing damage to the headlights and wiring.
- Fuel Pump Fuse:This fuse protects the fuel pump circuit from excessive current flow. If a short circuit or overload occurs in the fuel pump circuit, the fuel pump fuse will melt and break the circuit, preventing damage to the fuel pump and wiring.
- Starter Fuse:This fuse protects the starter circuit from excessive current flow. If a short circuit or overload occurs in the starter circuit, the starter fuse will melt and break the circuit, preventing damage to the starter motor and wiring.
Wiring Connections and the Electrical Harness, 2005 yamaha rhino 660 relay diagram
The relay diagram depicts the wiring connections between the various electrical components, including relays, fuses, switches, sensors, and actuators. These connections form the vehicle’s electrical wiring harness, which transmits electrical signals and power throughout the system. The diagram helps identify specific wires and their connections, facilitating troubleshooting and repair.
The electrical wiring harness is like the nervous system of the vehicle, transmitting signals and power throughout the system.
Common Relay Issues and Troubleshooting

Relays, those small but essential electrical components, play a vital role in the smooth operation of your 2005 Yamaha Rhino 660. While they are generally reliable, they can experience issues over time, leading to frustrating electrical problems. Understanding common relay problems and how to troubleshoot them can save you time and money in the long run.
Common Relay Problems
Relays, like any electrical component, can fail due to various factors. Common issues include:
- Worn Contacts:Over time, the contacts within a relay can wear down, leading to poor electrical connections and intermittent failures. This is especially common in relays that experience frequent switching, such as the starter relay.
- Corrosion:Moisture and dirt can corrode the relay contacts, hindering electrical flow and causing malfunctions. This is particularly prevalent in environments with high humidity or exposure to the elements.
- Burnt Coils:The coil inside a relay is responsible for activating the contacts. Excessive heat or electrical overload can burn out the coil, rendering the relay inoperable.
- Loose Connections:Loose connections at the relay terminals or within the wiring harness can interrupt the electrical circuit, causing intermittent problems.
Symptoms of Faulty Relays
Identifying the symptoms of a faulty relay is crucial for effective troubleshooting. Here are some common signs:
- Electrical Component Malfunctions:A faulty relay can prevent electrical components, such as lights, starter, or fuel pump, from functioning properly. You may experience intermittent or complete failure of these components.
- System Failures:A faulty relay can disrupt the entire electrical system, leading to complete system failures. For example, a faulty ignition relay could prevent the engine from starting.
- Clicking Sounds:When a relay is faulty, you may hear clicking sounds coming from the relay itself. This is usually an indication of worn contacts or a faulty coil.
- Overheating:A faulty relay may overheat, which can be a sign of a burnt coil or a loose connection.
Troubleshooting Relay Problems
Diagnosing relay problems involves a systematic approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Visual Inspection:Begin by visually inspecting the relay for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Look for any burnt or discolored areas on the relay or its terminals.
- Relay Testing with a Multimeter:A multimeter is essential for testing relay functionality. Here’s how to test a relay:
- Continuity Test:Set your multimeter to the “ohms” setting. Place the probes on the relay’s terminals to test the continuity of the contacts. You should get a reading of zero ohms when the relay is energized.
- Coil Resistance Test:Set your multimeter to the “ohms” setting. Place the probes on the relay’s coil terminals. You should get a reading within the manufacturer’s specifications for the specific relay.
- Voltage Drop Test:Set your multimeter to the “DC voltage” setting. Connect the probes to the relay’s terminals. Apply power to the relay and measure the voltage drop across the coil. The voltage drop should be within the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Relay Replacement:If your tests indicate a faulty relay, replace it with a new one. Ensure you use a relay with the same specifications as the original.
Additional Troubleshooting Tips
- Check Wiring Harness:Inspect the wiring harness for any loose connections, broken wires, or corrosion. Repair or replace any damaged wiring.
- Check Ground Connections:Ensure all ground connections are clean and tight. A poor ground connection can cause electrical problems, including relay malfunctions.
- Check Fuses:A blown fuse can sometimes mimic relay problems. Check all related fuses and replace any blown ones.
Relay Location and Identification

The relay box on your Yamaha Rhino 660 is a crucial component of the electrical system. Understanding the location and identification of these relays is vital for troubleshooting electrical issues and ensuring your vehicle operates smoothly. This section will guide you through the process of locating and identifying these relays, providing insights into their functionality and potential issues.
Relay Box Location
The relay box on a 2005 Yamaha Rhino 660 is typically situated under the hood, near the battery. It’s usually secured to the frame or firewall, making it readily accessible for inspection and maintenance.
Identifying Relays
- Each relay within the box is usually labeled with a number or code that corresponds to its function.
- Refer to the relay diagram to correlate these numbers or codes with specific components of the electrical system.
- The relays themselves are often rectangular or square in shape, with multiple terminals or pins for connecting wires.
- The relays may also have markings or symbols indicating their intended purpose, such as a depiction of headlights, starter motor, or fuel pump.
Accessing and Inspecting Relays
- To access the relays, you’ll typically need to open the hood and locate the relay box.
- The box may have a latch or clip securing it in place, which you can release to gain access to the relays.
- Once the box is open, carefully inspect each relay for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- You can also test the relays using a multimeter to verify their functionality.
Relay Replacement and Maintenance
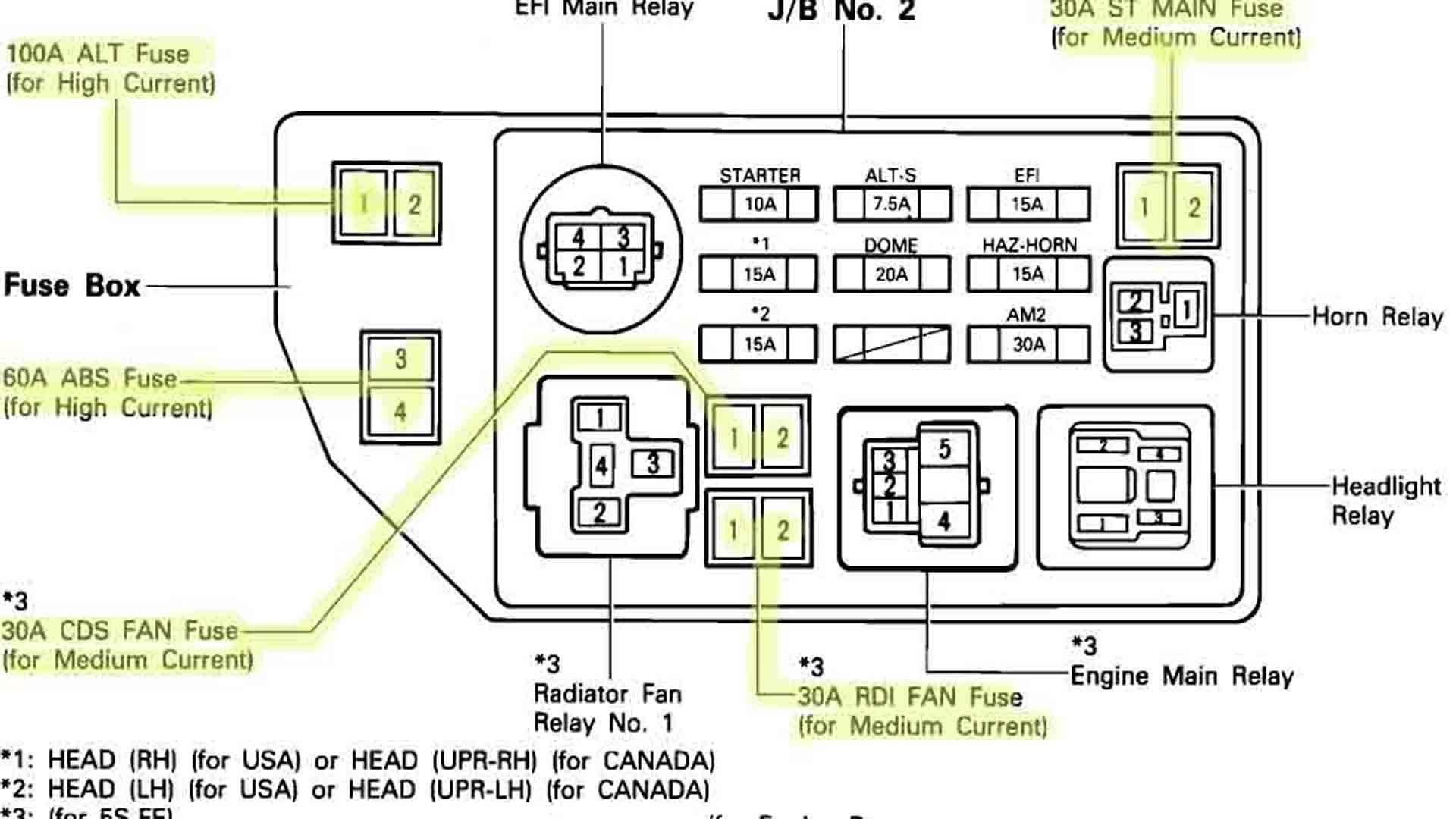
Replacing a faulty relay is a straightforward process that can restore your Yamaha Rhino 660’s functionality. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning the relay contacts, can extend the lifespan of your relays and prevent unexpected breakdowns.
Relay Replacement
Replacing a faulty relay involves a few simple steps that can be performed by anyone with basic mechanical skills.
- Locate the faulty relay:Consult the relay diagram to identify the location of the relay that needs replacement.
- Disconnect the battery:This is an essential safety precaution to prevent electrical shock.
- Remove the faulty relay:Unplug the electrical connectors from the relay and carefully remove it from its mounting position.
- Install the new relay:Ensure the new relay is compatible with the specific application and has the correct pin configuration. Connect the electrical connectors to the new relay and secure it in its mounting position.
- Reconnect the battery:Once the new relay is installed, reconnect the battery.
- Test the relay:Start the engine and check if the relay is functioning correctly.
Selecting the Correct Relay
Choosing the right replacement relay is crucial to ensure proper operation and avoid further damage to your vehicle.
- Check the relay’s specifications:The specifications, such as voltage rating, current rating, and pin configuration, should match the original relay.
- Consult the relay diagram:The diagram provides detailed information about the relay’s specifications and pin configuration.
- Seek professional advice:If you are unsure about the correct replacement relay, consult a qualified mechanic or your Yamaha dealer.
Relay Maintenance
Regular maintenance can extend the life of your relays and prevent premature failure.
- Clean the relay contacts:Over time, dirt and corrosion can build up on the relay contacts, hindering electrical conductivity. Use a small brush and contact cleaner to remove any debris or corrosion.
- Inspect the relay housing:Check for signs of damage or cracks in the relay housing.
- Replace worn-out relays:If a relay shows signs of wear or damage, it is best to replace it with a new one.
Safety Precautions and Considerations

Working with electrical systems in your Yamaha Rhino 660 requires a cautious approach to ensure your safety. Electrical components can pose potential hazards if handled improperly, so understanding and implementing safety precautions is crucial.
Disconnecting the Battery
Before attempting any work on the relay system, it’s paramount to disconnect the battery. This prevents accidental electrical shocks and short circuits that could damage the electrical system or cause injury. To disconnect the battery:
- Locate the battery, typically situated under the hood or in the rear compartment of your Rhino.
- Identify the negative terminal (usually marked with a “-” sign or black cable).
- Using a wrench or socket, loosen the nut securing the negative cable to the terminal.
- Carefully remove the negative cable from the terminal.
This simple step effectively isolates the electrical system, creating a safe environment for your work.
Additional Resources and Information
Your journey to understanding the 2005 Yamaha Rhino 660 relay diagram doesn’t end here. There are a wealth of resources available to help you troubleshoot electrical issues, learn about the intricacies of your ATV’s electrical system, and connect with a community of fellow Rhino owners.
Online Resources and Manuals
Finding the right information is crucial when tackling electrical problems. Here are some valuable resources that can help you:
- Yamaha’s Official Website:Yamaha provides comprehensive owner’s manuals and service information for all their vehicles, including the Rhino 660. You can access these resources directly from their website, often in PDF format, for easy download and printing.
- Online Repair Manuals:Several online platforms offer repair manuals specifically for the 2005 Yamaha Rhino 660. These manuals often provide detailed diagrams, troubleshooting guides, and step-by-step instructions for various repairs, including electrical system components.
- Parts Websites:Websites like Partzilla or BikeBandit offer detailed parts diagrams and exploded views for the Rhino 660. These diagrams can be incredibly helpful in identifying specific relays and their locations within the electrical system.
Online Forums and Communities
Connecting with other Rhino owners can be a valuable source of knowledge and support. Forums and online communities dedicated to the Yamaha Rhino 660 provide a platform for sharing experiences, troubleshooting tips, and finding solutions to common electrical problems.
- Rhino Forums:Websites like Yamaha Rhino Forums or Rhino Riders Forum are dedicated to the Yamaha Rhino 660. These forums host discussions on various topics, including electrical system issues, relay problems, and DIY repairs.
- Facebook Groups:Facebook groups dedicated to the Yamaha Rhino 660 provide another avenue for connecting with other owners. These groups often offer a platform for asking questions, sharing photos, and discussing technical issues, including electrical system troubleshooting.
Specialized Repair Shops and Technicians
For complex electrical issues or situations where you need professional assistance, finding a specialized repair shop or technician with expertise in ATV electrical systems is crucial.
- Local ATV Dealerships:While not all dealerships offer specialized electrical repairs, many have technicians with experience working on ATV electrical systems. Contact your local Yamaha dealership to inquire about their electrical repair services.
- Independent Repair Shops:Many independent repair shops specialize in ATV repair, including electrical systems. Look for shops that have a reputation for expertise in ATV electrical troubleshooting and repair.
- Online Directories:Websites like Yelp or Google Maps can help you find local repair shops and technicians specializing in ATV electrical systems. Read reviews and check for certifications or specializations to ensure you’re choosing a qualified professional.
FAQ
Where can I find a 2005 Yamaha Rhino 660 relay diagram?
You can find the relay diagram in your owner’s manual or online through reputable ATV parts websites and forums.
What tools do I need to work with the relay system?
Basic tools like a multimeter, screwdrivers, and wire cutters are essential for working with relays.
Can I replace a relay myself?
Yes, replacing a relay is a relatively straightforward task. However, it’s important to follow safety precautions and use the correct replacement relay.
What are some signs of a faulty relay?
Common symptoms include malfunctioning electrical components, system failures, and clicking sounds from the relay.
What are some tips for maintaining the relay system?
Regularly cleaning relay contacts and ensuring proper connections can prevent issues and extend the lifespan of your relays.