The 2001 Ford F150 fuse box diagram is your roadmap to understanding and navigating the intricate network of electrical components that power your truck. It’s a crucial tool for anyone seeking to troubleshoot electrical issues, from a flickering dashboard light to a malfunctioning power window.
This diagram, a visual representation of your vehicle’s electrical system, reveals the intricate web of fuses, relays, and circuits that ensure everything runs smoothly. Each fuse and relay plays a vital role in protecting your vehicle’s electrical system from overloads and damage, ensuring that your truck remains reliable and safe.
Understanding this diagram empowers you to diagnose and resolve electrical problems with confidence, allowing you to keep your F150 on the road.
The fuse box diagram acts as a visual guide to your truck’s electrical system, helping you identify and troubleshoot issues. It maps out the connections between various electrical components, providing a clear picture of how they are interconnected. With this diagram, you can easily locate specific fuses and relays, understand their functions, and determine if they are the root cause of any electrical problems.
Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a novice DIY enthusiast, this diagram serves as a valuable resource for understanding the intricacies of your 2001 Ford F150’s electrical system.
Troubleshooting Electrical Problems

The fuse box diagram for a 2001 Ford F150 is a crucial tool for diagnosing and resolving electrical issues. This diagram provides a visual representation of the fuse box layout, indicating the location of each fuse and its corresponding circuit.
By understanding this diagram, you can efficiently identify and address common electrical problems.
Identifying Electrical Problems
The fuse box diagram helps pinpoint the source of electrical issues by showing the relationship between fuses and specific electrical components. For example, if the headlights are not working, the diagram will indicate the fuse responsible for powering the headlights.
Common electrical problems that can be diagnosed using the fuse box diagram include:
- Headlights not working: A blown fuse in the headlight circuit can cause the headlights to malfunction.
- Power windows not operating: A blown fuse in the power window circuit can prevent the windows from moving up or down.
- Radio or CD player not working: A blown fuse in the radio circuit can disable the audio system.
- Turn signals not functioning: A blown fuse in the turn signal circuit can prevent the turn signals from flashing.
- Instrument cluster not displaying: A blown fuse in the instrument cluster circuit can cause the gauges and warning lights to stop working.
- Power outlets not providing power: A blown fuse in the power outlet circuit can prevent the outlets from supplying electricity.
Checking Fuses
Checking fuses for blown or damaged elements is a straightforward process:
- Locate the fuse box: The fuse box is typically located under the dashboard or in the engine compartment. Refer to the owner’s manual or the fuse box diagram for the exact location.
- Identify the fuse: Use the fuse box diagram to find the fuse corresponding to the malfunctioning electrical component.
- Inspect the fuse: Carefully examine the fuse for any signs of damage, such as a broken filament or a melted wire. A blown fuse will have a broken filament, appearing as a gap or a clear space within the fuse.
Replacing a Blown Fuse
Replacing a blown fuse with a suitable replacement is essential to restore the electrical system’s functionality:
- Turn off the ignition: Ensure the vehicle’s ignition is switched off to prevent electrical shock or damage to the system.
- Remove the blown fuse: Use fuse puller tool or pliers to carefully remove the blown fuse from its socket.
- Insert the new fuse: Insert the new fuse of the same amperage rating into the empty socket. The amperage rating is usually printed on the fuse itself. Ensure the fuse is properly seated in the socket.
- Test the electrical component: Turn on the ignition and check if the electrical component is now working. If the problem persists, there might be a more serious issue requiring further investigation.
Important Note:Always use fuses with the correct amperage rating. Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating can lead to overheating and damage to electrical components.
Understanding Relay Functionality
Relays are electromechanical switches that control electrical circuits by using a small electrical current to activate a mechanical switch. They are essential components in the electrical system of a 2001 Ford F150, playing a vital role in controlling various functions, including headlights, power windows, and fuel pumps.Relays act as intermediaries between the electrical control unit (ECU) and the load, allowing the ECU to control high-power circuits without the risk of damage or overheating.
They essentially isolate the ECU from the high current loads, protecting it from potential damage.
Types of Relays
Relays in the 2001 Ford F150 are typically categorized based on their functionality and application. The most common types include:
- Normally Open (NO) Relays: These relays are open in their default state, allowing current to flow through the circuit only when the relay is activated. When activated, the relay closes the circuit, completing the path for current to flow. NO relays are commonly used for controlling functions such as headlights, power windows, and windshield wipers.
- Normally Closed (NC) Relays: These relays are closed in their default state, blocking current flow. When activated, the relay opens the circuit, interrupting the current flow. NC relays are often used for safety-related functions, such as disabling the fuel pump in case of a collision.
- Single-Pole, Single-Throw (SPST) Relays: These relays have one input and one output. When activated, the relay connects the input to the output, allowing current to flow. SPST relays are simple and commonly used for basic circuit control.
- Single-Pole, Double-Throw (SPDT) Relays: These relays have one input and two outputs. When activated, the relay connects the input to one of the outputs, while disconnecting it from the other output. SPDT relays offer more versatility, allowing for switching between two different circuits.
Troubleshooting Faulty Relays
Identifying a faulty relay is crucial for resolving electrical problems in the 2001 Ford F
150. Here’s a breakdown of the troubleshooting process
- Visual Inspection: Begin by visually inspecting the relay for signs of damage, such as burnt contacts, corrosion, or loose connections. If any damage is evident, replace the relay.
- Continuity Testing: Use a multimeter to test the continuity of the relay’s contacts. With the relay in its default state, there should be no continuity between the input and output terminals for a NO relay, and continuity for an NC relay.
Activate the relay and check for continuity again. If the continuity does not change as expected, the relay is likely faulty.
- Relay Click Test: Listen for a distinct clicking sound when the relay is activated. If the clicking sound is absent or irregular, the relay may be malfunctioning. This test can be performed by applying power to the relay’s coil and observing the mechanical movement.
- Relay Swap Test: If the previous tests suggest a faulty relay, try swapping it with a known good relay from another circuit. If the problem shifts to the other circuit, the original relay was indeed faulty. This method helps isolate the faulty component.
Safety Precautions
Working with electrical systems, including the fuse box of your 2001 Ford F150, requires a high level of caution. Improper handling of fuses and electrical components can lead to serious injuries, including electric shock, burns, and fire hazards. It is crucial to prioritize safety throughout the process.
Safety Tips for Working on the Fuse Box
Prior to working on the fuse box or any electrical component, it is essential to understand the potential risks and implement appropriate safety measures. Here are some critical tips to follow:
- Always disconnect the battery’s negative terminal before working on any electrical component. This will prevent the flow of electricity and reduce the risk of electric shock.
- Wear appropriate safety gear, including insulated gloves, safety glasses, and closed-toe shoes. This will provide protection from electrical hazards and potential contact with sharp objects.
- Never work on electrical components while they are energized. Ensure the ignition is off and all electrical accessories are turned off before starting any work.
- Avoid touching any exposed wires or metal parts that may be carrying electricity.
- Always use the correct fuse for the circuit you are working on. Using a fuse with an incorrect amperage rating can lead to overheating and fire hazards.
- Never attempt to repair a damaged fuse. Replace it with a new fuse of the correct amperage rating.
- If you are unsure about any aspect of working on the fuse box or electrical system, consult a qualified automotive technician.
Additional Resources and Information
This section provides valuable resources and information to enhance your understanding of the 2001 Ford F150 fuse box diagram and electrical troubleshooting. These resources can help you locate additional information, identify specialized tools, and understand the benefits of professional assistance.
Online Resources
Accessing reliable online resources can significantly aid your troubleshooting efforts.
- Owner’s Manual:The owner’s manual provides a comprehensive guide to your vehicle, including detailed information about the fuse box layout, fuse ratings, and electrical system components. You can often find a digital copy of your owner’s manual on the Ford website or through third-party resources.
- Repair Guides:Several online platforms offer detailed repair guides and technical information for various vehicle models, including the 2001 Ford F150. These guides can provide step-by-step instructions, diagrams, and troubleshooting tips for electrical problems.
- Online Forums:Engaging with online forums dedicated to Ford F150 owners can provide valuable insights and troubleshooting tips from experienced individuals. You can search for specific electrical issues or post questions to receive guidance from the community.
Specialized Tools and Equipment
Specialized tools can significantly improve your electrical troubleshooting process.
- Digital Multimeter:A digital multimeter (DMM) is essential for measuring voltage, current, and resistance. This tool helps identify electrical faults, check circuit continuity, and diagnose component failures.
- Test Light:A test light is a simple tool that uses a bulb to indicate the presence of an electrical circuit. It is helpful for checking fuse continuity and verifying power supply to components.
- Wire Stripper:A wire stripper is used to remove insulation from electrical wires, allowing you to connect test leads or make repairs.
- Crimping Tool:A crimping tool is used to secure electrical connectors and ensure a reliable connection.
Consulting a Qualified Automotive Technician
While you can troubleshoot many electrical problems independently, complex issues often require the expertise of a qualified automotive technician.
- Advanced Diagnostics:Automotive technicians have access to specialized diagnostic tools and equipment that can pinpoint electrical problems with greater accuracy. These tools can read fault codes, monitor electrical signals, and perform advanced tests.
- Safety and Expertise:Electrical systems in vehicles can be dangerous if handled improperly. Consulting a technician ensures the work is done safely and effectively, minimizing the risk of damage or injury.
- Specialized Knowledge:Automotive technicians have extensive knowledge of vehicle electrical systems, including wiring diagrams, component specifications, and troubleshooting procedures. This expertise allows them to identify and resolve complex electrical issues efficiently.
Fuse Box Diagram Variations
The 2001 Ford F150 is a popular truck model, and like many vehicles, it comes in different trims and configurations. These variations can affect the location and layout of the fuse box, so it’s crucial to understand the differences to ensure you’re working with the correct fuse box diagram.The fuse box diagram is an essential tool for troubleshooting electrical problems.
Finding the right fuse for a specific component in your 2001 Ford F150 can be a real headache, especially if you’re unfamiliar with the layout of the fuse box. Thankfully, there are plenty of resources available online to help you navigate this process.
If you’re looking for a similar diagram for a different vehicle, you can find a 2007 FJ Cruiser fuse box diagram PDF online as well. Once you’ve got the diagram for your 2001 Ford F150, you’ll be able to quickly identify the fuse you need and replace it with a new one, restoring functionality to your vehicle.
It provides a visual representation of the fuses and relays, along with their corresponding circuits. This information is vital for identifying blown fuses, replacing them, and diagnosing electrical issues.
Identifying the Correct Fuse Box Diagram
To determine the specific fuse box diagram for your 2001 Ford F150, you need to consider the following factors:
- Model Year:While the 2001 Ford F150 is the focus, there may be slight variations within the model year. Ensure you are using a diagram specifically for the 2001 model year.
- Trim Level:Different trim levels, such as XL, XLT, or King Ranch, can have different electrical configurations. Look for a diagram specific to your truck’s trim level.
- Engine Type:The engine powering your F150 can also influence the fuse box layout. Consult a diagram that corresponds to your specific engine (e.g., 4.6L V8, 5.4L V8, etc.).
- Options and Accessories:Certain factory-installed options, such as power seats, sunroof, or towing packages, can impact the fuse box. Check for diagrams that cater to these features.
Fuse Box Layout Variations
The fuse box layout can vary depending on the factors mentioned above. Here is a table comparing the differences in fuse box layouts:
| Feature | 2001 F150 XL (4.6L V8) | 2001 F150 XLT (5.4L V8) | 2001 F150 King Ranch (5.4L V8, Towing Package) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fuse Box Location | Under the hood, driver’s side | Under the hood, driver’s side | Under the hood, driver’s side |
| Fuse Box Size | Medium | Large | Extra Large |
| Number of Fuses | 25 | 35 | 45 |
| Relay Location | Separate box near fuse box | Integrated with fuse box | Integrated with fuse box |
Note:This table is a simplified example. Actual fuse box layouts may differ depending on specific options and configurations. It’s always best to consult the owner’s manual or a reputable online resource for the most accurate information.
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques

Delving deeper into the intricacies of electrical diagnostics, this section explores advanced techniques and tools commonly employed by experienced technicians.
Using a Multimeter for Comprehensive Diagnosis
A multimeter is an indispensable tool for electrical troubleshooting. This versatile device allows you to measure voltage, current, and resistance, providing valuable insights into the health of your electrical system.
Voltage measurements are crucial for assessing the flow of electrical energy.
Current measurements help determine the amount of electrical charge flowing through a circuit.
Resistance measurements reveal the opposition to electrical current flow, often indicating a faulty component.
- Voltage Measurement:Connect the multimeter’s probes to the appropriate points in the circuit to measure voltage. For instance, testing the voltage across a fuse can determine if it’s blown.
- Current Measurement:To measure current, you must break the circuit and insert the multimeter in series. This involves temporarily disconnecting a wire and connecting the multimeter in its place.
- Resistance Measurement:Disconnect the component from the circuit and measure its resistance. This helps determine if the component is functioning correctly.
Identifying Intermittent Electrical Faults
Intermittent electrical faults are notoriously difficult to diagnose. They occur sporadically, making it challenging to pinpoint the exact cause.
- Loose Connections:Loose connections can cause intermittent electrical problems. The connection might be good enough to work sometimes but not consistently.
- Corrosion:Corrosion on electrical terminals can lead to intermittent resistance, causing the electrical signal to be interrupted.
- Worn Wiring:Over time, wiring can become frayed or worn, leading to intermittent connections.
- Temperature Sensitivity:Some electrical components are sensitive to temperature fluctuations. A component might work fine at room temperature but malfunction when exposed to extreme heat or cold.
- Vibration:Vibrations can cause loose connections or worn wiring to intermittently disconnect, leading to electrical problems.
Common Fuse Box Issues: 2001 Ford F150 Fuse Box Diagram
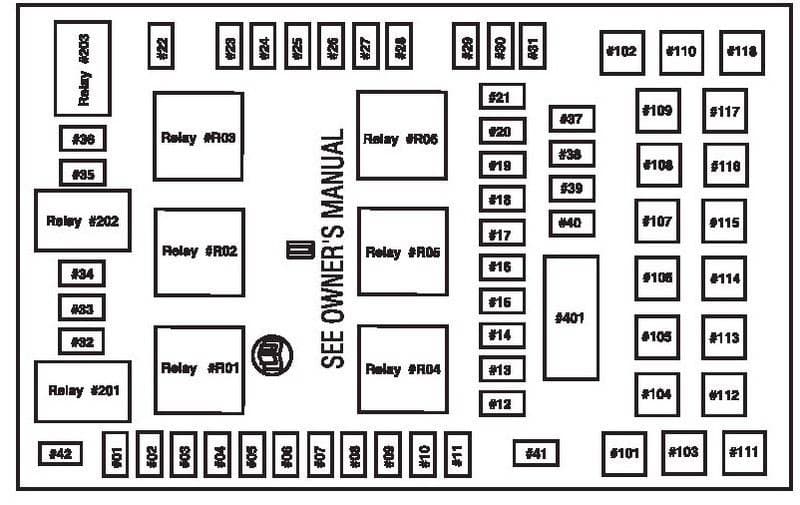
The fuse box in your 2001 Ford F150 is a crucial component of your vehicle’s electrical system. Over time, various issues can arise, impacting the functionality of your vehicle’s electrical components. Understanding these common problems and their causes can help you prevent them or resolve them quickly and efficiently.
Corrosion
Corrosion is a common problem in fuse boxes, particularly in humid or salty environments. It can occur when moisture penetrates the fuse box, causing the metal contacts to corrode. This corrosion can lead to poor electrical connections, resulting in blown fuses, intermittent electrical problems, or even complete electrical failure.
Preventing Corrosion
- Keep the fuse box clean and dry. Regularly inspect the fuse box for any signs of moisture or corrosion. Use a dry cloth to wipe away any dust or debris.
- Apply a corrosion inhibitor to the metal contacts. This can help prevent corrosion from forming in the first place.
- Avoid driving through deep water. If you must drive through water, do so slowly and avoid submerging the fuse box.
Resolving Corrosion
- Clean the corroded contacts. Use a small wire brush or a piece of sandpaper to clean the corroded contacts. Be careful not to damage the contacts.
- Apply a dielectric grease to the contacts. This will help prevent future corrosion.
- Replace any severely corroded fuses or fuse holders.
Overheating, 2001 ford f150 fuse box diagram
Overheating is another common issue that can affect the fuse box. This can occur when too much current flows through the fuse box, causing the wires and components to overheat. Overheating can damage the fuse box and its components, leading to electrical problems.
Preventing Overheating
- Use the correct fuses. Always use fuses with the correct amperage rating for the circuit they are protecting. Using a fuse with too low of an amperage rating can cause it to blow prematurely, while using a fuse with too high of an amperage rating can allow too much current to flow, leading to overheating.
- Avoid overloading circuits. Do not connect too many electrical devices to a single circuit. This can overload the circuit and cause overheating.
Resolving Overheating
- Identify and address the cause of the overheating. This may involve checking for faulty wiring, overloaded circuits, or other electrical problems.
- Replace any damaged or melted fuses or fuse holders.
Faulty Wiring
Faulty wiring is a common cause of fuse box issues. This can occur due to damage to the wires, loose connections, or corrosion. Faulty wiring can lead to blown fuses, intermittent electrical problems, or even electrical fires.
Preventing Faulty Wiring
- Inspect the wiring regularly. Look for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires, loose connections, or corrosion.
- Use high-quality wiring. Avoid using cheap or substandard wiring, as this can increase the risk of faulty wiring.
Resolving Faulty Wiring
- Repair or replace any damaged wiring.
- Tighten any loose connections.
- Clean any corroded connections.
FAQ Resource
Where is the fuse box located in a 2001 Ford F150?
The fuse box is typically located in the engine compartment, on the driver’s side, near the battery. However, there may be a second fuse box inside the vehicle, usually under the dashboard.
What are the different types of fuses found in the 2001 Ford F150 fuse box?
The most common types of fuses are blade fuses and ATO fuses. They are identified by their shape and size. The fuse box diagram will clearly indicate the type of fuse required for each circuit.
What is the difference between a fuse and a relay?
A fuse is a safety device that breaks a circuit when an overload occurs, protecting the electrical system from damage. A relay is an electrically controlled switch that allows a small electrical signal to control a larger electrical circuit.
Relays are often used to control high-power components, such as headlights or the starter motor.
How do I replace a blown fuse?
Always disconnect the battery before working on the fuse box. Locate the blown fuse using the diagram and carefully remove it. Replace it with a fuse of the same amperage rating. Never use a fuse with a higher amperage rating, as this could cause damage to the electrical system.