1996 Marquis Automatic AC Electrical Diagram: Ever wondered how your car’s AC system works its magic? This diagram is your key to understanding the electrical flow that keeps you cool on those hot Makassar days. It’s like a map of the electrical pathways that power your AC system, and with a little know-how, you can decipher it to troubleshoot any issues.
Imagine you’re cruising down the road, and suddenly, the AC starts acting up. Knowing how to read this diagram can help you identify the culprit, whether it’s a faulty sensor, a blown fuse, or a wiring problem. This guide will walk you through the basics of AC system components, common electrical issues, and even some troubleshooting tips.
You’ll be a pro at keeping your ride cool in no time!
Introduction
The 1996 Lincoln Marquis is a full-size luxury sedan known for its comfort and spacious interior. Its automatic air conditioning system is a complex system that relies on various electrical components to function properly. Understanding the electrical diagram for this system is crucial for effective troubleshooting and maintenance.Electrical diagrams provide a visual representation of the electrical circuits within the vehicle’s AC system.
They show the connections between components, the flow of electricity, and the location of fuses and relays. By understanding the electrical diagram, technicians can diagnose problems efficiently, identify the root cause of malfunctions, and repair or replace faulty components.
The Importance of Electrical Diagrams
Electrical diagrams are essential tools for anyone working on the 1996 Marquis’s AC system. They provide valuable information that helps in:
- Identifying the location and function of each component: The diagram clearly illustrates the placement of each component within the system, enabling technicians to easily locate and access them during troubleshooting or repairs.
- Tracing the flow of electricity: The diagram maps the electrical pathways, revealing the connections between components and how electricity travels through the system. This information is crucial for diagnosing electrical problems and ensuring proper operation.
- Understanding the role of fuses and relays: Fuses and relays act as protective devices, safeguarding the electrical system from overloads and short circuits. The diagram shows the location of these devices and their corresponding circuits, aiding in identifying and addressing potential issues.
- Interpreting diagnostic codes: Modern vehicles use diagnostic codes to signal problems within the system. The electrical diagram helps interpret these codes, providing valuable insights into the nature of the malfunction and the specific component affected.
Components of the Automatic AC System
The 1996 Marquis automatic AC system is a complex network of components working together to regulate the temperature and airflow inside the vehicle. Understanding these components and their functions is crucial for diagnosing and repairing any issues that may arise.
Major Components of the Automatic AC System
The following table Artikels the major components of the 1996 Marquis automatic AC system, their descriptions, functions, and locations:
| Component Name | Description | Function | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compressor | A pump that compresses the refrigerant, increasing its pressure and temperature. | Circulates the refrigerant through the system, driving the cooling process. | Mounted on the engine, driven by a belt. |
| Condenser | A radiator-like component that dissipates heat from the refrigerant. | Cools the high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant, converting it from a gas to a liquid. | Located in front of the radiator. |
| Expansion Valve | A valve that regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator. | Reduces the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant, allowing it to absorb heat from the air. | Located near the evaporator. |
| Evaporator | A coil-like component that absorbs heat from the air. | Cools the air passing through it, providing cold air to the cabin. | Located behind the dashboard, near the blower motor. |
| Blower Motor | A motor that drives the fan, circulating air through the system. | Provides airflow through the evaporator and into the cabin. | Located behind the dashboard. |
| Thermostat | A sensor that monitors the temperature of the air inside the cabin. | Sends signals to the control unit to adjust the AC system’s operation based on the desired temperature. | Located in the cabin, typically near the dashboard. |
| Control Unit | An electronic module that receives signals from the thermostat and other sensors. | Controls the operation of the AC system, including the compressor, expansion valve, and blower motor. | Located under the dashboard. |
| Refrigerant | A chemical substance that circulates through the AC system. | Absorbs heat from the air and releases it to the condenser. | Flows through the entire AC system. |
| Receiver/Drier | A component that stores and filters the refrigerant. | Removes moisture and contaminants from the refrigerant, preventing system damage. | Located near the condenser. |
| Pressure Switch | A safety device that monitors the pressure of the refrigerant. | Shuts off the compressor if the pressure is too high or too low, protecting the system from damage. | Located near the compressor. |
Electrical Diagram Interpretation
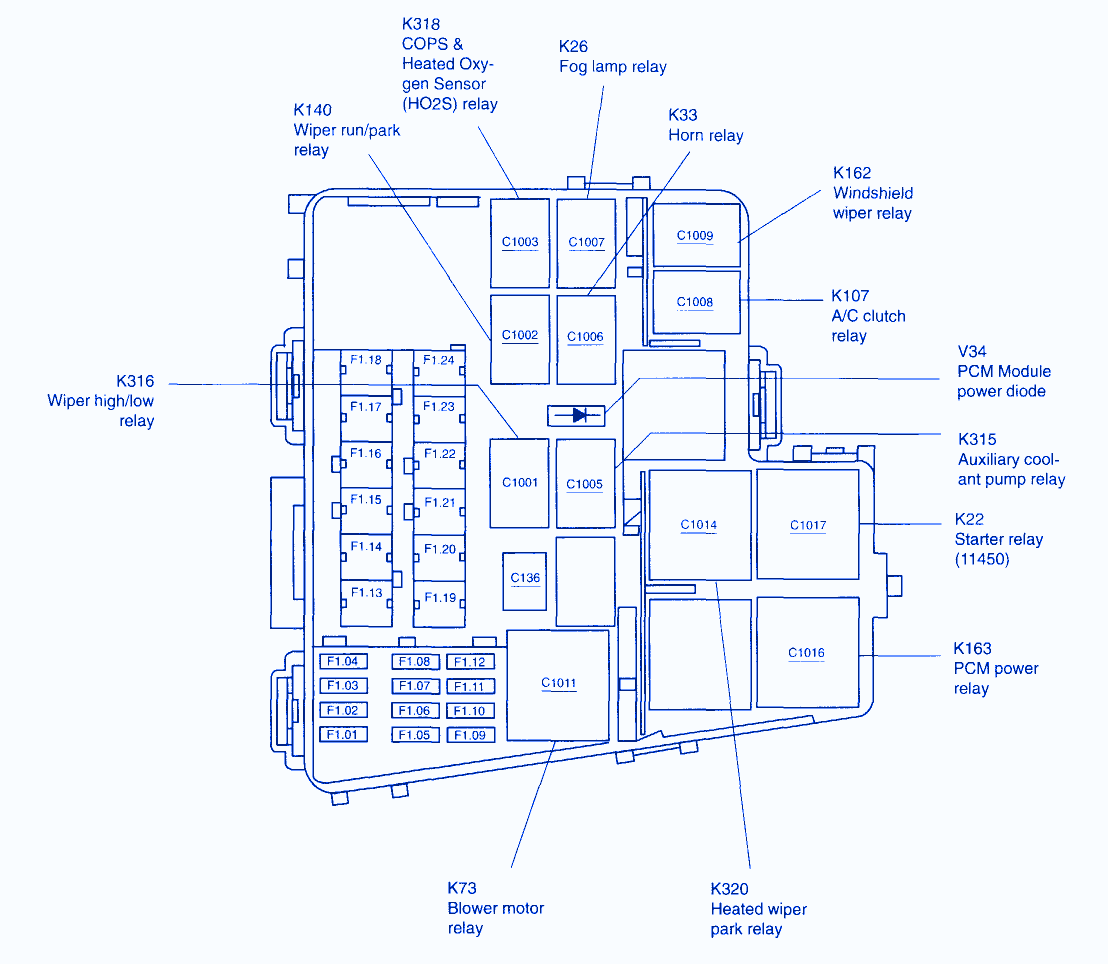
The electrical diagram for a 1996 Marquis automatic AC system provides a visual representation of the electrical components and their connections. Understanding the diagram is crucial for troubleshooting and diagnosing any issues with the AC system.
Symbol Interpretation
Electrical diagrams utilize standardized symbols to represent different components and their relationships. These symbols are essential for interpreting the diagram and understanding the flow of electricity.
- Wires:Solid lines represent wires, with different colors indicating different circuits.
- Resistors:A zig-zag line represents a resistor, which limits the flow of current.
- Capacitors:A parallel line with a gap represents a capacitor, which stores electrical energy.
- Switches:Different symbols are used to represent different types of switches, such as toggle switches, push-button switches, and relays.
- Relays:A rectangular box with internal contacts represents a relay, which uses a small current to control a larger current.
- Sensors:Symbols representing sensors vary depending on the type, such as temperature sensors, pressure sensors, and flow sensors.
- Motors:A circle with a curved arrow represents a motor, which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
- Ground:A triangular symbol represents a ground connection, which provides a path for current to flow to the earth.
Tracing the Flow of Electricity
The electrical diagram can be used to trace the flow of electricity through the AC system. Starting from the battery, follow the wires and components to understand how electricity powers the AC system. For example, tracing the path of electricity from the battery to the AC compressor can reveal potential points of failure.
- Battery:The battery provides the primary source of power for the AC system.
- Fuse:A fuse protects the circuit from overloads.
- Relay:A relay is activated by the AC control switch, allowing current to flow to the compressor.
- Compressor:The compressor uses electricity to compress refrigerant, driving the cooling process.
- Condenser:The condenser dissipates heat from the refrigerant.
- Expansion Valve:The expansion valve regulates the flow of refrigerant.
- Evaporator:The evaporator absorbs heat from the air inside the vehicle.
Interpreting Specific Sections
The electrical diagram can be broken down into specific sections to understand the functionality of different parts of the AC system.
- AC Control Switch:This section shows the wiring and components associated with the AC control switch, including the relay that activates the compressor.
- Compressor Circuit:This section shows the wiring and components that control the compressor, including the fuse, relay, and motor.
- Temperature Sensor Circuit:This section shows the wiring and components associated with the temperature sensor, which monitors the temperature of the air inside the vehicle.
Understanding the intricacies of a 1996 Marquis automatic AC electrical diagram can be a daunting task, especially when dealing with complex circuits and components. However, a similar approach can be applied when navigating the workings of a 98 Chevy S10 windshield nozzle diagram , where tracing the flow of fluid and electrical signals is crucial.
Both systems rely on a clear understanding of their respective components and their interactions to ensure proper functionality.
- Pressure Switch Circuit:This section shows the wiring and components associated with the pressure switch, which monitors the pressure of the refrigerant system.
Common Electrical Issues
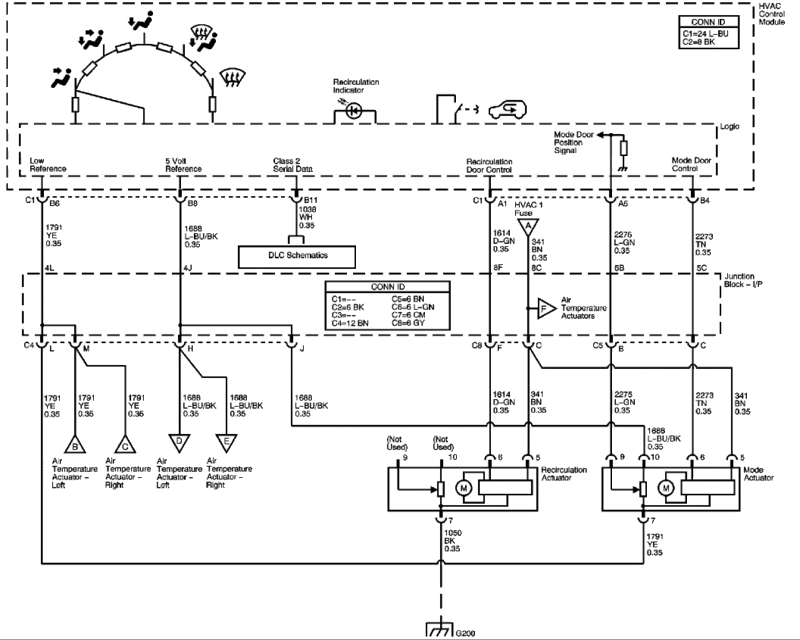
The 1996 Marquis automatic AC system, like any other electrical system, is susceptible to a range of electrical issues. These issues can cause various malfunctions, affecting the overall performance and comfort of the vehicle. Understanding the common electrical problems, their symptoms, and troubleshooting tips is essential for diagnosing and resolving these issues effectively.
Identifying Common Electrical Problems
Common electrical problems in the 1996 Marquis automatic AC system can manifest in various ways, impacting the system’s functionality. These issues often arise due to factors such as aging components, faulty wiring, or environmental conditions. Recognizing these problems and their symptoms is crucial for efficient troubleshooting.
- Faulty AC Compressor Clutch Relay: This relay controls the AC compressor clutch, enabling it to engage and disengage. A faulty relay can prevent the compressor from turning on, leading to a lack of cold air.
- Defective AC Compressor Clutch: The AC compressor clutch engages the compressor, allowing it to circulate refrigerant. A defective clutch can fail to engage, resulting in a lack of cold air.
- Blown Fuse: Fuses protect electrical circuits from overloads. A blown fuse in the AC system can interrupt power flow to specific components, causing malfunctions.
- Open or Short Circuit in Wiring: Damaged or corroded wiring can create open circuits, interrupting power flow, or short circuits, causing excessive current draw. These issues can affect various AC system components.
- Faulty AC Pressure Switch: This switch monitors the refrigerant pressure in the system. A faulty pressure switch can trigger incorrect signals, leading to compressor cycling issues or complete shutdown.
- Malfunctioning Temperature Sensor: The temperature sensor monitors the cabin temperature, sending signals to the control unit. A faulty sensor can provide inaccurate readings, resulting in inconsistent cooling.
- Defective Blower Motor: The blower motor circulates air through the vents. A faulty blower motor can fail to operate, resulting in a lack of airflow.
- Defective Blower Motor Resistor: The blower motor resistor controls the blower motor speed. A defective resistor can cause the blower motor to operate at a single speed or not at all.
Troubleshooting Common Electrical Issues
Troubleshooting electrical issues in the 1996 Marquis automatic AC system requires a systematic approach. By carefully examining the symptoms and using appropriate diagnostic tools, you can identify the root cause of the problem.
- Check for Blown Fuses: Inspect the fuses associated with the AC system. A blown fuse will have a broken filament, indicating a short circuit or overload. Replace any blown fuses with the correct amperage.
- Inspect Wiring for Damage or Corrosion: Visually inspect the AC system wiring for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires, broken connections, or corrosion. Repair or replace any damaged wiring.
- Test the AC Compressor Clutch Relay: Use a multimeter to test the continuity of the AC compressor clutch relay. If the relay is faulty, replace it with a new one.
- Test the AC Compressor Clutch: Check the AC compressor clutch for proper engagement. If the clutch is not engaging, it may be defective and need replacement.
- Test the AC Pressure Switch: Use a multimeter to check the resistance of the AC pressure switch. If the switch is faulty, replace it with a new one.
- Test the Temperature Sensor: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance of the temperature sensor. If the sensor is faulty, replace it with a new one.
- Test the Blower Motor: Use a multimeter to check the voltage and current flow to the blower motor. If the motor is not receiving power, check the wiring and fuses. If the motor is faulty, replace it.
- Test the Blower Motor Resistor: Use a multimeter to check the resistance of the blower motor resistor. If the resistor is faulty, replace it with a new one.
Electrical Testing Procedures: 1996 Marquis Automatic Ac Electrical Diagram
Performing electrical tests on your 1996 Marquis automatic AC system is crucial for diagnosing and resolving any electrical issues. By understanding the necessary tools, procedures, and safety precautions, you can effectively identify and address electrical problems in the system.
Tools and Equipment
Having the right tools is essential for accurate and safe electrical testing. The following tools are commonly used:
- Digital Multimeter (DMM):This versatile tool measures voltage, current, and resistance. It is indispensable for testing electrical circuits and components.
- Test Light:A simple yet effective tool for checking continuity in circuits. It indicates the presence of current by illuminating a bulb.
- Circuit Tester:A specialized tool designed for testing the integrity of electrical circuits, especially for identifying shorts or open circuits.
- Wire Strippers:Used for removing insulation from wires to expose the conductor for connections.
- Crimping Tool:Used for securing electrical connections by crimping terminals onto wires.
- Soldering Iron:Used for making permanent electrical connections by melting solder to join wires or components.
- Safety Glasses:Always wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from potential hazards.
- Gloves:Insulating gloves are essential for protecting your hands from electrical shocks.
Basic Electrical Tests
Basic electrical tests help identify common electrical problems in the AC system. These tests can be performed using a digital multimeter.
- Voltage Test:Measure the voltage at various points in the circuit to ensure proper voltage supply. For example, test the voltage at the AC compressor clutch, the blower motor, and the temperature sensor.
- Continuity Test:Check the continuity of wires and components to ensure there are no breaks or open circuits. For example, test the continuity of the AC compressor clutch relay coil, the blower motor windings, and the temperature sensor wires.
- Resistance Test:Measure the resistance of components, such as the AC compressor clutch coil, the blower motor windings, and the temperature sensor. Compare the measured resistance to the manufacturer’s specifications to determine if the component is faulty.
Safety Precautions
Safety should always be your top priority when working with electrical components. Here are some essential precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery:Always disconnect the battery’s negative terminal before performing any electrical work. This will prevent accidental electrical shocks.
- Use Insulated Tools:Ensure all tools used are properly insulated to prevent electrical shocks.
- Avoid Contact with Live Wires:Never touch live wires with bare hands. Use insulated tools or probes to make connections.
- Wear Safety Gear:Always wear safety glasses, insulated gloves, and appropriate footwear when working with electricity.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area:Avoid working in enclosed spaces or areas with poor ventilation. Carbon monoxide fumes can be dangerous.
Wiring Diagrams and Schematics
Understanding the difference between wiring diagrams and schematics is crucial for effectively troubleshooting electrical issues in the 1996 Marquis automatic AC system. While both diagrams depict the electrical system, they do so in different ways, each serving a unique purpose.
Wiring Diagram
The wiring diagram provides a visual representation of the physical layout of the AC system’s electrical components and their connections. It shows the actual path of wires, including their color coding and routing through the vehicle. This diagram is essential for locating and identifying specific wires and components during troubleshooting.
- Color-Coded Wires:The wiring diagram clearly indicates the color of each wire, making it easier to trace the path of a specific circuit. For instance, the wiring diagram might show a red wire connecting the AC compressor relay to the battery positive terminal.
- Component Locations:The diagram provides a visual representation of where each component is located in the vehicle, such as the AC compressor, blower motor, and temperature sensor. This information helps technicians locate the component quickly and efficiently.
- Connectors and Junctions:The wiring diagram displays all connectors and junctions, showing how multiple wires are connected. This helps in understanding how different circuits interact and how a problem in one circuit might affect another.
Using the Wiring Diagram for Troubleshooting
The wiring diagram is a valuable tool for troubleshooting electrical issues in the 1996 Marquis automatic AC system.
- Tracing Circuit Paths:The wiring diagram helps technicians trace the path of a specific circuit from the source (e.g., battery) to the load (e.g., AC compressor). This allows them to identify potential points of failure along the circuit.
- Locating Faulty Components:By following the wiring diagram, technicians can locate the component connected to a specific circuit that is malfunctioning. This can help them determine if the problem lies with the component itself or with a wiring issue.
- Identifying Open Circuits:The wiring diagram can help identify open circuits, which occur when a wire is broken or disconnected. By tracing the path of a circuit, technicians can pinpoint the location of the break.
- Checking for Short Circuits:The wiring diagram can also help identify short circuits, which occur when two wires touch or come into contact with a grounded surface. By tracing the path of the circuit, technicians can identify the location of the short circuit.
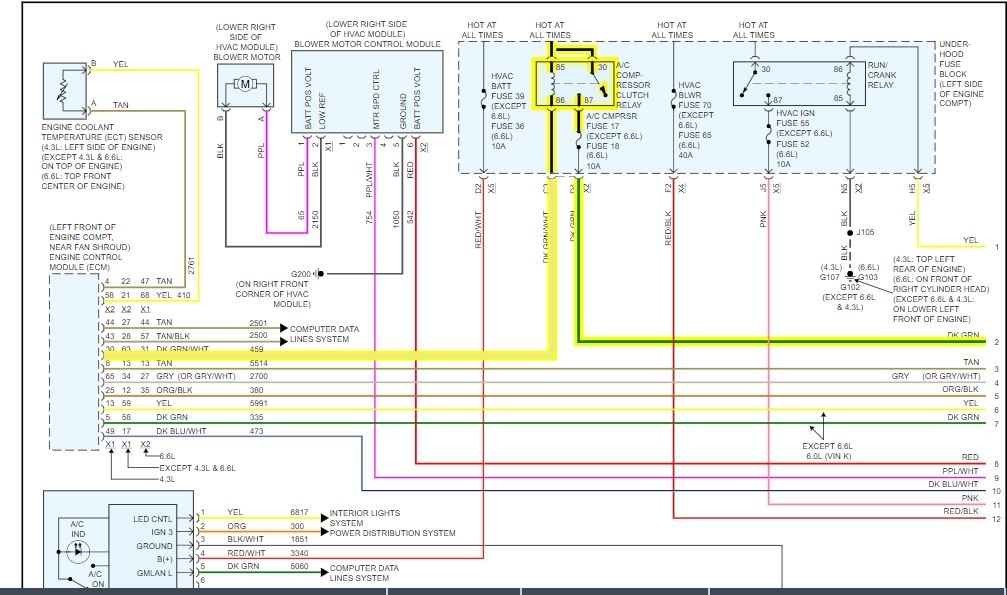
Relay and Fuse Identification

Relays and fuses play a crucial role in protecting the electrical components of the automatic AC system in a 1996 Marquis. These devices act as safety mechanisms, preventing damage to the system by interrupting the flow of electricity in case of an overload or short circuit.
Relays and Fuses in the Automatic AC System
The following table lists the key relays and fuses associated with the automatic AC system in a 1996 Marquis, along with their location, function, and amperage rating:
| Relay/Fuse Name | Location | Function | Amperage |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC Clutch Relay | Underhood Fuse Box | Controls the operation of the AC clutch, engaging and disengaging the compressor. | 30 Amps |
| AC Blower Motor Relay | Underhood Fuse Box | Controls the operation of the AC blower motor, regulating the airflow through the vents. | 20 Amps |
| AC Pressure Switch | Underhood Fuse Box | Monitors the pressure within the AC system, preventing the compressor from running when the pressure is too low or too high. | N/A |
| AC System Fuse | Underhood Fuse Box | Provides a safety measure for the entire AC system, protecting it from electrical overloads. | 15 Amps |
Sensor and Actuator Function
The automatic AC system in a 1996 Marquis relies on a network of sensors and actuators to maintain optimal climate control within the vehicle. These components work together to monitor various conditions and adjust the AC system accordingly, ensuring passenger comfort and efficiency.
Sensors
Sensors play a crucial role in gathering information about the vehicle’s environment and AC system performance. This data is then used by the control unit to adjust the AC system’s operation.
- Temperature Sensor:This sensor monitors the air temperature inside the vehicle. It provides feedback to the control unit, which adjusts the AC system’s output to maintain the desired temperature. For example, if the temperature sensor detects a rise in cabin temperature, the control unit might increase the blower speed or activate the compressor to cool the air.
- Pressure Sensor:The pressure sensor measures the refrigerant pressure within the AC system. This information is vital for monitoring the refrigerant charge and ensuring proper system operation. Low refrigerant pressure can indicate a leak, while high pressure might signal a blockage or other issue.
- Sun Load Sensor:This sensor, typically located on the dashboard, detects the intensity of sunlight entering the vehicle. Based on the detected sunlight level, the control unit can adjust the AC system’s output to compensate for the added heat load.
- Evaporator Temperature Sensor:This sensor monitors the temperature of the evaporator, which is responsible for cooling the air. This information is used by the control unit to adjust the refrigerant flow and optimize cooling performance.
Actuators
Actuators receive signals from the control unit and respond by adjusting the AC system’s operation. These components are responsible for physically changing the AC system’s settings.
- Blower Motor:The blower motor drives the fan, which circulates air through the vehicle’s cabin. The control unit adjusts the blower motor speed based on the desired airflow and temperature settings.
- Compressor Clutch:The compressor clutch engages and disengages the compressor, which is responsible for compressing the refrigerant. The control unit activates the compressor clutch when cooling is required and disengages it when the desired temperature is reached.
- Expansion Valve:The expansion valve controls the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator. The control unit adjusts the expansion valve’s opening to regulate the amount of refrigerant entering the evaporator, thereby affecting the cooling capacity.
- Blend Door Actuator:This actuator controls the mix of fresh and recirculated air entering the cabin. It allows the driver to select between fresh air from outside the vehicle or recirculated air from inside the cabin. This feature is particularly useful in situations where the outside air is polluted or excessively hot or cold.
Troubleshooting and Repair
Troubleshooting electrical problems in a 1996 Marquis automatic AC system can be a complex process. This section provides a step-by-step guide to help you identify and resolve common electrical issues, ensuring a comfortable and functional air conditioning system.
Electrical Troubleshooting Techniques
When addressing electrical problems in the 1996 Marquis AC system, it is crucial to prioritize safety. Always disconnect the battery before working on any electrical components to prevent potential shocks. Use insulated tools and follow proper safety procedures.
- Visual Inspection: Start by visually inspecting all wires, connectors, and components for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Look for chafed wires, melted insulation, or any other signs of wear and tear.
- Continuity Testing: Use a multimeter to test the continuity of wires and circuits. Continuity testing involves checking for a complete path for electricity to flow. This helps identify broken or open circuits.
- Voltage Testing: Measure the voltage at various points in the circuit to ensure proper voltage levels are present. Voltage testing helps identify issues with the power supply or faulty components.
- Resistance Testing: Measure the resistance of components like sensors and actuators. Resistance testing helps identify faulty components that may be preventing proper operation.
Common Electrical Issues and Solutions
The following table Artikels common electrical issues encountered in the 1996 Marquis AC system and their potential solutions.
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| AC System Not Working | Blown fuse, faulty relay, defective compressor, or open circuit | Check fuses and relays. Inspect the compressor for damage. Trace the circuit for any breaks or open connections. |
| AC Blows Warm Air | Low refrigerant charge, faulty compressor, clogged condenser, or malfunctioning temperature sensor | Recharge the refrigerant system, inspect the compressor, clean the condenser, or replace the temperature sensor. |
| AC System Cycles On and Off | Faulty pressure switch, malfunctioning temperature sensor, or refrigerant leak | Inspect the pressure switch, replace the temperature sensor, or repair any refrigerant leaks. |
| AC System Makes Noise | Faulty compressor, worn bearings, or loose fan blades | Inspect the compressor, replace worn bearings, or tighten loose fan blades. |
Component Testing Procedures, 1996 marquis automatic ac electrical diagram
- Compressor: To test the compressor, use a multimeter to check for continuity across the compressor windings. A reading of zero ohms indicates a shorted compressor, while an infinite reading suggests an open circuit.
- Pressure Switch: The pressure switch is responsible for turning the compressor on and off based on refrigerant pressure. To test the pressure switch, use a multimeter to check for continuity at different pressure levels.
- Temperature Sensor: The temperature sensor measures the temperature of the air inside the vehicle. To test the sensor, use a multimeter to check for resistance at different temperatures.
- Actuator: Actuators control the flow of air through the vents. To test an actuator, apply voltage to it and check for movement.
Resources and References
This section provides a compilation of reliable resources that can be used for further information on 1996 Marquis automatic AC systems. It includes links to online forums, repair manuals, and other helpful resources. It also suggests additional reading materials for advanced troubleshooting and repair.
Online Forums
Online forums are valuable resources for accessing information from other Marquis owners and technicians. They offer a platform to ask questions, share experiences, and find solutions to common problems.
- Ford Truck Enthusiasts (FTE):A popular online forum dedicated to Ford trucks, including the Marquis. It hosts a dedicated section for AC issues, where users can find discussions, troubleshooting tips, and advice from experienced members.
- Marquis Owners Club:A specialized forum for Marquis owners, providing a space for technical discussions, maintenance tips, and troubleshooting guides. It is a valuable resource for finding information specific to the Marquis model.
Repair Manuals
Repair manuals are essential for detailed information on the 1996 Marquis AC system. They provide comprehensive diagrams, specifications, troubleshooting procedures, and repair instructions.
- Chilton Repair Manual:A well-known resource for automotive repair information, offering detailed coverage of the 1996 Marquis AC system, including electrical diagrams, component descriptions, and step-by-step repair procedures.
- Haynes Repair Manual:Another reputable source for repair manuals, providing comprehensive information on the 1996 Marquis AC system, including electrical diagrams, troubleshooting guides, and component specifications.
Additional Reading Materials
For advanced troubleshooting and repair, specialized resources can provide in-depth knowledge on specific aspects of the AC system.
- Automotive Air Conditioning:This book by John A. Tomczyk provides a comprehensive understanding of automotive AC systems, covering principles of operation, troubleshooting techniques, and repair procedures. It is a valuable resource for advanced technicians.
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology:This textbook by William C. Whitman and others offers a thorough explanation of refrigeration and air conditioning principles, including system components, operation, troubleshooting, and maintenance. It is suitable for professionals seeking a deeper understanding of AC systems.
Query Resolution
What are some common electrical problems in the 1996 Marquis AC system?
Common issues include blown fuses, faulty relays, sensor malfunctions, and wiring problems. These can cause symptoms like lack of cooling, inconsistent airflow, or even a complete AC system failure.
Where can I find a wiring diagram for my 1996 Marquis?
You can find wiring diagrams in the owner’s manual, online repair manuals, or at your local auto parts store. You can also check online forums or communities for specific model information.
What safety precautions should I take when working with electrical components?
Always disconnect the battery before working on electrical components. Wear safety glasses and gloves to protect yourself from potential hazards. Never touch live wires, and be aware of the risks of electrical shock.