The 1996 Marquis Automatic AC Electrical Diagram is your roadmap to understanding the intricate workings of your car’s air conditioning system. This diagram is a vital tool for anyone who wants to troubleshoot, repair, or even upgrade their AC system.
It’s like a blueprint, showing you how all the components connect and interact, from the compressor to the blower motor. Think of it as your guide to keeping your ride cool and comfortable.
This document will take you step-by-step through the diagram, explaining each component, its function, and how it fits into the bigger picture. We’ll also cover common AC issues, how to troubleshoot them, and some helpful maintenance tips. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or just a curious car owner, this guide has something for you.
Introduction
The 1996 Marquis Automatic AC system is a complex and sophisticated system that uses a combination of electrical and mechanical components to regulate the temperature inside the vehicle. The system relies on a variety of sensors, actuators, and control modules to ensure optimal comfort for the occupants.
Understanding the electrical diagram is essential for diagnosing and troubleshooting issues related to the AC system.This document provides a detailed explanation of the electrical diagram for the 1996 Marquis Automatic AC system. It is intended for technicians, mechanics, and other individuals who need to understand the operation of the system and its components.
This document will provide a comprehensive guide to the electrical system of the 1996 Marquis Automatic AC, encompassing its functionality, components, and troubleshooting procedures.
Components of the 1996 Marquis Automatic AC System
The 1996 Marquis Automatic AC system consists of several key components, including:
- Compressor
- Condenser
- Evaporator
- Expansion valve
- Refrigerant lines
- Fan motor
- Temperature sensor
- Pressure sensor
- Control module
Electrical Diagram Overview
The electrical diagram provides a visual representation of the electrical connections and circuits within the 1996 Marquis Automatic AC system. It shows the flow of electricity from the battery to the various components, as well as the control signals that regulate the operation of the system.
The diagram is essential for understanding how the different components interact with each other and how they are controlled by the control module.
The electrical diagram is an invaluable tool for technicians and mechanics, enabling them to diagnose and troubleshoot issues related to the AC system.
Electrical System Components
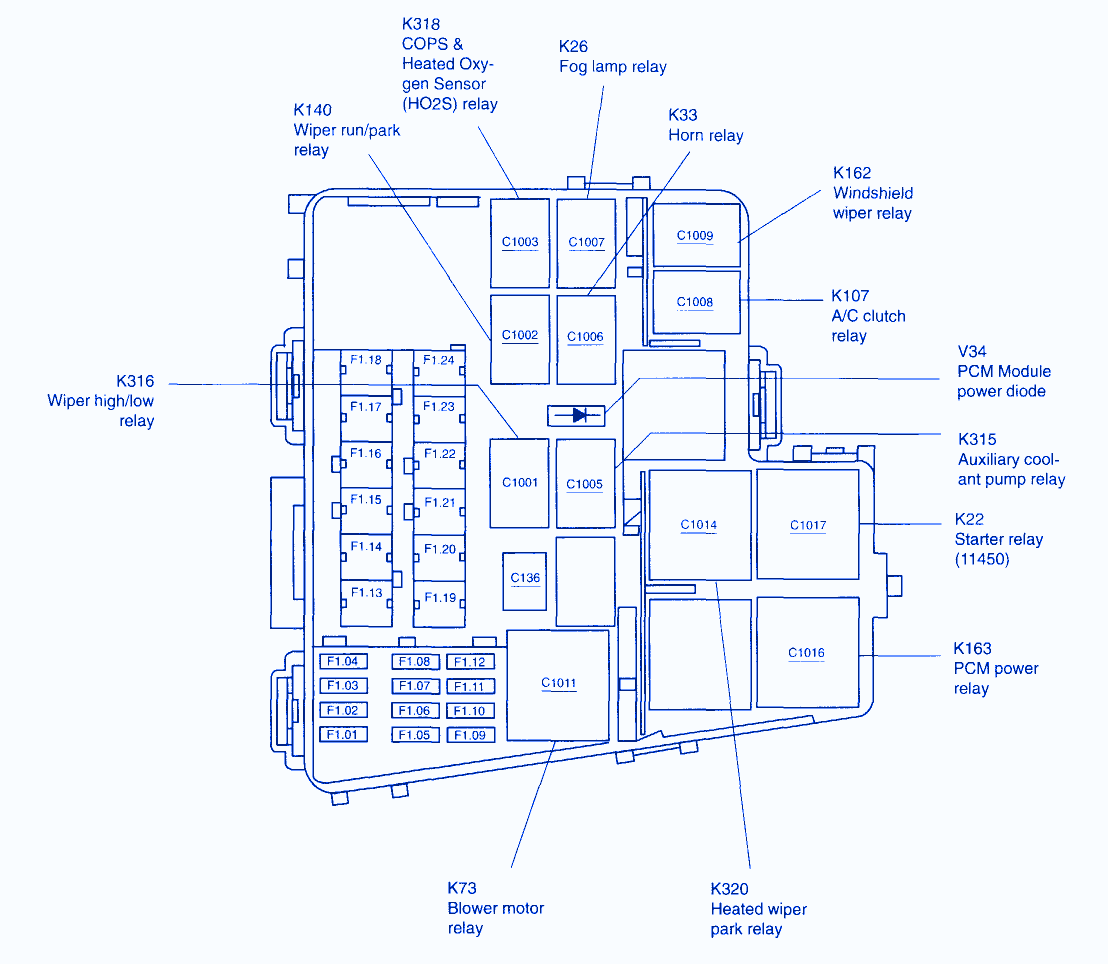
The 1996 Marquis AC system relies on a complex interplay of electrical components to regulate temperature and airflow within the vehicle. These components work in unison to deliver cool air to the cabin, ensuring passenger comfort.
Components of the 1996 Marquis AC System, 1996 marquis automatic ac electrical diagram
The following table Artikels the key components of the 1996 Marquis AC system, their functions, locations, and relevant diagram references:
| Component Name | Function | Location | Diagram Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compressor | Compresses refrigerant, increasing its pressure and temperature | Mounted on the engine | [Diagram reference, if applicable] |
| Condenser | Cools and condenses the high-pressure refrigerant into a liquid | Located in front of the radiator | [Diagram reference, if applicable] |
| Expansion Valve | Reduces the pressure of the liquid refrigerant, causing it to evaporate and absorb heat | Located near the evaporator | [Diagram reference, if applicable] |
| Evaporator | Absorbs heat from the cabin air, cooling it down | Located behind the dashboard | [Diagram reference, if applicable] |
| Receiver/Drier | Stores refrigerant and removes moisture from the system | Located near the condenser | [Diagram reference, if applicable] |
| Fan Motor | Circulates air over the condenser and evaporator | Located behind the condenser and evaporator | [Diagram reference, if applicable] |
| Thermostat | Senses cabin temperature and controls the AC system’s operation | Located on the dashboard | [Diagram reference, if applicable] |
| Pressure Switch | Monitors the pressure of the refrigerant system and shuts off the compressor if pressure is too low | Located near the compressor | [Diagram reference, if applicable] |
| Relay | Controls the flow of electricity to the compressor | Located near the compressor | [Diagram reference, if applicable] |
| Wiring Harness | Connects all the electrical components of the AC system | Throughout the vehicle | [Diagram reference, if applicable] |
Electrical Diagram Interpretation
The electrical diagram for the 1996 Marquis AC system provides a visual representation of the components, wiring, and connections involved in the operation of the air conditioning system. It is an essential tool for troubleshooting and understanding the electrical flow within the system.The diagram employs standardized symbols to represent various components and their interconnections.
These symbols are universally recognized and simplify the understanding of complex electrical systems.
Symbol Interpretation and Component Relationship
The electrical diagram utilizes symbols to represent different components. These symbols are standardized and easily recognizable, enabling technicians to quickly identify components and their functions. Each symbol corresponds to a specific component, allowing for a clear visual representation of the electrical system’s layout.
For instance, a circle with a “+” inside might represent a positive terminal, while a circle with a “-” inside might represent a negative terminal. A wavy line might indicate a wire, while a rectangle with a label might represent a fuse or relay.The relationships between components are illustrated by the connections between symbols on the diagram.
Lines connecting symbols represent the electrical path, indicating the flow of current through the system. By following these lines, technicians can trace the path of electricity from the power source to the various components and actuators.
Tracing Electrical Flow
The electrical diagram serves as a roadmap for tracing the flow of electricity through the AC system. By following the lines connecting symbols, technicians can understand how power is distributed and how components interact.For example, tracing the path of electricity from the battery to the AC compressor, technicians can identify the relay, fuse, and wiring involved in this circuit.
This process allows for the identification of potential issues, such as a blown fuse or a faulty relay, which could be preventing the compressor from receiving power.The diagram provides a comprehensive overview of the electrical connections within the system, facilitating the diagnosis and repair of electrical problems.
Common AC System Issues: 1996 Marquis Automatic Ac Electrical Diagram
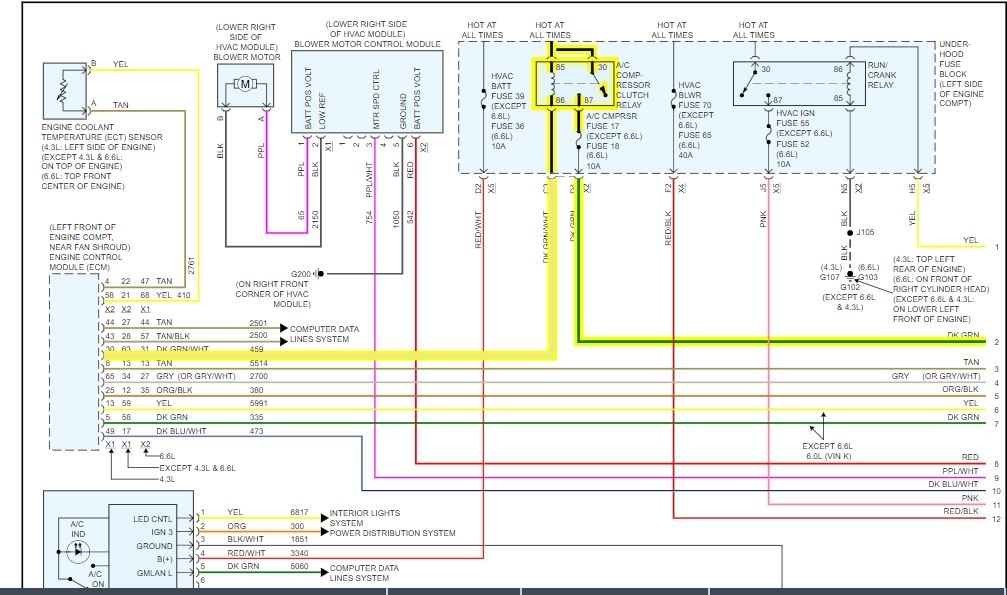
The 1996 Marquis AC system, like any other automotive AC system, is susceptible to various electrical issues that can hinder its performance. These issues can stem from faulty components, wiring problems, or even environmental factors. Understanding these common issues, their potential causes, and troubleshooting steps is crucial for diagnosing and resolving AC problems effectively.
Component Failures
Component failures are a common source of AC problems. Here’s a list of common components that can fail and their associated symptoms:
- AC Compressor:The AC compressor is the heart of the system, responsible for compressing refrigerant. If it fails, the AC will not blow cold air. Symptoms of a failing compressor include a loud clicking or grinding noise, a lack of cold air, and a refrigerant leak.
- Condenser:The condenser is responsible for dissipating heat from the refrigerant. If it fails, the AC will not cool effectively. Symptoms of a failing condenser include a lack of cold air, a refrigerant leak, and a clogged condenser.
- Evaporator:The evaporator is responsible for absorbing heat from the air inside the car. If it fails, the AC will not cool effectively. Symptoms of a failing evaporator include a lack of cold air, a refrigerant leak, and a frozen evaporator.
- Expansion Valve:The expansion valve controls the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator. If it fails, the AC will not cool effectively. Symptoms of a failing expansion valve include a lack of cold air, a refrigerant leak, and a frozen evaporator.
- AC Clutch:The AC clutch engages and disengages the compressor. If it fails, the AC will not turn on. Symptoms of a failing AC clutch include a lack of cold air, a clicking noise when the AC is turned on, and a slipping clutch.
- Pressure Switch:The pressure switch monitors the pressure in the AC system. If it fails, the AC may not turn on. Symptoms of a failing pressure switch include a lack of cold air, a blinking AC light, and a compressor that doesn’t cycle on.
- Temperature Sensor:The temperature sensor monitors the temperature of the air inside the car. If it fails, the AC may not cool effectively. Symptoms of a failing temperature sensor include a lack of cold air, an AC that blows too cold, and an AC that blows too hot.
- Fan Motor:The fan motor circulates air through the AC system. If it fails, the AC will not cool effectively. Symptoms of a failing fan motor include a lack of cold air, a noisy fan, and a fan that doesn’t spin.
- Fan Relay:The fan relay controls the fan motor. If it fails, the fan motor may not turn on. Symptoms of a failing fan relay include a lack of cold air, a noisy fan, and a fan that doesn’t spin.
- Thermostat:The thermostat controls the temperature of the air inside the car. If it fails, the AC may not cool effectively. Symptoms of a failing thermostat include a lack of cold air, an AC that blows too cold, and an AC that blows too hot.
Electrical Wiring Issues
Wiring problems can cause a range of AC system malfunctions. These issues are often difficult to diagnose, requiring a thorough inspection of the wiring harness.
- Open Circuits:An open circuit occurs when a wire is broken or disconnected. This can prevent power from reaching the AC system, resulting in a lack of cold air. Troubleshooting an open circuit involves checking the continuity of the wiring using a multimeter.
- Short Circuits:A short circuit occurs when two wires touch, creating an unintended path for electricity to flow. This can cause the AC system to overheat or even fail completely. Troubleshooting a short circuit involves checking the wiring for any signs of damage or chafing, and using a multimeter to measure the resistance of the wiring.
- Loose Connections:Loose connections can prevent power from flowing to the AC system, resulting in a lack of cold air. Troubleshooting loose connections involves checking all the connectors in the AC system, ensuring they are securely connected.
- Corrosion:Corrosion can damage wiring, causing it to fail. This can prevent power from reaching the AC system, resulting in a lack of cold air. Troubleshooting corrosion involves checking the wiring for any signs of corrosion and cleaning or replacing any corroded wiring.
Refrigerant Leaks
Refrigerant leaks can cause the AC system to lose its cooling capacity. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Damaged Components:Damaged components, such as the condenser, evaporator, or expansion valve, can leak refrigerant. Troubleshooting a refrigerant leak involves inspecting the AC system for any signs of damage and using a leak detector to identify the source of the leak.
- Loose Connections:Loose connections in the AC system can cause refrigerant to leak. Troubleshooting loose connections involves checking all the connections in the AC system, ensuring they are securely connected.
- Corrosion:Corrosion can damage the AC system, causing refrigerant to leak. Troubleshooting corrosion involves checking the AC system for any signs of corrosion and replacing any corroded components.
System Operation and Functionality
The 1996 Marquis’s automatic AC system relies on a complex interplay of electrical components to regulate the temperature inside the vehicle. When the AC system is activated, a series of events transpire, culminating in the delivery of cool air into the cabin.
Refrigerant Flow Control
The electrical system plays a crucial role in controlling the flow of refrigerant, the substance responsible for heat transfer. The refrigerant cycle involves four primary stages:
- Compressor:The compressor, driven by an electric motor, compresses the refrigerant, raising its temperature and pressure.
- Condenser:The hot, high-pressure refrigerant flows through the condenser, typically located in front of the radiator. The condenser dissipates heat into the surrounding air, cooling the refrigerant and converting it into a liquid state.
- Expansion Valve:The liquid refrigerant then passes through the expansion valve, which reduces the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant.
- Evaporator:The low-pressure, cold refrigerant flows through the evaporator, a coil located inside the vehicle’s cabin. The refrigerant absorbs heat from the air inside the cabin, cooling it down.
The electrical system controls the compressor’s operation, regulating the flow of refrigerant and the overall cooling capacity of the system.
Airflow Control
The AC system also controls the flow of air throughout the cabin. The blower motor, powered by the electrical system, circulates air over the evaporator, drawing in air from outside the vehicle and delivering cool air to the cabin.
Sensors and Actuators
Sensors and actuators are vital components that monitor and regulate the AC system’s performance.
- Temperature Sensor:The temperature sensor, located inside the cabin, measures the air temperature and sends a signal to the control unit.
- Pressure Sensor:The pressure sensor monitors the refrigerant pressure in the system, providing feedback to the control unit.
- Control Unit:The control unit receives signals from the sensors and actuates various components, such as the compressor clutch, expansion valve, and blower motor, to maintain the desired cabin temperature.
These sensors and actuators ensure that the AC system operates efficiently and effectively, maintaining a comfortable cabin temperature.
Safety Precautions
Working on the electrical system of a 1996 Marquis, including the AC system, requires a high degree of caution and adherence to safety protocols to prevent potential hazards. The risks associated with working on electrical components are significant, and proper handling procedures are crucial to ensure personal safety.
Electrical System Safety
The electrical system of a vehicle, including the AC system, carries high voltage and can deliver a lethal electric shock. The risks associated with working on electrical components are substantial, and proper handling procedures are critical to ensure personal safety.
- Always disconnect the battery’s negative terminal before working on any electrical component. This disconnects the electrical circuit and prevents the flow of electricity, minimizing the risk of electric shock.
- Use insulated tools and equipment whenever working on electrical components. Insulated tools provide a barrier between you and the electrical current, reducing the risk of shock.
- Avoid contact with exposed wires or electrical terminals. Exposed wires or terminals can carry live electricity, posing a significant shock hazard.
- Never work on electrical components when the engine is running. The engine’s electrical system is live and can deliver a lethal shock.
- Be aware of the location of high-voltage components, such as the alternator, starter, and ignition system. These components carry high voltage and should be handled with extreme caution.
- Use a voltage tester to confirm that a circuit is de-energized before working on it. A voltage tester provides a visual indication of the presence of electricity, allowing you to avoid contact with live wires.
- Always wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from flying debris or electrical sparks.
- Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid exposure to potentially hazardous fumes.
- If you are unsure about any aspect of electrical work, consult a qualified technician. Attempting repairs without proper knowledge or experience can be dangerous and lead to further damage to the vehicle.
Handling and Disconnecting Electrical Components
Proper handling and disconnection of electrical components are crucial for safety and preventing damage to the vehicle’s electrical system.
- When disconnecting electrical connectors, always pull on the connector itself, not on the wires. Pulling on the wires can damage the connector or the wires, leading to electrical problems.
- Before disconnecting any electrical connector, visually inspect it for signs of damage, such as corrosion, loose terminals, or broken wires. If any damage is present, repair or replace the connector before disconnecting it.
- When connecting electrical connectors, ensure that they are securely seated and make proper contact. Loose connections can cause electrical problems and potentially lead to a fire.
- Use a wire crimping tool to ensure proper connections when working with wires. A crimping tool ensures a secure and reliable connection, preventing loose wires and potential electrical problems.
- Use a wire stripper to remove insulation from wires before connecting them. A wire stripper ensures that the wire is properly exposed for a secure connection.
- Always use the correct type of fuse or circuit breaker for the specific electrical circuit. Using the wrong fuse or circuit breaker can lead to overheating, damage, or a fire.
- Use a multimeter to check the voltage and current of electrical circuits. A multimeter can help identify problems with the electrical system, such as a short circuit or a blown fuse.
- Always use a ground strap when working on electrical components. A ground strap provides a safe path for electricity to flow to the ground, reducing the risk of electric shock.
Maintenance and Repair

Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of your 1996 Marquis AC system. By adhering to a routine maintenance schedule, you can prevent costly repairs and ensure a comfortable driving experience. This section will discuss essential maintenance procedures and common repair methods for electrical components in the AC system.
Routine Maintenance Procedures
Routine maintenance procedures help to prevent minor issues from escalating into major problems. Here’s a list of essential tasks to perform regularly:
- Inspect the AC System Components:Visually inspect the AC system components for any signs of wear, damage, or leaks. This includes the condenser, evaporator, compressor, hoses, belts, and refrigerant lines.
- Check the Refrigerant Level:Ensure the refrigerant level is adequate. Low refrigerant levels can significantly impact the AC system’s performance and efficiency.
- Inspect the Belts and Hoses:Regularly check the belts and hoses for cracks, fraying, or leaks. Replace any damaged components promptly.
- Clean the Condenser:The condenser, located at the front of the vehicle, can become clogged with debris, reducing its efficiency. Clean the condenser regularly using a garden hose and a soft brush.
- Replace the Cabin Air Filter:A clogged cabin air filter can restrict airflow and reduce the effectiveness of the AC system. Replace the cabin air filter every 12,000 to 15,000 miles or as recommended by the manufacturer.
Repair Procedures for Electrical Components
The electrical system plays a vital role in the AC system’s operation. Common repair procedures for electrical components include:
- Inspecting and Replacing Fuses and Relays:Fuses and relays protect electrical circuits from damage. If a fuse blows or a relay fails, it needs to be replaced. Use a fuse tester to verify if a fuse is blown and replace it with one of the same amperage.
- Troubleshooting Electrical Wiring:Inspect the wiring for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Use a multimeter to test the continuity of the wiring and ensure proper voltage is reaching the components.
- Repairing or Replacing the AC Control Module:The AC control module regulates the AC system’s operation. If the module malfunctions, it may need to be repaired or replaced.
- Diagnosing and Repairing the AC Compressor Clutch:The AC compressor clutch engages and disengages the compressor, allowing it to cycle on and off as needed. If the clutch fails to engage or disengage properly, it may need to be repaired or replaced.
Resources and Tools
To perform maintenance and repair on your 1996 Marquis AC system, you’ll need access to certain resources and tools:
- Service Manual:A service manual provides detailed information on the AC system, including wiring diagrams, specifications, and repair procedures.
- Diagnostic Scanner:A diagnostic scanner can read trouble codes from the AC system’s control module, helping to identify potential issues.
- Multimeter:A multimeter is essential for testing electrical components, including fuses, relays, and wiring.
- Refrigerant Gauge Set:A refrigerant gauge set is used to check the refrigerant level and pressure.
- Vacuum Pump:A vacuum pump is used to evacuate the AC system before charging it with refrigerant.
- Refrigerant Charging Kit:A refrigerant charging kit is used to add refrigerant to the AC system.
System Upgrades and Modifications
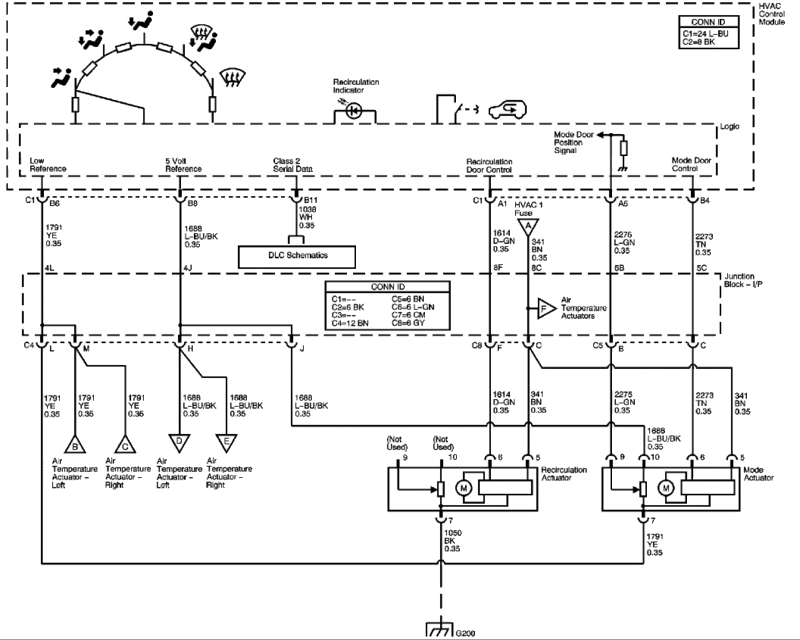
Upgrading or modifying the AC system in a 1996 Marquis can improve its performance, efficiency, and comfort. These changes can range from simple upgrades to more complex modifications, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks. Understanding these aspects is crucial for making informed decisions about enhancing your vehicle’s AC system.
AC System Refrigerant Upgrade
Upgrading the refrigerant used in the AC system is a common modification. Older vehicles like the 1996 Marquis may use R-12 refrigerant, which has been phased out due to its environmental impact. Replacing R-12 with a compatible alternative, such as R-134a, can improve the system’s efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
It is important to note that converting from R-12 to R-134a requires specific modifications to the system, including the addition of an orifice tube or expansion valve designed for R-134a, as well as the proper sealing of the system to prevent leaks.
AC System Compressor Upgrade
Replacing the original compressor with a newer, more efficient model can enhance the cooling capacity and overall performance of the AC system. Modern compressors often have improved lubrication and sealing mechanisms, leading to greater reliability and longevity.
When considering a compressor upgrade, it is essential to ensure compatibility with the existing system. Factors such as mounting points, belt size, and electrical connections must be carefully matched. It is recommended to consult with a qualified mechanic or AC specialist for proper installation.
AC System Condenser Upgrade
The condenser plays a vital role in cooling the refrigerant. Replacing a worn or damaged condenser with a larger or more efficient model can improve heat dissipation and enhance cooling performance.
Upgrading the condenser requires careful consideration of size and airflow. A larger condenser can improve cooling capacity but may require modifications to the vehicle’s front end to accommodate the increased size. Proper airflow is essential for effective heat dissipation, so any modifications must ensure sufficient air circulation.
Sorting out the 1996 Marquis automatic AC electrical diagram can be a right pain, especially if you’re not a whizz with circuits. It’s a bit like trying to decipher the wiring on a 90-113 boiler wiring diagram , but with more moving parts.
Thankfully, there are plenty of resources out there that can help you make sense of it all, so you can get that air conditioning working properly again.
Resources and Further Information
The 1996 Ford Marquis AC system is a complex and sophisticated system that requires a thorough understanding of its components, operation, and troubleshooting techniques. This document has provided a basic overview of the system, but further research and ongoing learning are encouraged to enhance your knowledge and skills.
Several resources can provide additional information and support for your AC system needs.
Technical Manuals
Technical manuals offer comprehensive information about the 1996 Marquis AC system, including wiring diagrams, component specifications, troubleshooting guides, and repair procedures.
- Factory Service Manual:The Ford factory service manual is the most comprehensive resource for information on the 1996 Marquis AC system. It includes detailed diagrams, specifications, and repair procedures for every component.
- Chilton Repair Manual:Chilton repair manuals provide a more user-friendly approach to AC system information, offering step-by-step instructions and troubleshooting guides.
- Haynes Repair Manual:Haynes repair manuals offer a balance of technical information and practical guidance, making them a good option for both professionals and DIY enthusiasts.
Online Forums
Online forums are valuable platforms for connecting with other Marquis owners and experts, seeking advice, sharing experiences, and troubleshooting common AC system issues.
- Ford Forums:Ford-specific forums, such as Ford-trucks.com, provide a dedicated space for Marquis owners to discuss AC system problems and solutions.
- Automotive Forums:General automotive forums, such as CarTalk.com and AutoZone.com, offer a wider range of perspectives and advice from experienced mechanics and enthusiasts.
Expert Resources
For more in-depth knowledge and specialized assistance, consider consulting with experts in the field.
- Certified Automotive Technicians:Certified technicians have the training and experience to diagnose and repair complex AC systems.
- AC Specialists:AC specialists have specialized knowledge and equipment for servicing and repairing AC systems.
Key Questions Answered
What does the “A” in “AC” stand for?
The “A” in “AC” stands for “air.” It’s short for “air conditioning,” which is the process of cooling and dehumidifying air.
Where can I find a copy of the 1996 Marquis AC Electrical Diagram?
You can often find a copy of the diagram online through automotive forums, repair manuals, or websites specializing in car parts.
What is the difference between an automatic and a manual AC system?
An automatic AC system has a thermostat that automatically adjusts the temperature based on your settings, while a manual system requires you to manually adjust the temperature controls.