1966 Chevelle Ignition Coil Wiring Diagram PDF: Dive into the intricate world of your classic car’s ignition system. This diagram is your roadmap to understanding how the spark that ignites your engine is generated, and how to troubleshoot any issues that might arise.
The 1966 Chevelle, a beloved muscle car, relies on a well-functioning ignition system for its power and performance. This wiring diagram serves as a crucial tool for both experienced mechanics and DIY enthusiasts who want to delve into the heart of their Chevelle’s engine.
The ignition coil is a vital component in the engine’s combustion process. It transforms low-voltage electrical energy from the battery into high-voltage current, which is used to create a spark at the spark plugs. This spark ignites the air-fuel mixture in the cylinders, driving the pistons and ultimately propelling the car forward.
Understanding the ignition coil wiring diagram allows you to trace the flow of electricity through the system, identifying potential points of failure and enabling you to effectively diagnose and repair any problems that might occur.
Analyzing the Wiring Diagram
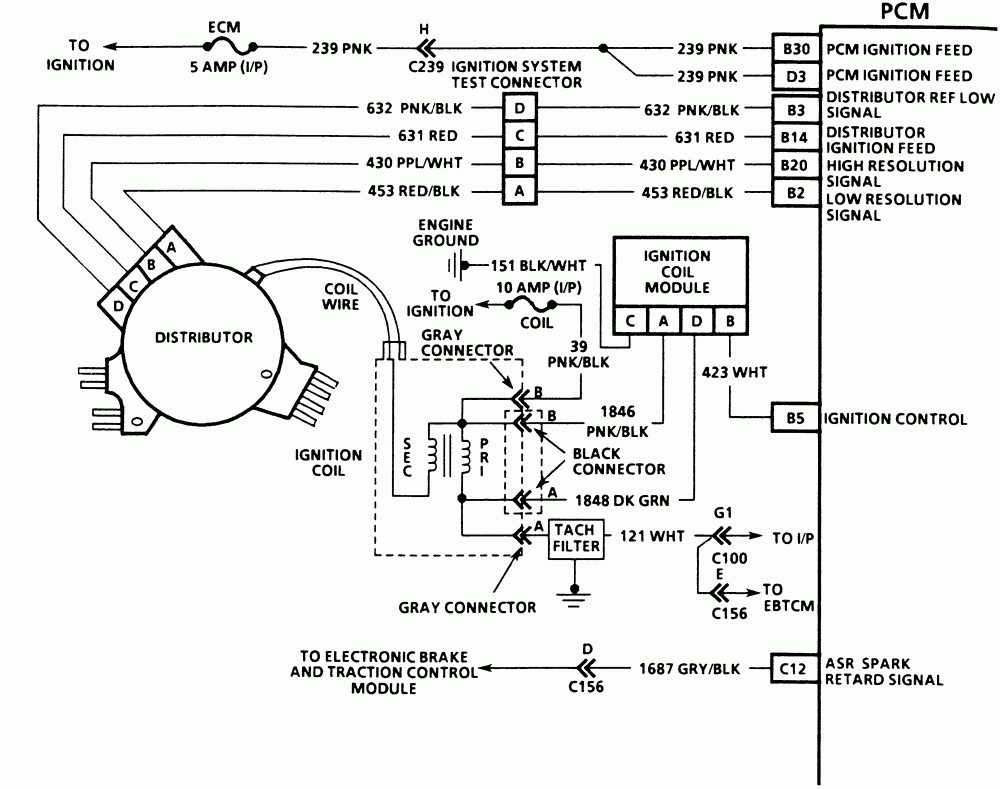
The wiring diagram for a 1966 Chevelle ignition system is a visual representation of the electrical connections between the various components. Understanding this diagram is essential for troubleshooting problems, performing maintenance, and making modifications to the system.
Symbols Used in the Wiring Diagram
The wiring diagram uses standardized symbols to represent different components and connections. These symbols provide a concise and universally understood way to depict the electrical system.
- Wires: Solid lines represent wires, with different colors indicating different circuits. For example, a red line might represent a positive (+) wire, while a black line might represent a negative (-) wire.
- Components: Each component in the system is represented by a specific symbol. For instance, the ignition coil might be depicted as a rectangle with a coil symbol inside, while the distributor might be represented by a circle with a rotating arm.
- Connections: Points where wires connect to components are indicated by dots or junctions. These junctions show where the electrical current flows from one component to another.
Key Components and Their Connections
The 1966 Chevelle ignition system consists of several essential components that work together to create a spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture in the cylinders. The wiring diagram shows how these components are connected electrically.
- Ignition Coil: The ignition coil is a transformer that converts low-voltage current from the battery into high-voltage current, which is needed to create a spark at the spark plugs. The coil is connected to the battery through a wire that carries the low-voltage current.
Another wire connects the coil to the distributor, which sends the high-voltage current to the spark plugs.
- Distributor: The distributor is a mechanical device that distributes the high-voltage current from the ignition coil to the appropriate spark plug at the correct time. It has a rotating arm that makes contact with a set of terminals, each connected to a different spark plug.
The distributor is also connected to the ignition switch, which allows the driver to turn the ignition system on and off.
- Spark Plugs: Spark plugs are located in the cylinder head and are responsible for igniting the air-fuel mixture. Each spark plug is connected to a terminal on the distributor cap, which receives the high-voltage current from the ignition coil.
- Ignition Switch: The ignition switch is a mechanical device that controls the flow of current to the ignition system. When the key is turned to the “on” position, the ignition switch closes the circuit, allowing current to flow to the ignition coil and distributor.
When the key is turned to the “start” position, the ignition switch also activates the starter motor, which turns the engine over.
Flow of Electrical Current Through the Ignition System
The flow of electrical current through the ignition system is a crucial part of the ignition process. This flow is controlled by the various components and connections depicted in the wiring diagram.
- Battery to Ignition Coil: When the ignition switch is turned to the “on” position, current flows from the battery through a wire to the ignition coil. This current is relatively low voltage and is used to energize the coil.
- Ignition Coil to Distributor: The ignition coil transforms the low-voltage current into high-voltage current. This high-voltage current then flows through a wire to the distributor.
- Distributor to Spark Plugs: The distributor’s rotating arm distributes the high-voltage current to the appropriate spark plug at the correct time. The current flows from the distributor cap through a wire to the spark plug terminal, where it creates a spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture in the cylinder.
Troubleshooting Ignition Issues
The ignition system in your 1966 Chevelle is responsible for providing the spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture in the cylinders. When the ignition system malfunctions, it can cause a variety of problems, ranging from difficulty starting to misfiring or complete engine failure.
Identifying Potential Issues Using the Wiring Diagram
The wiring diagram serves as a roadmap for tracing the flow of electricity through the ignition system. By carefully examining the diagram, you can identify potential points of failure and isolate the specific component responsible for the problem.
- Tracing the Circuit:Start by identifying the component that is causing the problem. For example, if you’re experiencing a misfire, you might suspect a faulty spark plug or a broken wire leading to it. Use the wiring diagram to follow the circuit from the ignition coil to the spark plug in question, noting all the components along the way.
- Checking Connections:The wiring diagram will show you where each wire connects to the various components. Carefully inspect each connection, looking for signs of corrosion, loose wires, or broken connections. These can disrupt the flow of electricity and cause ignition problems.
- Identifying Components:The wiring diagram labels each component, including the ignition coil, distributor, spark plugs, and wiring harness. This allows you to quickly identify the specific part that might be faulty. For example, if the wiring diagram indicates that the ignition coil is connected to a specific terminal on the distributor, you can easily verify if the connection is secure.
The 1966 Chevelle ignition coil wiring diagram is a crucial document for anyone working on the car’s electrical system, offering a visual map to ensure proper connection and function. Just as important is understanding the layout of a troy bilt bronco drive belt diagram for anyone wanting to tackle a lawnmower repair.
Both diagrams are essential for successful troubleshooting and repair, providing a clear guide to navigate the intricacies of each system.
Troubleshooting Steps
Troubleshooting ignition issues involves a systematic approach, eliminating potential problems one by one until you find the root cause.
- Visual Inspection:Start by visually inspecting the ignition system components. Look for signs of damage, corrosion, loose connections, or broken wires. For example, inspect the spark plugs for wear and tear, the distributor cap for cracks or carbon buildup, and the wiring harness for any frayed or broken wires.
- Testing Components:Use a multimeter or other appropriate testing tools to check the functionality of each component in the ignition system. For example, you can test the ignition coil for proper resistance, the distributor for proper timing, and the spark plugs for proper spark.
These tests will help you determine if the component is working correctly or if it needs to be replaced.
- Continuity Testing:Use a multimeter to check the continuity of each wire in the ignition system. This ensures that the electrical circuit is complete and that there are no breaks in the wiring. If you find a broken wire, you’ll need to repair or replace it.
- Checking Ground Connections:A poor ground connection can disrupt the flow of electricity and cause ignition problems. Ensure that all ground connections in the ignition system are clean and secure. This includes the ground connection on the ignition coil, the distributor, and the engine block.
- Timing Adjustment:If you suspect that the ignition timing is off, you can use a timing light to check and adjust it. The correct ignition timing is crucial for optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency.
Repairing the Ignition System

A faulty ignition coil can cause a range of issues, including misfires, difficulty starting, and a complete loss of power. This section Artikels the steps involved in replacing a faulty ignition coil on a 1966 Chevelle.
Replacing a Faulty Ignition Coil
Replacing a faulty ignition coil is a relatively straightforward process. However, it’s crucial to follow the proper steps and safety precautions to avoid any complications. The following tools and materials are necessary for the repair:
- Socket wrench set
- Torque wrench
- Wire cutters
- Crimping tool
- New ignition coil
- Wire connectors
- Electrical tape
- Gloves
- Safety glasses
Before starting the repair, disconnect the battery to prevent any electrical shocks. The following steps should be taken when replacing a faulty ignition coil:
- Locate the ignition coil. On a 1966 Chevelle, it is typically located near the distributor on the engine.
- Disconnect the wires connected to the ignition coil. Use wire cutters to carefully remove any wire ties or clamps securing the wires.
- Remove the bolts holding the ignition coil in place using a socket wrench.
- Carefully remove the old ignition coil. Ensure that no wires are snagged or damaged during removal.
- Install the new ignition coil in the same position as the old one. Secure it with the bolts and tighten them to the specified torque.
- Connect the wires to the new ignition coil. Ensure that the wires are connected to the correct terminals. Use wire connectors and electrical tape to secure the connections.
- Reconnect the battery and start the engine. Check for any misfires or other issues.
Alternative Ignition Systems: 1966 Chevelle Ignition Coil Wiring Diagram Pdf
While the original points system on your 1966 Chevelle is reliable, there are alternative ignition systems that can offer improved performance and reliability. These systems, often referred to as “electronic ignition,” have replaced the points system in many modern vehicles and can be retrofitted to older cars.
Electronic Ignition Systems
Electronic ignition systems eliminate the mechanical points and condenser found in traditional ignition systems. They utilize electronic components to control the timing and duration of the spark, resulting in several advantages.
Advantages of Electronic Ignition Systems
- Improved Spark Quality:Electronic ignition systems produce a more consistent and powerful spark, leading to better combustion and increased engine efficiency.
- Eliminates Points Wear:Electronic ignition systems eliminate the need for points, which are prone to wear and require regular adjustment. This reduces maintenance and increases reliability.
- Precise Timing Control:Electronic ignition systems offer precise timing control, allowing for optimal engine performance across different operating conditions.
- Reduced Maintenance:Electronic ignition systems are virtually maintenance-free, as they do not require regular adjustment or replacement of parts like points and condensers.
Types of Electronic Ignition Systems
- Solid-State Ignition Systems:These systems use solid-state electronic components to control the timing and duration of the spark. They are typically more reliable than points systems and offer improved performance.
- Electronic Distributorless Ignition Systems (DIS):DIS systems eliminate the distributor altogether. They use a separate ignition coil for each cylinder, resulting in improved spark quality and more precise timing control. DIS systems are commonly found in modern vehicles.
Upgrading to a Modern Ignition System
Upgrading to a modern ignition system can provide significant benefits for your 1966 Chevelle, including improved performance, increased reliability, and reduced maintenance. However, there are also some potential drawbacks to consider.
Advantages of Upgrading
- Improved Performance:Modern ignition systems offer a more consistent and powerful spark, leading to better combustion and increased horsepower and torque.
- Enhanced Reliability:Electronic ignition systems are more reliable than traditional points systems, as they do not have any moving parts that are prone to wear.
- Reduced Maintenance:Modern ignition systems are virtually maintenance-free, as they do not require regular adjustment or replacement of parts like points and condensers.
Disadvantages of Upgrading
- Cost:Upgrading to a modern ignition system can be expensive, as it may require replacing several components, including the ignition coil, distributor, and wiring.
- Complexity:Modern ignition systems can be more complex to install and troubleshoot than traditional points systems, requiring some technical knowledge.
- Compatibility Issues:It’s essential to ensure that the modern ignition system is compatible with your car’s existing electrical system. Some modifications may be necessary.
Historical Context
The evolution of the ignition system in automobiles is a testament to the ingenuity of engineers and the constant pursuit of efficiency and performance. From the rudimentary spark plugs of the early 20th century to the sophisticated electronic systems of today, the ignition system has undergone significant transformations, mirroring the advancements in engine technology.The ignition coil, a crucial component of the ignition system, has played a pivotal role in this evolution.
Its primary function is to transform the low-voltage electrical current from the battery into a high-voltage current that ignites the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber.
Evolution of the Ignition Coil
The development of the ignition coil can be traced back to the early days of the automobile. Early ignition systems relied on a simple coil and a mechanical distributor to generate and distribute the spark. However, these systems were often unreliable and prone to breakdowns.
- Early Ignition Systems (1900s):These systems utilized a simple coil and a mechanical distributor. The coil was typically a single winding of wire wrapped around an iron core. The distributor was responsible for directing the high-voltage current to the correct spark plug at the appropriate time.
- Dual-Coil Systems (1930s):The introduction of dual-coil systems improved reliability and performance. These systems used two separate coils, one for each cylinder, eliminating the need for a distributor. The dual-coil system allowed for a more powerful spark and better ignition timing.
- Electronic Ignition Systems (1970s):The development of electronic ignition systems revolutionized the automotive industry. These systems replaced the mechanical distributor with electronic components, resulting in improved accuracy, reliability, and fuel efficiency. The ignition coil in electronic systems is typically a high-energy coil with a more robust design.
The 1966 Chevelle and its Ignition System, 1966 chevelle ignition coil wiring diagram pdf
The 1966 Chevelle, a popular muscle car of the era, featured a traditional ignition system with a distributor and a single coil. The ignition coil in the 1966 Chevelle was responsible for generating the high-voltage spark that ignited the air-fuel mixture in the engine’s cylinders.
The ignition system in the 1966 Chevelle was known for its simplicity and reliability. However, like all mechanical systems, it was prone to wear and tear. Common problems included a worn distributor cap, faulty spark plugs, and a failing ignition coil.
The 1966 Chevelle was a popular choice for enthusiasts, and its ignition system played a critical role in its performance.
Safety Considerations
Working on a classic car’s ignition system, particularly a high-voltage component like the ignition coil, requires a strong emphasis on electrical safety. Failure to prioritize safety can lead to severe electrical shocks, burns, and even death. Understanding and adhering to safety practices is crucial for a successful and safe repair experience.
Potential Hazards
The ignition system of a 1966 Chevelle, or any classic car for that matter, operates at high voltage, typically around 12,000 volts. This high voltage presents a significant electrical hazard, capable of causing severe injury or even death if not handled properly.
The following hazards are associated with working on the ignition system:
- Electrical Shock:Contact with live electrical components, such as the ignition coil or wiring, can result in a severe electrical shock. The high voltage can cause muscle spasms, burns, and even cardiac arrest.
- Burns:Contact with hot components, such as the ignition coil or wiring, can cause severe burns. The high voltage can generate heat, which can lead to burns if not handled carefully.
- Fire:A spark from a faulty ignition system component, such as the ignition coil, can ignite flammable materials, such as gasoline or engine oil. This can lead to a fire, which can cause serious damage and injury.
Safe Handling and Repair Procedures
The following recommendations are crucial for ensuring safety while working on the ignition system:
- Disconnect the Battery:Before working on any electrical component, always disconnect the battery’s negative terminal. This will prevent any accidental electrical shocks.
- Use Insulated Tools:Always use insulated tools when working on electrical components. This will help prevent electrical shocks and burns.
- Avoid Contact with Live Components:Do not touch any live electrical components, such as the ignition coil or wiring, while the system is energized.
- Wear Safety Glasses:Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from sparks or flying debris.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area:Work in a well-ventilated area to prevent the buildup of flammable gases.
- Be Aware of Your Surroundings:Be aware of your surroundings and avoid working near flammable materials, such as gasoline or engine oil.
Additional Safety Tips
- Inspect the Ignition System for Damage:Before working on the ignition system, carefully inspect it for any signs of damage, such as frayed wiring, cracked insulation, or corrosion.
- Use a Multimeter to Test Components:Use a multimeter to test the ignition system components for proper operation before reinstalling them.
- Seek Professional Help:If you are not comfortable working on the ignition system, seek professional help from a qualified mechanic.
Always remember, safety should be your top priority when working on any electrical system. Taking the necessary precautions can help prevent serious injury or death.
Resources and Further Information

The world of classic car restoration and maintenance is vast, and the 1966 Chevelle is no exception. There are many resources available to help you understand and repair your car’s ignition system. Here are some of the best places to start your journey.
Online Resources
The internet is a treasure trove of information for Chevelle enthusiasts. Here are a few excellent places to start your research:
- Chevelle.com:This website is a comprehensive resource for all things Chevelle, with forums, articles, and a parts marketplace.
- The Chevelle Club of America:The CCOA is a national organization dedicated to preserving and promoting the Chevelle. They offer a wealth of information, including a technical library and a forum for members.
- Classic Industries:This website specializes in parts and accessories for classic cars, including the 1966 Chevelle. They have a large library of technical information and how-to guides.
- YouTube:Many enthusiasts have created YouTube channels dedicated to restoring and maintaining classic cars. Search for videos on 1966 Chevelle ignition systems to find helpful tutorials and tips.
Books and Manuals
For in-depth information, consider investing in a few essential books and manuals:
- Chevrolet Shop Manual:The factory service manual for the 1966 Chevelle provides detailed instructions on every aspect of the car, including the ignition system.
- Chilton’s Repair Manual:This comprehensive manual covers a wide range of models, including the 1966 Chevelle. It provides step-by-step instructions for repairs and maintenance.
- “How to Rebuild Your Small-Block Chevrolet Engine” by David Vizard:This book offers a thorough guide to rebuilding the engine, including the ignition system.
FAQ Guide
Where can I find a 1966 Chevelle Ignition Coil Wiring Diagram PDF?
You can often find these diagrams online through automotive forums, specialized websites, or even by searching for “1966 Chevelle service manual.”
What if I don’t understand the symbols on the diagram?
Many online resources offer explanations of common electrical symbols used in wiring diagrams. You can also consult a mechanic or an experienced enthusiast for help deciphering the symbols.
Can I replace the ignition coil myself?
Replacing an ignition coil is generally a straightforward task, but it’s important to follow safety precautions and consult a repair manual for specific instructions.