The 2005 Yamaha Rhino 660 relay diagram is your key to unlocking the mysteries of your ATV’s electrical system. Imagine this: you’re out on the trails, enjoying the thrill of the ride, when suddenly, your engine sputters and dies. A quick glance at the relay diagram could be the difference between a frustrating breakdown and a swift return to the action.
It’s not just about fixing problems, though. Understanding the relay diagram allows you to proactively maintain your Rhino, ensuring it runs smoothly for years to come.
Relays act like miniature traffic cops for your electrical system, directing power to different components. Each relay is a small, but crucial, part of a larger network. Think of it like a circuit board in a computer, but instead of processing data, it’s controlling the flow of electricity to your lights, starter, fuel pump, and other essential systems.
This diagram is your roadmap, helping you navigate the complex web of wires and connections, making sense of the electrical symphony that keeps your Rhino roaring.
Introduction
The 2005 Yamaha Rhino 660 is a popular recreational utility vehicle (RUV) known for its rugged design, off-road capabilities, and versatility. It’s a workhorse for tasks like hauling cargo, navigating challenging terrain, and providing recreational enjoyment. Its powerful 660cc engine and durable chassis make it a reliable choice for various applications.Understanding the relay diagram for the 2005 Yamaha Rhino 660 is crucial for effective troubleshooting and maintenance.
Relays act as electrical switches, controlling the flow of power to various components within the vehicle. By comprehending the relay diagram, owners and mechanics can quickly identify the function of each relay, pinpoint potential issues, and efficiently resolve electrical problems.
Relay Diagram Interpretation
The relay diagram provides a visual representation of the electrical circuits within the Rhino Each relay is depicted with its corresponding number, location, and the components it controls. This information is essential for:
- Troubleshooting electrical problems:When a component malfunctions, the relay diagram helps identify the specific relay responsible for its operation. This allows technicians to focus their troubleshooting efforts on the relevant circuit.
- Diagnosing electrical faults:The diagram helps pinpoint the location of a faulty relay, allowing for quick replacement and restoration of functionality.
- Performing maintenance:Understanding the relay diagram enables owners to safely perform routine maintenance tasks like checking relay connections and ensuring proper operation.
Relay Diagram Basics
Relays are essential components in automotive electrical systems, acting as electrically controlled switches that allow small electrical signals to control larger electrical circuits. They play a crucial role in various functions, from activating headlights and windshield wipers to controlling fuel pumps and ignition systems.
Relay Components
Relays consist of three primary components: the coil, the contacts, and the terminals. The coil is an electromagnet that activates the relay when an electrical current flows through it. The contacts are a pair of conductive elements that open or close the electrical circuit depending on the state of the coil.
The terminals are connection points for the electrical wires that connect the relay to the rest of the electrical system.
Relay Types
Different types of relays are used in vehicles, each designed for specific functions. Here’s a breakdown of common relay types:
- Single-Pole Single-Throw (SPST) Relays:These relays have one set of contacts that can either be open or closed, providing a simple on/off switching function. They are often used for basic applications like activating headlights or turning on a fan.
- Single-Pole Double-Throw (SPDT) Relays:These relays have one set of contacts that can be connected to either of two different terminals. They allow for switching between two different circuits, such as selecting between high and low beam headlights.
- Double-Pole Single-Throw (DPST) Relays:These relays have two sets of contacts that open or close simultaneously. They are used for controlling multiple circuits simultaneously, such as activating both front and rear windshield wipers.
- Double-Pole Double-Throw (DPDT) Relays:These relays have two sets of contacts that can be connected to two different terminals each. They allow for switching between two pairs of circuits, providing more complex switching functions.
2005 Yamaha Rhino 660 Relay Diagram Overview
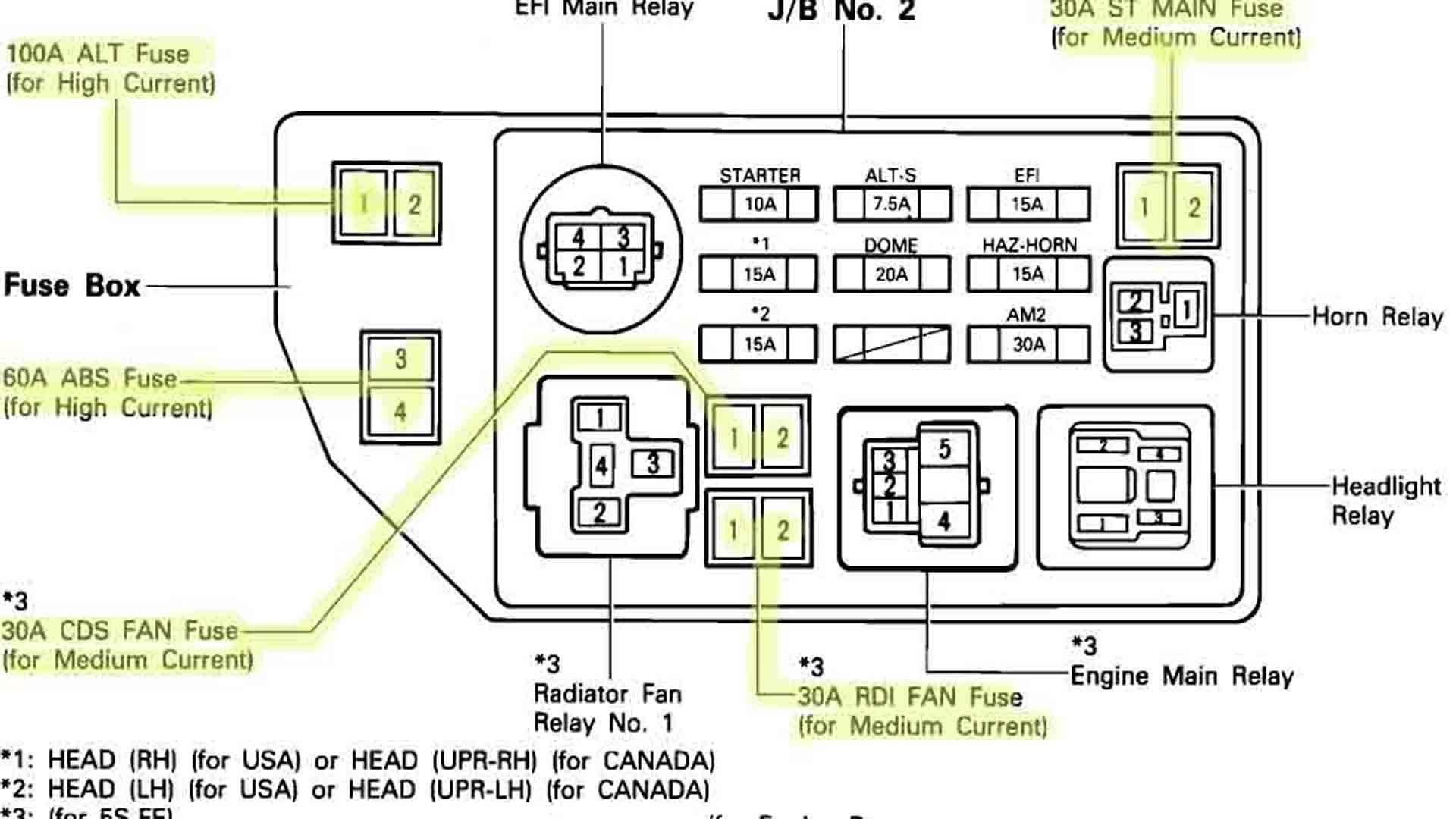
The 2005 Yamaha Rhino 660 relay diagram is a visual representation of the electrical system, showing the interconnections between relays, fuses, and other components. It provides a comprehensive understanding of how electrical signals flow through the system.The diagram is organized by functional groups, making it easier to trace the path of specific circuits.
Each relay is identified by a unique number and symbol, and its corresponding function is clearly labeled. The diagram also indicates the color coding of wires, which helps in identifying and troubleshooting electrical issues.
Relay Functions and Locations
The 2005 Yamaha Rhino 660 relay diagram includes various relays responsible for controlling different electrical components. These relays act as switches, allowing or interrupting the flow of electricity to specific circuits based on signals from other components. The following table summarizes the key relays and their functions:
| Relay Number | Relay Function | Location |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Starter Relay | Under the hood, near the battery |
| 2 | Headlight Relay | Under the hood, near the battery |
| 3 | Fuel Pump Relay | Under the hood, near the battery |
| 4 | Horn Relay | Under the hood, near the battery |
| 5 | Cooling Fan Relay | Under the hood, near the battery |
Color Coding System
The 2005 Yamaha Rhino 660 relay diagram uses a color coding system to identify wires and components. This system helps technicians quickly and accurately identify specific wires and their connections.
The color coding system typically follows a standard convention, where each color represents a specific circuit or function. For example, red wires might represent positive (+) power, black wires might represent ground (-), and blue wires might represent a specific sensor or control signal.
Understanding the color coding system is crucial for troubleshooting electrical issues. It allows technicians to trace the path of a specific circuit, identify potential problems, and repair them efficiently.
Analyzing Specific Relays
This section delves into the intricacies of a specific relay within the 2005 Yamaha Rhino 660’s electrical system, dissecting its function, the circuits it controls, and the troubleshooting steps necessary for diagnosing potential issues.
The Starter Relay
The starter relay plays a pivotal role in the vehicle’s starting sequence. When the ignition key is turned to the “start” position, the relay receives a signal from the ignition switch, energizing the starter motor, which in turn rotates the engine.
This relay acts as a bridge between the ignition switch and the starter motor, providing a high-current path for the starter motor’s operation.The starter relay controls two primary circuits:
- Starter Motor Circuit:This circuit carries a high current from the battery to the starter motor. The relay’s contacts close when the ignition key is turned to the “start” position, allowing the high current to flow and energize the starter motor.
- Starter Solenoid Circuit:This circuit carries a low current from the ignition switch to the starter relay, triggering the relay’s activation. The relay’s coil receives the signal from the ignition switch, causing the relay’s contacts to close and complete the high-current circuit to the starter motor.
The 2005 Yamaha Rhino 660 relay diagram, like any automotive schematic, provides a crucial roadmap for understanding the complex interplay of electrical components. Similar to the need for a 2004 Kia Sorento fuel tank vent location diagram to pinpoint the proper venting system for safe fuel storage, the Rhino’s diagram is essential for diagnosing and troubleshooting electrical issues.
By deciphering the relay’s role in the system’s intricate circuitry, a mechanic can effectively address problems, ensuring the Rhino’s performance and safety remain optimal.
Diagnosing problems with the starter relay involves a systematic approach. The troubleshooting steps include:
- Visual Inspection:Inspect the starter relay for any visible damage, such as burnt contacts, corrosion, or loose connections. Ensure the relay is securely mounted and the wiring is intact.
- Continuity Check:Using a multimeter, test the continuity of the relay’s contacts. The relay should have continuity when energized and no continuity when de-energized. This test verifies if the relay is closing properly when energized.
- Voltage Check:Measure the voltage across the relay’s coil when the ignition key is turned to the “start” position. There should be a voltage present, indicating that the relay is receiving power. If there is no voltage, check the wiring and the ignition switch for any faults.
- Starter Motor Check:If the starter relay appears to be functioning correctly, check the starter motor itself. Verify that the starter motor is receiving power and that the starter motor is not seized or damaged.
Relay Location and Access

The 2005 Yamaha Rhino 660’s relay box is strategically positioned for accessibility and optimal electrical performance. Its location allows for easy inspection, replacement, and troubleshooting of relays, critical components in the vehicle’s electrical system.The relay box is located under the hood, on the driver’s side, near the battery.
This placement provides convenient access for routine maintenance and repairs, ensuring the vehicle’s electrical system functions reliably.
Accessing the Relay Box
To access the relay box, follow these steps:
- Open the hood of the Rhino 660.
- Locate the battery on the driver’s side of the engine compartment.
- The relay box is a black rectangular box situated near the battery, typically mounted to the inner fender wall.
- Remove the cover of the relay box by unscrewing the screws securing it.
- Once the cover is removed, you will have access to the relays within the box.
Relay Box and Relay Identification
The relay box itself is a compact, robust component that houses the relays responsible for various electrical functions. The box is typically made of durable plastic to protect the relays from environmental factors.Each relay within the box is identifiable by its unique shape, size, and labeling.
- The relays are usually rectangular or square in shape, with a protruding terminal on one side.
- Each relay is marked with a number or code that corresponds to its specific function.
- The relay box may also have a diagram or label that identifies the location and function of each relay.
Relay Replacement
To replace a relay, follow these steps:
- Identify the relay that needs replacement based on its function and labeling.
- Disconnect the electrical connector from the relay.
- Remove the relay from its socket by gently pulling it out.
- Insert the new relay into the socket, ensuring it is properly aligned.
- Reconnect the electrical connector to the new relay.
- Secure the relay box cover with the screws.
Relay Testing and Diagnosis
Diagnosing relay problems is crucial for ensuring the proper functioning of your Yamaha Rhino 660. Relays are electromechanical switches that control the flow of electricity to various components, and a malfunctioning relay can lead to a range of issues, from a non-starting engine to inoperable lights.
This section will guide you through the process of testing and diagnosing relay problems, providing you with the knowledge and tools to effectively troubleshoot and resolve these issues.
Testing Relay Functionality
Testing a relay involves verifying its ability to switch electrical current when activated. This can be done using a multimeter or a test light.
- Using a Multimeter:
- Set the multimeter to the continuity or resistance setting.
- Connect the multimeter probes to the relay’s terminals, typically labeled 85 and 86 for the coil and 30 and 87 for the contacts.
- Check for continuity or a low resistance reading between terminals 85 and 86 when the relay is energized (power applied to the coil).
- Check for continuity or a low resistance reading between terminals 30 and 87 when the relay is energized.
- If you don’t get continuity or a low resistance reading, the relay may be faulty.
- Using a Test Light:
- Connect the test light’s positive lead to the relay’s terminal 30 and the negative lead to a good ground.
- Energize the relay (apply power to the coil). The test light should illuminate if the relay is functioning properly.
- If the test light does not illuminate, the relay may be faulty.
Common Symptoms of a Faulty Relay
A faulty relay can manifest itself in various ways, depending on the circuit it controls. Some common symptoms include:
- Engine Failure to Start:A faulty starter relay can prevent the starter motor from engaging, resulting in a no-start condition.
- Inoperable Lights:A faulty headlight relay can prevent the headlights from functioning, leaving you in the dark.
- Electrical Component Malfunctions:Faulty relays can disrupt the operation of various electrical components, such as the fuel pump, ignition system, or other accessories.
- Clicking Noise:A relay that is clicking repeatedly but not engaging may indicate a faulty coil or contact problem.
- Overheating:A relay that is constantly energized or experiencing a short circuit can overheat and potentially melt or cause a fire.
Replacing a Faulty Relay
Once you have diagnosed a faulty relay, replacing it is a relatively straightforward process.
- Locate the Relay:Refer to your Yamaha Rhino 660 service manual or consult a wiring diagram to identify the location of the faulty relay. Relays are often located in fuse boxes, under the hood, or near the electrical components they control.
- Disconnect the Battery:Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent electrical shocks and damage to electrical components during the replacement process.
- Remove the Faulty Relay:Carefully remove the faulty relay from its socket. Note the orientation of the relay before removing it, as some relays have a specific direction they need to be installed in.
- Install the New Relay:Install the new relay in the same location and orientation as the old one. Ensure that the relay is properly seated in its socket and making good contact.
- Reconnect the Battery:Reconnect the negative terminal of the battery and test the functionality of the affected component or system.
Safety Precautions
Working with electrical systems, including relays, requires utmost caution. Improper handling or modifications can lead to serious hazards, including electrical shocks, fires, and damage to your vehicle. Always prioritize safety when working on your Yamaha Rhino 660’s electrical system.
Electrical Safety Precautions
It is crucial to understand the potential hazards associated with working on electrical systems. Before starting any work, ensure you disconnect the battery. This will prevent accidental electrical shocks and short circuits.
- Always disconnect the battery terminals before working on any electrical component, including relays.
- Use insulated tools and wear appropriate safety gear, such as gloves and eye protection.
- Never work on electrical systems when the engine is running or the ignition is on.
- Be mindful of exposed wires and components. Avoid touching them directly, as they can carry a dangerous electrical current.
Relay Handling Precautions, 2005 yamaha rhino 660 relay diagram
Relays are delicate components that can be easily damaged if mishandled.
- Handle relays carefully, avoiding dropping or applying excessive force.
- Inspect relays for signs of damage, such as cracks, corrosion, or loose connections, before installation.
- Ensure the relay is properly seated in its socket and that all connections are secure.
- Avoid over-tightening screws or terminals, as this can damage the relay or its connections.
Wiring and Relay Replacement Precautions
Incorrect wiring or relay replacement can cause serious damage to your vehicle, including electrical fires and malfunctions.
- Always refer to the Yamaha Rhino 660’s wiring diagram and service manual for accurate wiring information.
- Use only genuine Yamaha parts or high-quality aftermarket replacements that meet the specifications of the original relay.
- Double-check all connections and ensure they are secure before reconnecting the battery.
- If you are unsure about any aspect of the repair, consult a qualified mechanic.
Common Relay Problems: 2005 Yamaha Rhino 660 Relay Diagram
Relays, essential components in the electrical system of your 2005 Yamaha Rhino 660, are susceptible to various issues that can lead to malfunctions and hinder the vehicle’s performance. These problems can range from simple electrical shorts to more complex issues like corrosion and wear and tear.
Understanding these common problems and their causes is crucial for effective troubleshooting and maintenance.
Relay Failure Causes
The failure of relays in your Rhino 660 can stem from several factors, each impacting the relay’s functionality in different ways. Understanding these causes helps in identifying the root of the problem and taking appropriate steps to prevent further issues.
- Electrical Shorts:A common culprit for relay failure is an electrical short circuit. This occurs when an unintended path for electricity is created, often due to frayed wiring, loose connections, or damaged insulation. The excessive current flow through the short circuit can overheat and damage the relay’s internal components.
- Corrosion:Exposure to moisture, dirt, and other environmental factors can lead to corrosion on the relay’s terminals and internal components. Corrosion hinders the flow of electricity, causing intermittent or complete failure of the relay.
- Wear and Tear:Over time, the mechanical components of the relay, such as the contacts and coil, can wear out due to repeated operation. This wear can lead to poor contact, reduced switching efficiency, and eventual failure of the relay.
Preventing Relay Failure
Preventing relay failure involves taking proactive measures to address the common causes discussed earlier. By implementing these preventative steps, you can extend the lifespan of your relays and minimize the risk of unexpected malfunctions.
- Regular Inspection:Regularly inspect the relays for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. This visual inspection can help identify potential problems early on, allowing for timely repairs.
- Clean Connections:Clean the relay terminals and surrounding areas using a contact cleaner or a soft brush. This removes dirt, grime, and corrosion, ensuring proper electrical contact.
- Proper Wiring:Ensure all wiring connected to the relays is properly routed and secured to prevent chafing or damage. Use wire loom or protective sleeves to protect wires from abrasion and moisture.
- Moisture Protection:Protect the relays from moisture by sealing them with a waterproof sealant or using a relay box with a protective cover. This prevents corrosion and extends the relay’s lifespan.
- Replace Worn Relays:Replace relays that show signs of excessive wear or damage to prevent potential failures. Using high-quality, OEM-approved relays ensures proper functionality and reliability.
Alternative Resources
It’s essential to have access to multiple sources of information when troubleshooting your 2005 Yamaha Rhino 660’s relay system. This section explores valuable resources that can provide additional insights and support.
Manufacturer Website and Repair Manuals
Yamaha’s official website offers a wealth of information for their vehicles, including the 2005 Rhino 660. You can access technical specifications, repair manuals, parts diagrams, and service bulletins directly from the manufacturer. These resources provide the most accurate and up-to-date information regarding your vehicle.
- Visit the Yamaha website and navigate to the “Support” or “Owners” section.
- Search for your specific model, the 2005 Rhino 660, and browse the available resources.
- Download the relevant repair manual for your model year, which contains detailed diagrams and troubleshooting steps.
Online Forums and Communities
Engaging with online forums and communities dedicated to the Yamaha Rhino 660 can be a valuable source of support and knowledge. These platforms offer a space for owners, enthusiasts, and technicians to share experiences, troubleshoot issues, and exchange information.
- Search for Yamaha Rhino 660 forums or communities on popular platforms like Reddit, Facebook, or specialized automotive forums.
- Look for forums that have active members, a positive reputation, and a focus on technical discussions.
- Before posting, read the forum rules and guidelines to ensure your contributions are appropriate.
Conclusion

The Yamaha Rhino 660 relay diagram is a critical tool for anyone who wants to understand how the vehicle’s electrical system works. By understanding the diagram, you can quickly identify and troubleshoot problems, saving yourself time and money.Understanding the relay diagram allows you to pinpoint the root cause of electrical issues, preventing costly repairs and ensuring the longevity of your Rhino.
This is especially important for off-road vehicles, which are subjected to harsh conditions and frequent use.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance of your Rhino’s electrical system is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. By inspecting and cleaning the relays, you can prevent potential problems and ensure the smooth operation of your vehicle.
Expert Answers
Where can I find a free copy of the 2005 Yamaha Rhino 660 relay diagram?
You can often find free relay diagrams online, but make sure they’re specifically for your 2005 Rhino 660 model. Reputable sources include Yamaha’s official website, online repair manuals, and forums dedicated to Yamaha Rhino owners.
What is the most common relay issue in a 2005 Yamaha Rhino 660?
The starter relay is a common culprit for problems. It can get stuck, preventing the starter motor from engaging. You’ll notice this as a clicking sound when you try to start the engine.
Can I replace a relay myself?
Absolutely! Replacing a relay is a relatively simple procedure. Just make sure to disconnect the battery before working on any electrical components. Follow the steps in your relay diagram carefully, and you’ll be good to go.